一. What’s machine learning
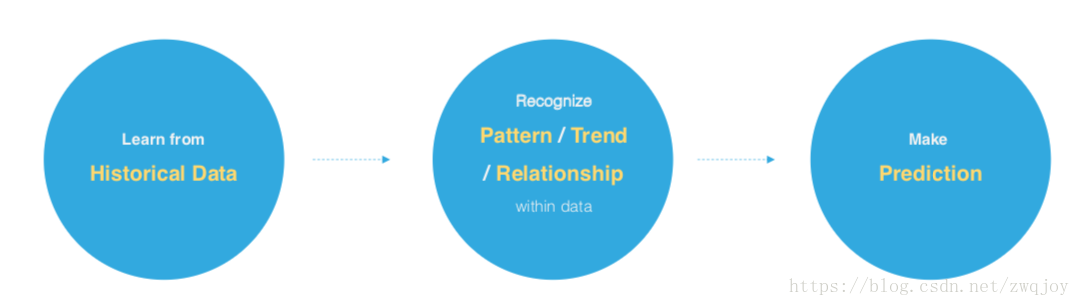
Machine Learning is the science of gettingcomputers to act without being explicitly programmed --- Andrew Ng
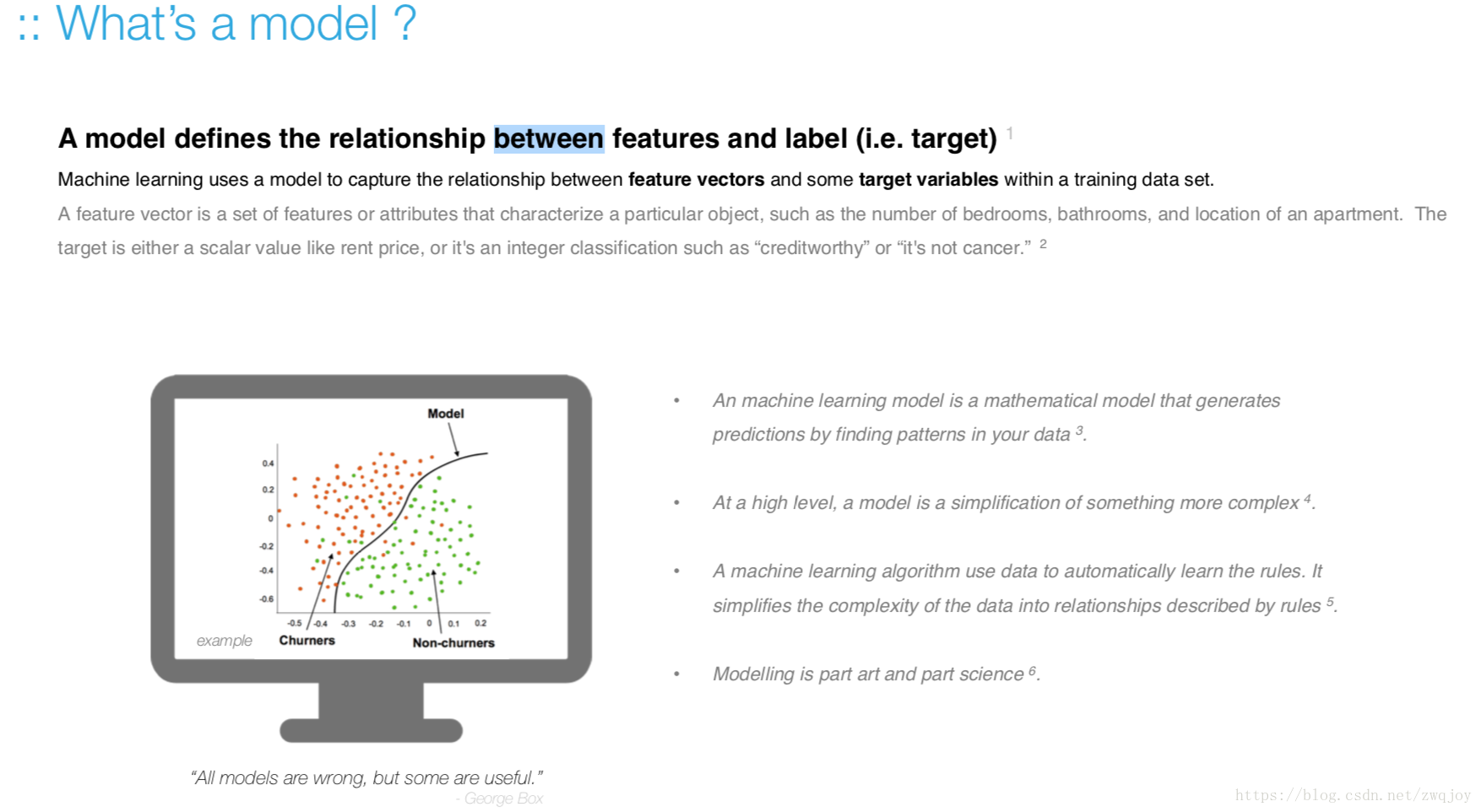
Machine learning is a technique of data science that helps computers learn from existing data in order to forecast future behaviors, outcomes, and trends. --- Microsoft
二. The difference between traditional approach and Machine Learning
From business problem to Machine learning problem: a Recipe
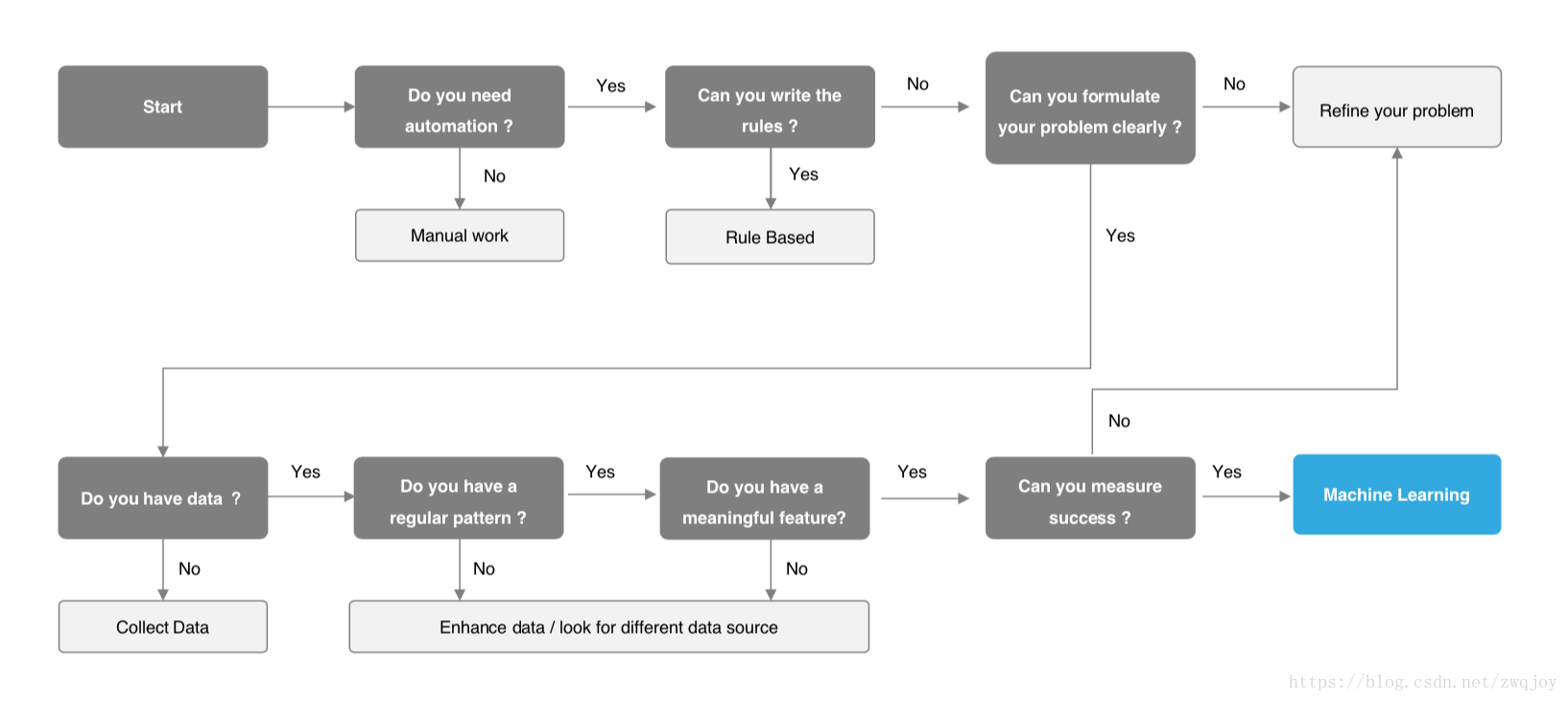
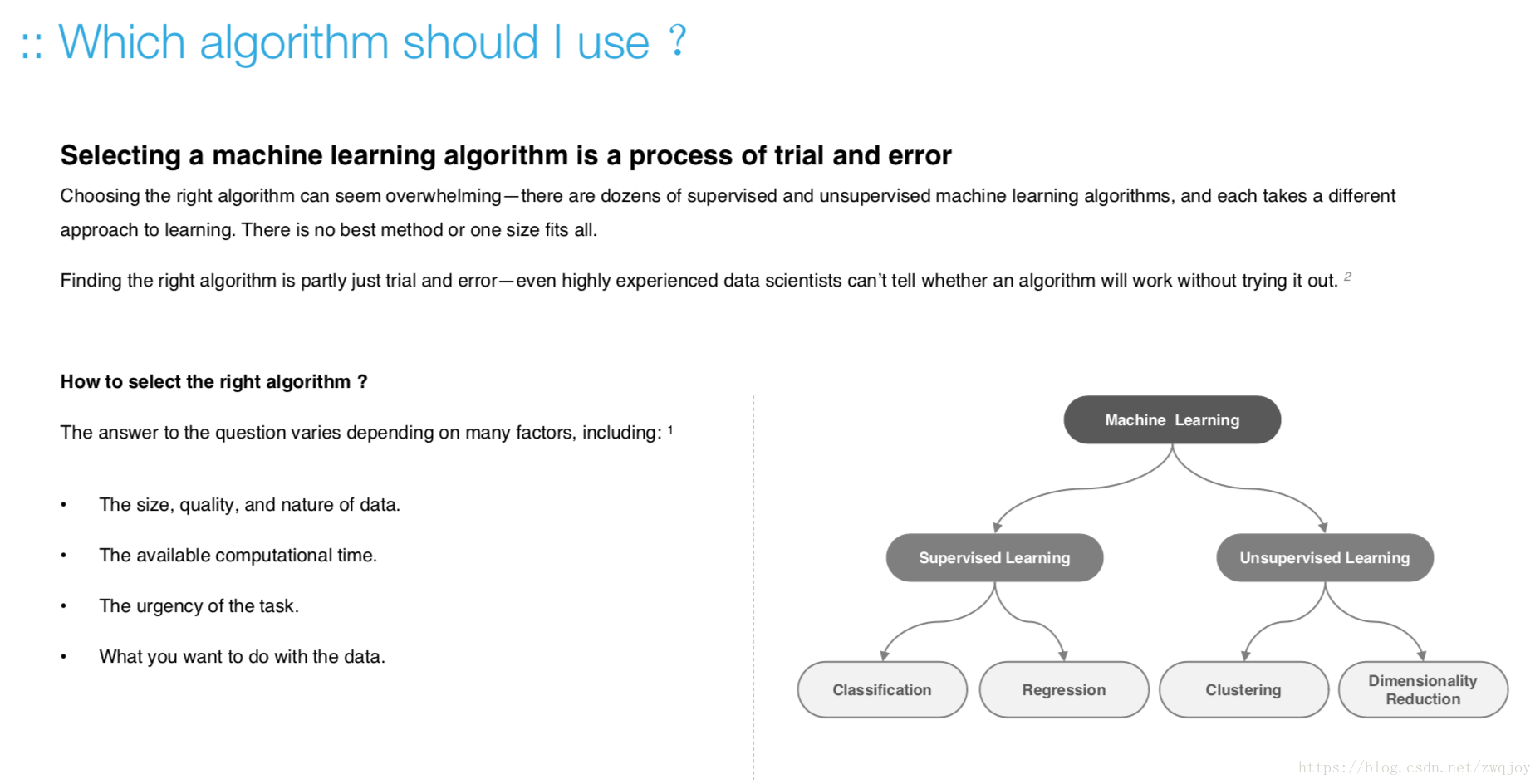
Step-by-step “recipe” for qualifying a business problem as a machine learning problem
- Do you need machine learning?
- Can you formulate your problem clearly?
- Do you have sufficient examples?
- Does your problem have a regular pattern?
- Can you find meaningful representations of your data?
- How do you define success?
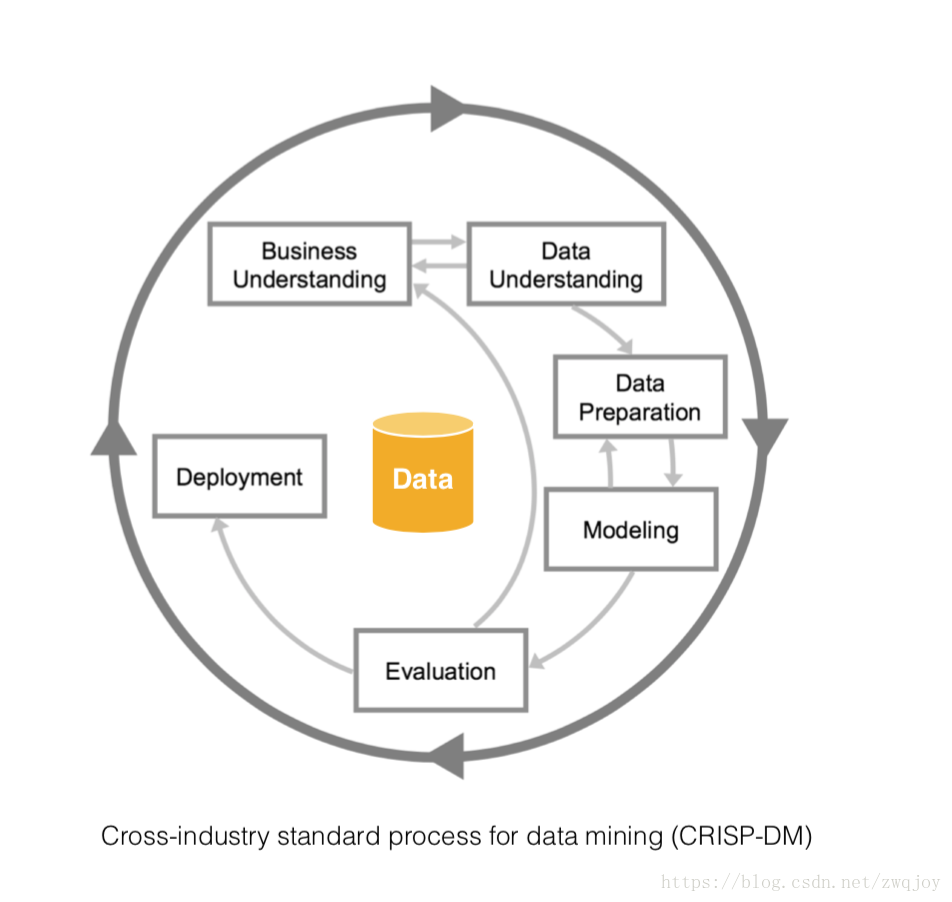
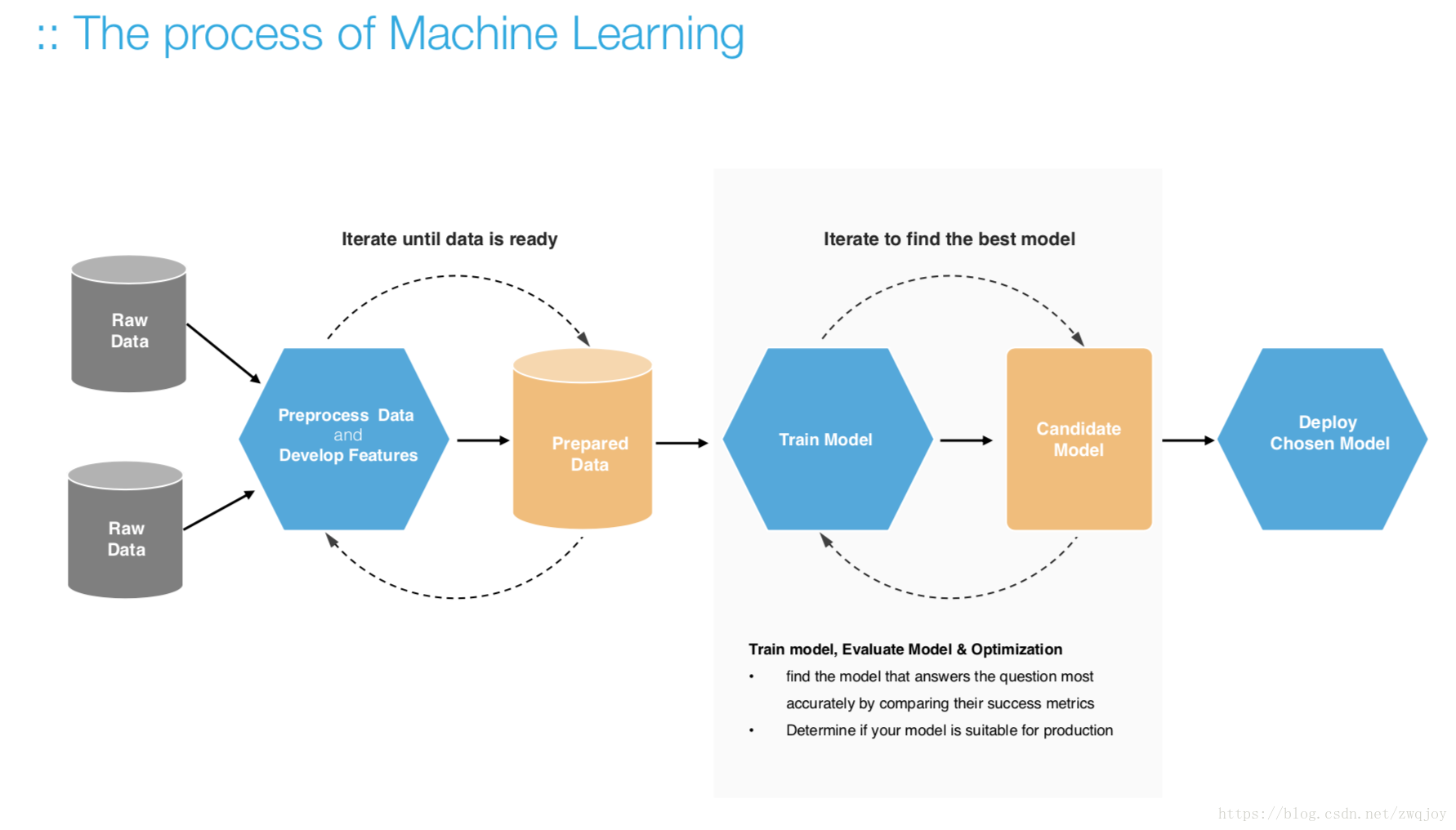
三. How to create machine learning models

四. The Core --- Data
Data understanding
Data Preparation

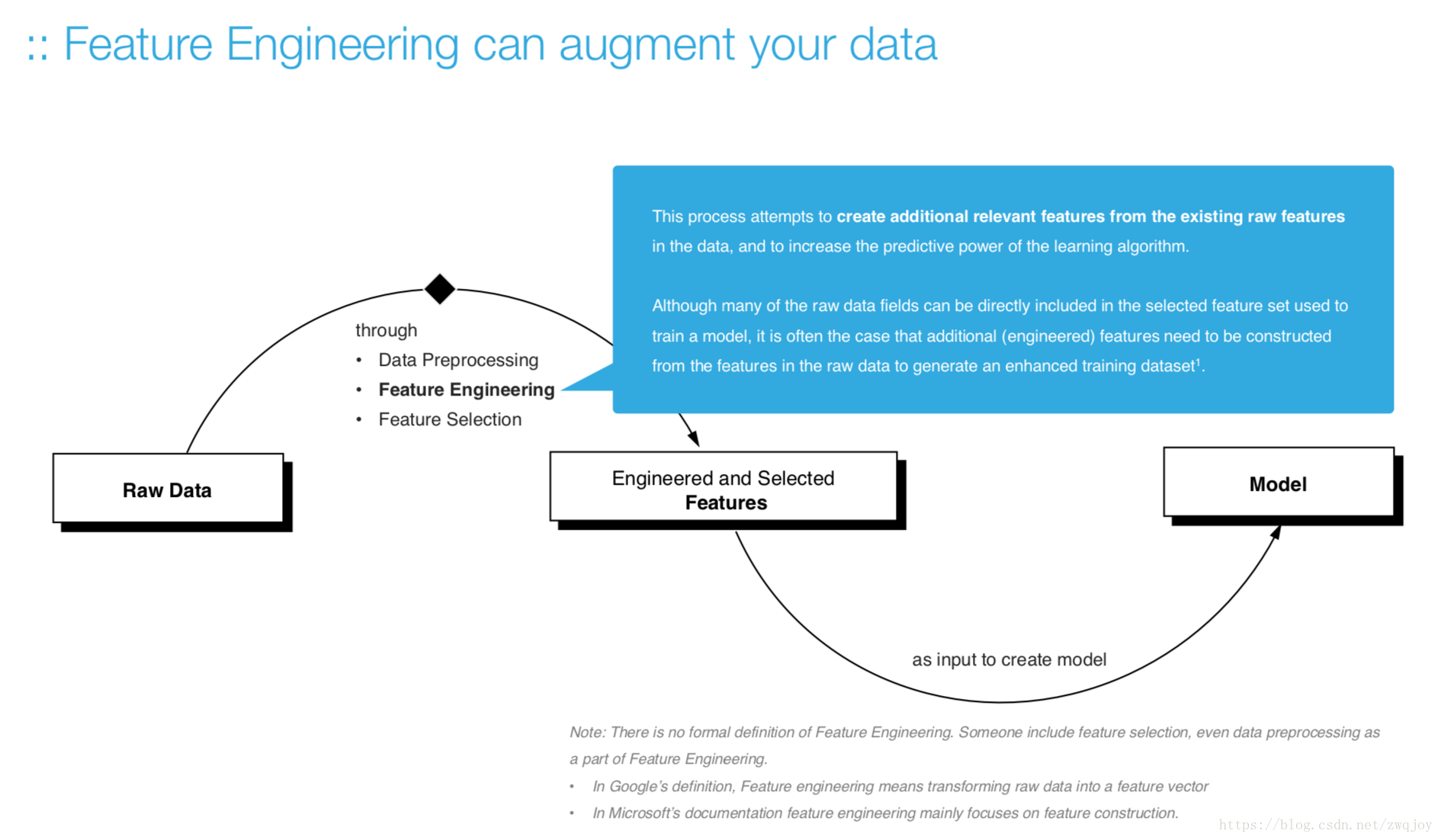

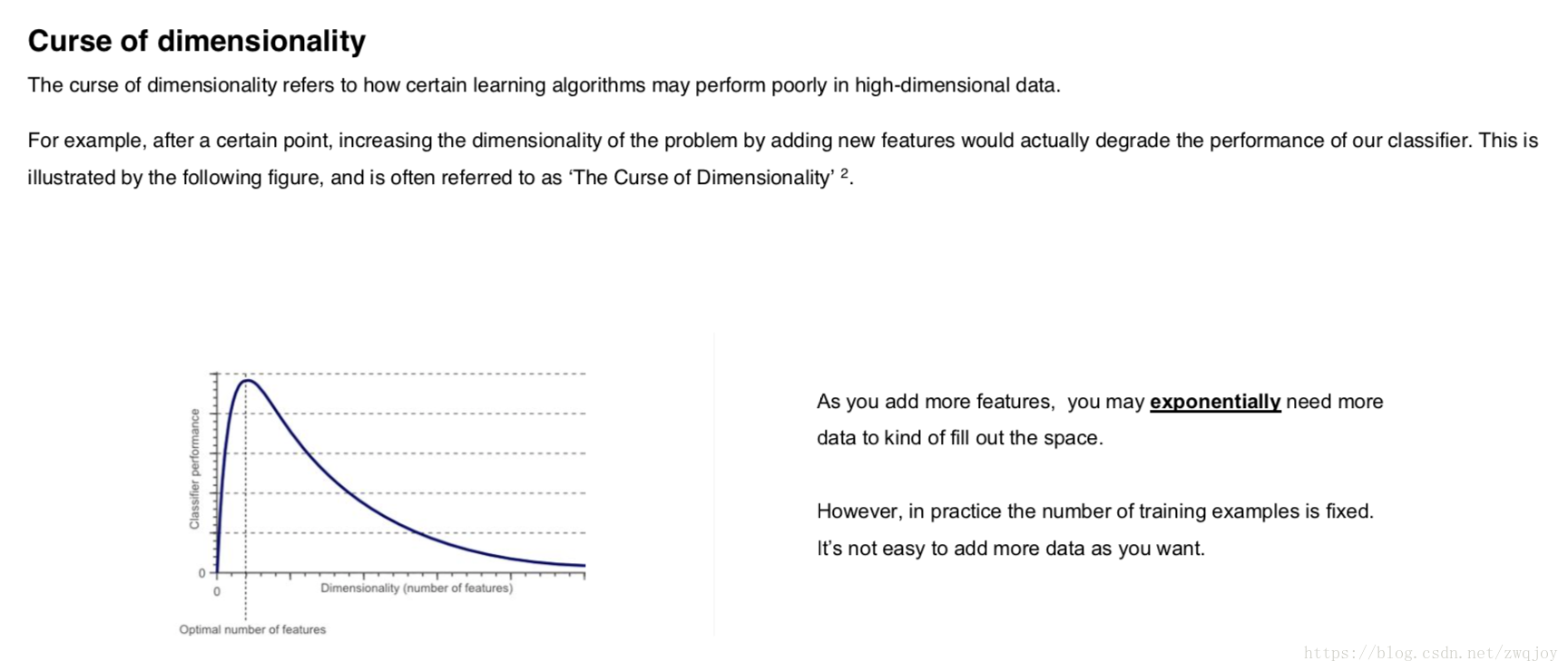
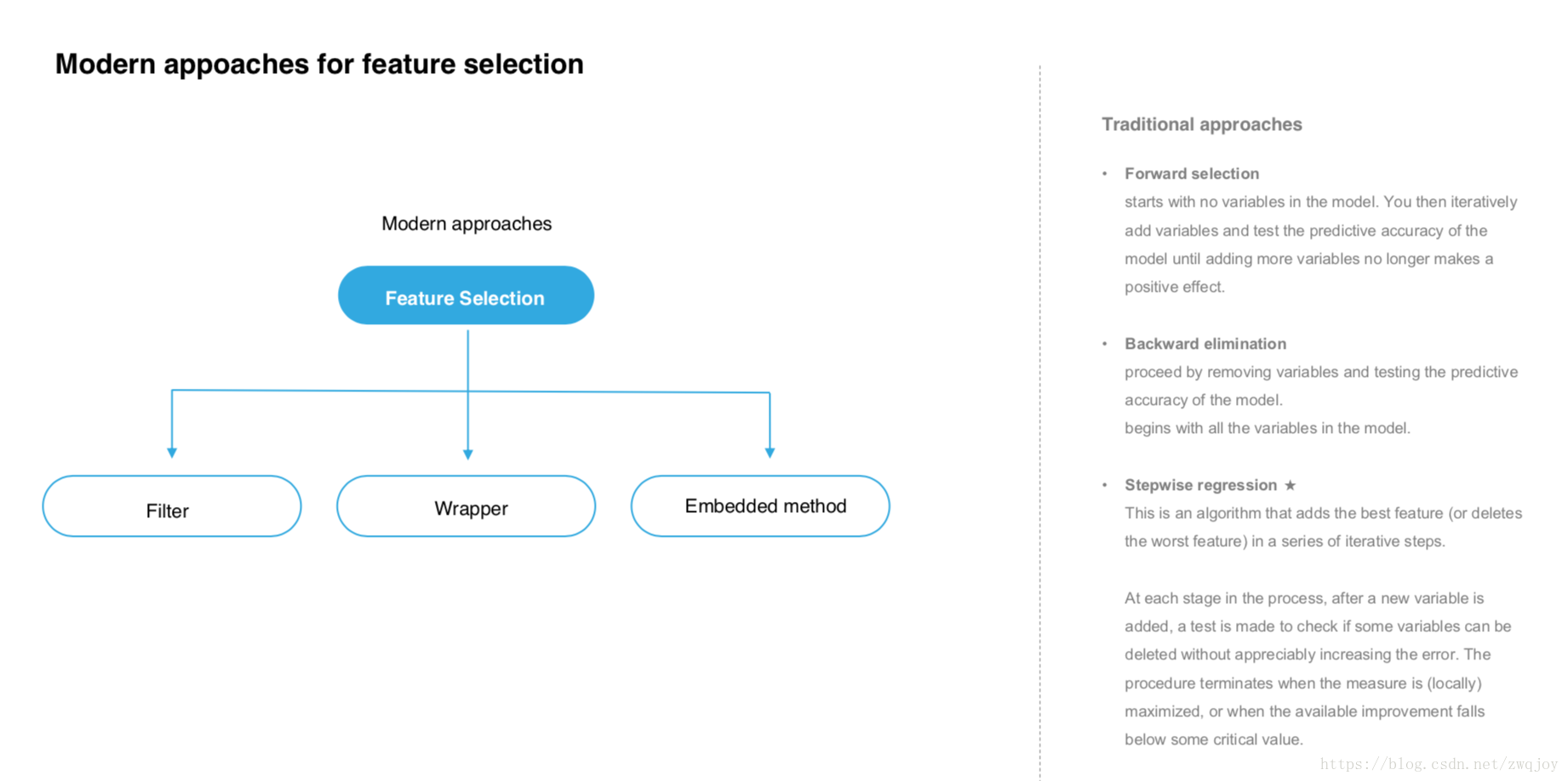
Approaches for Feature Selection

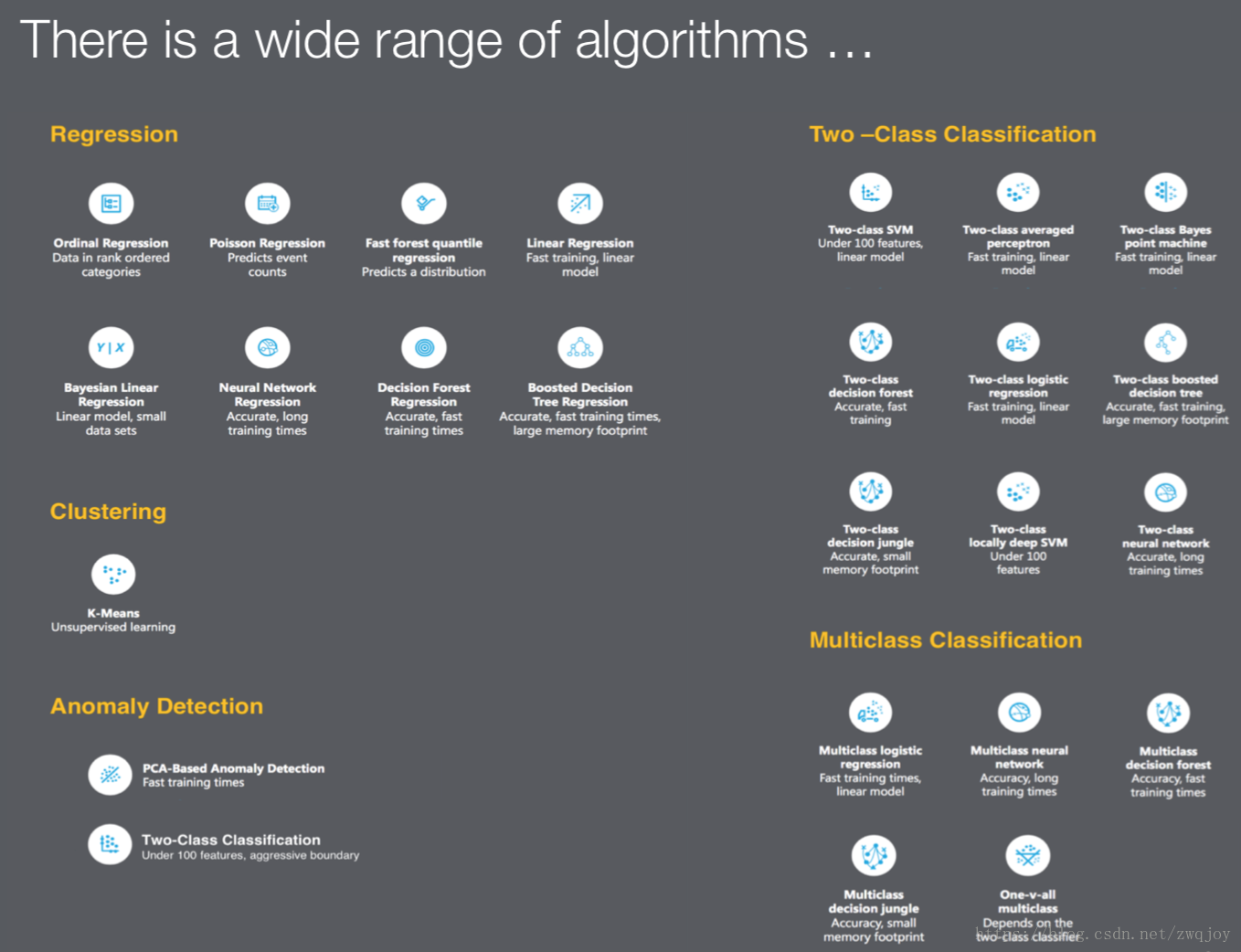
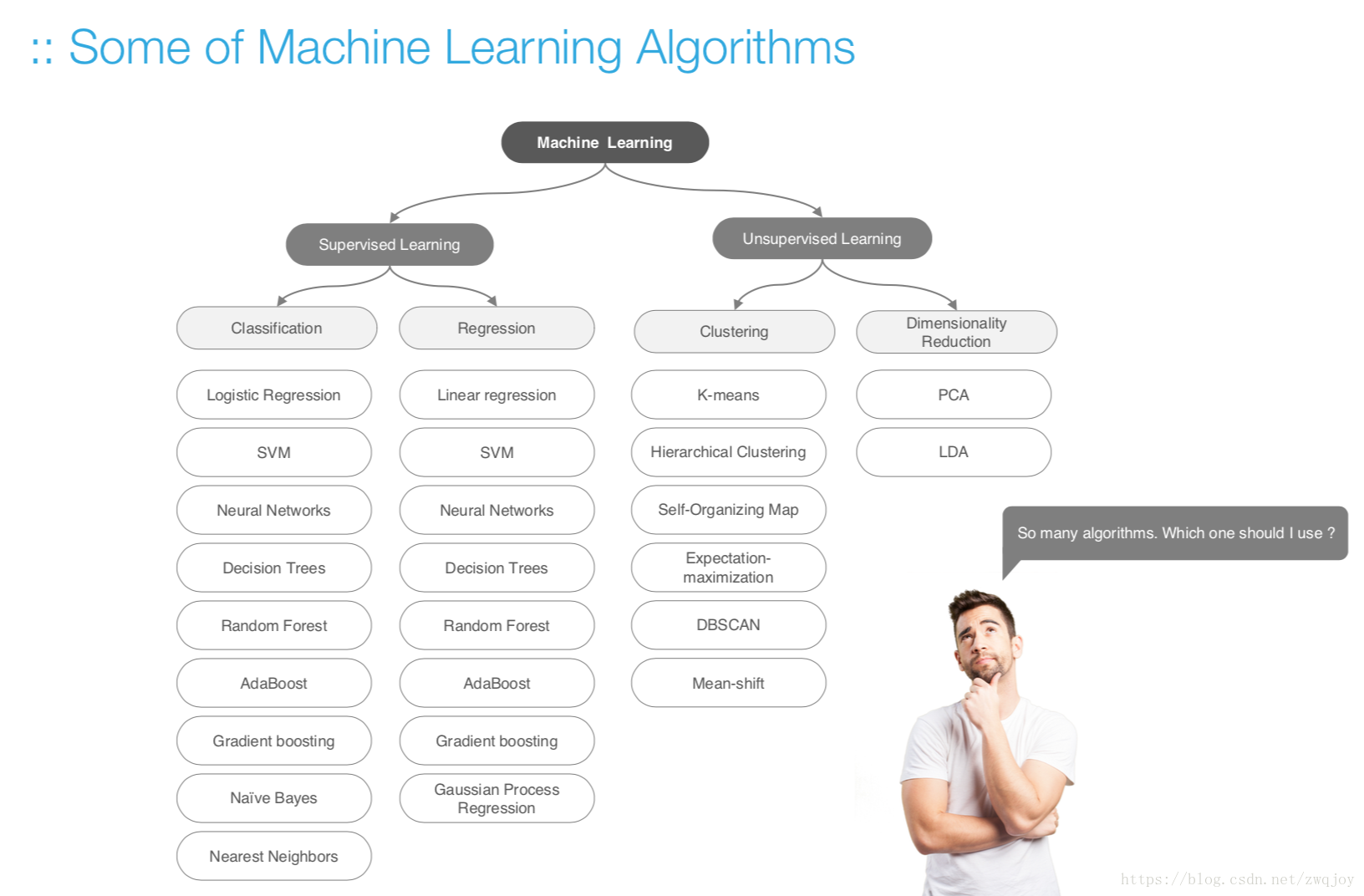
五. Modelling
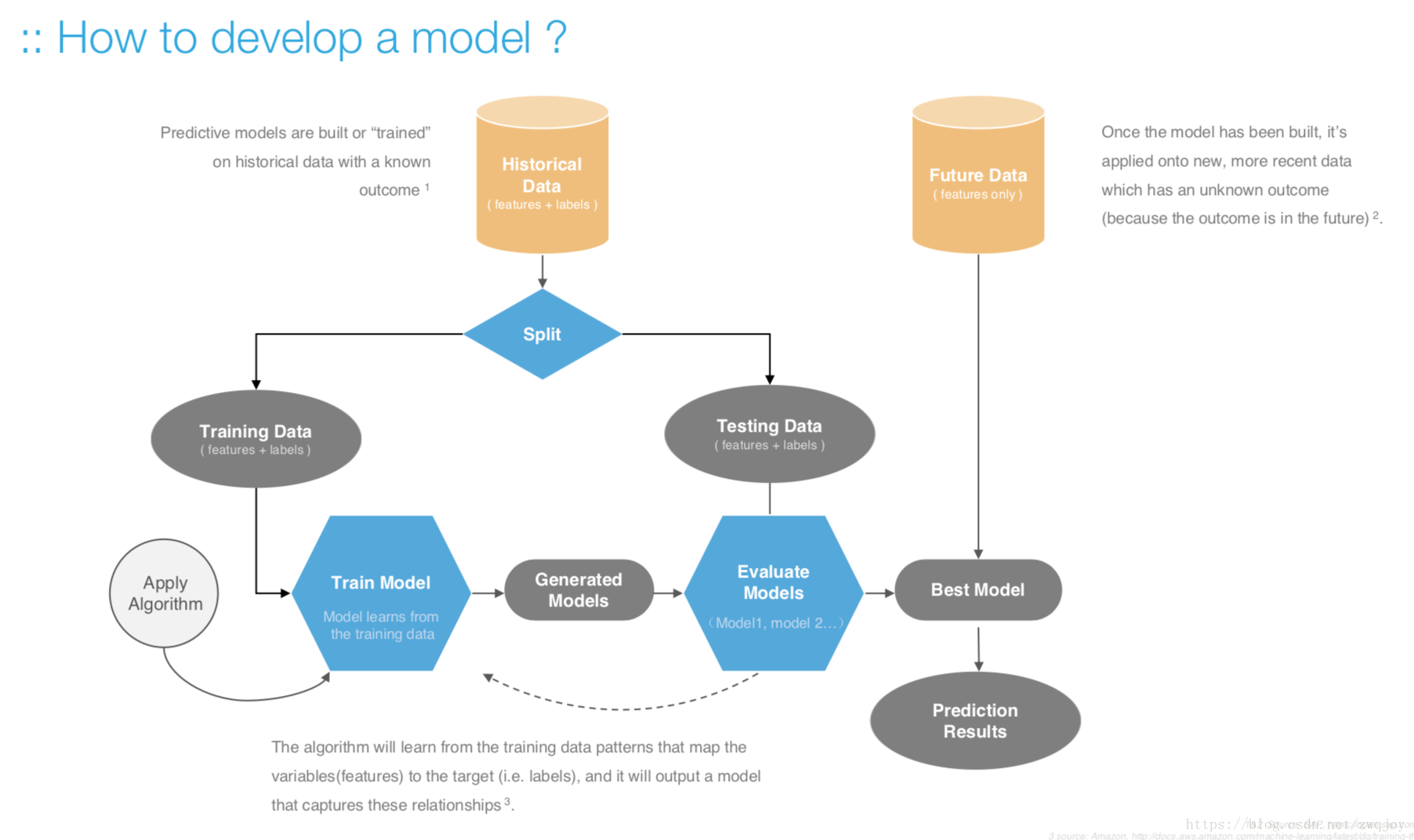
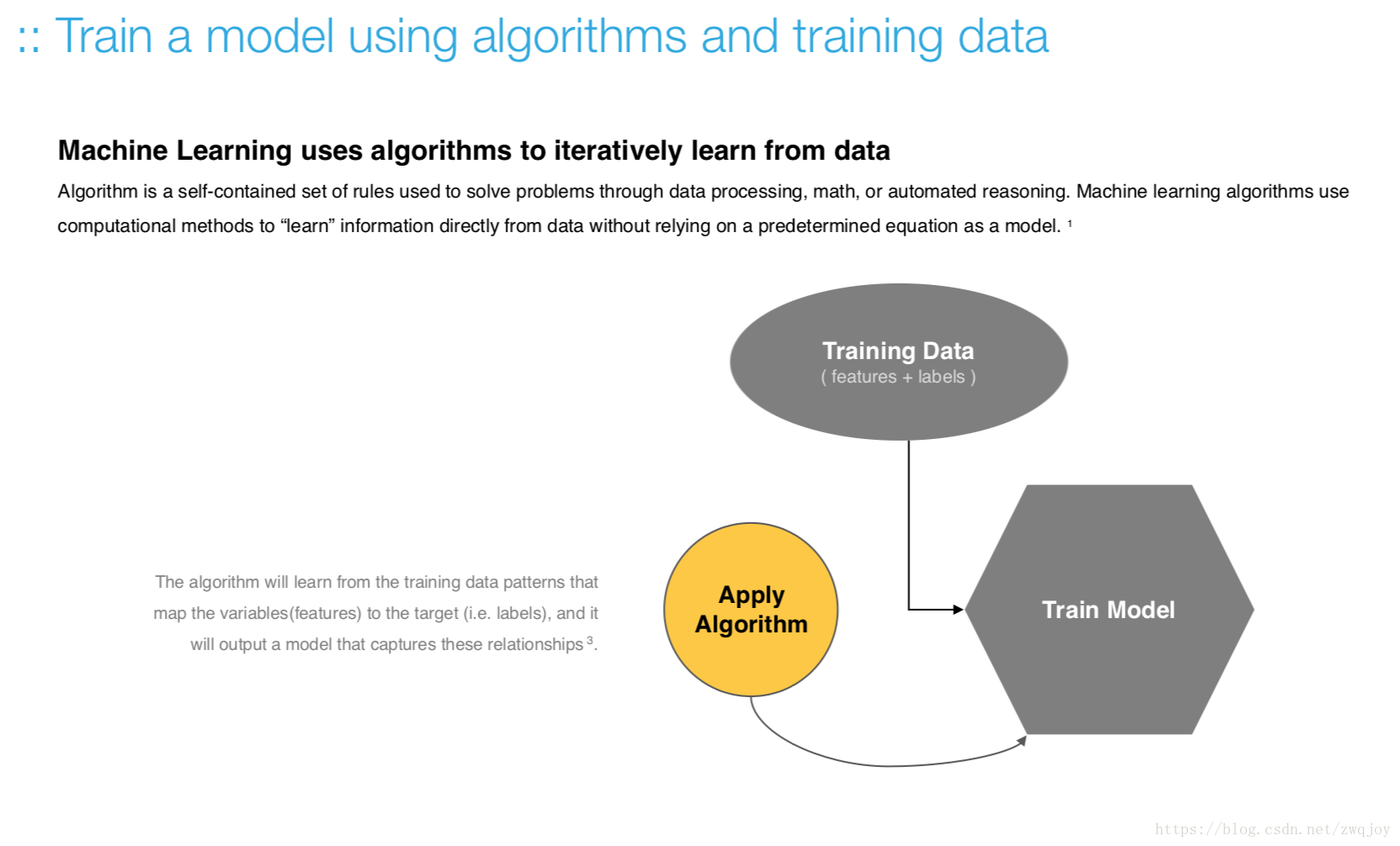
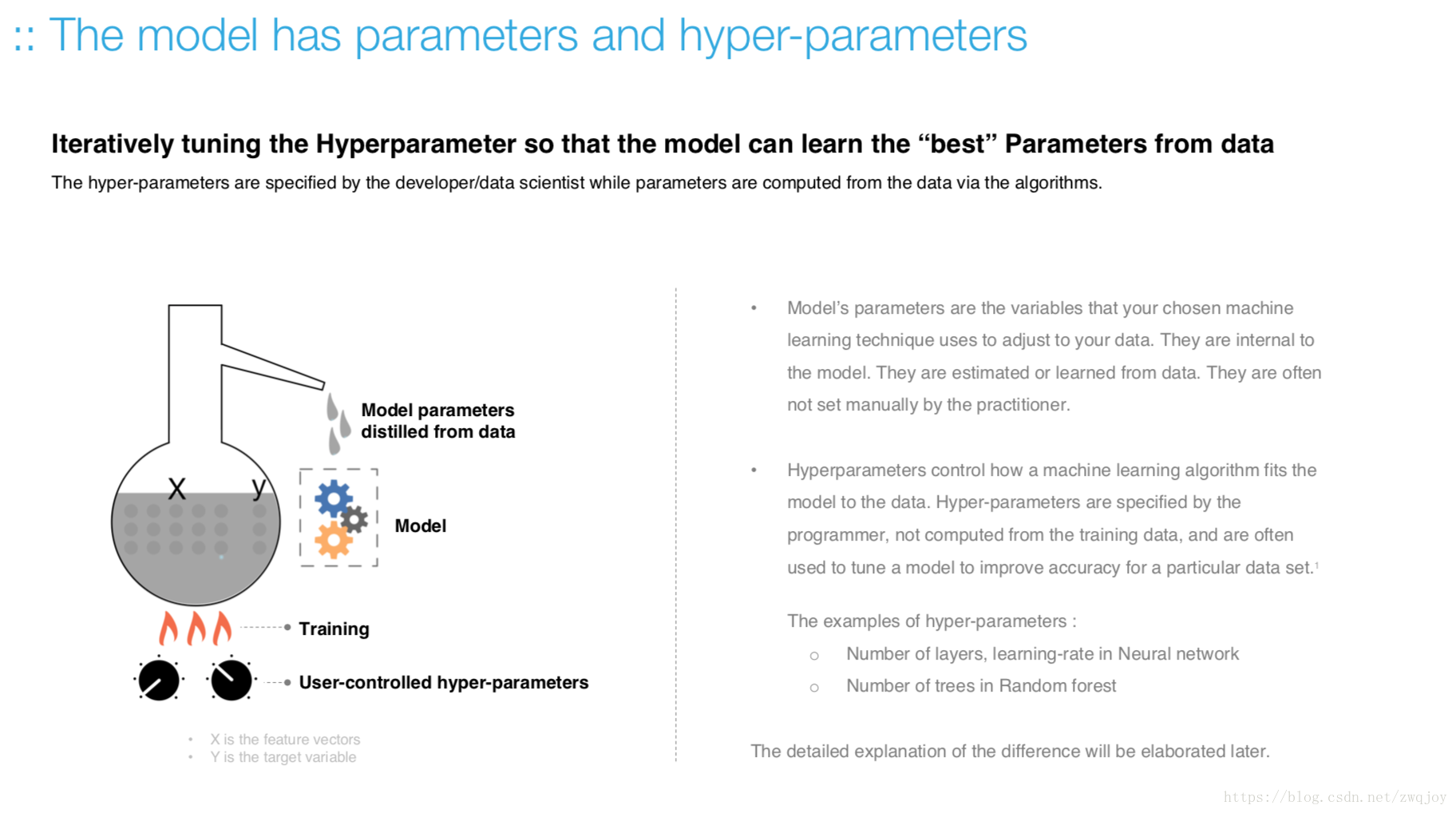
Train the model
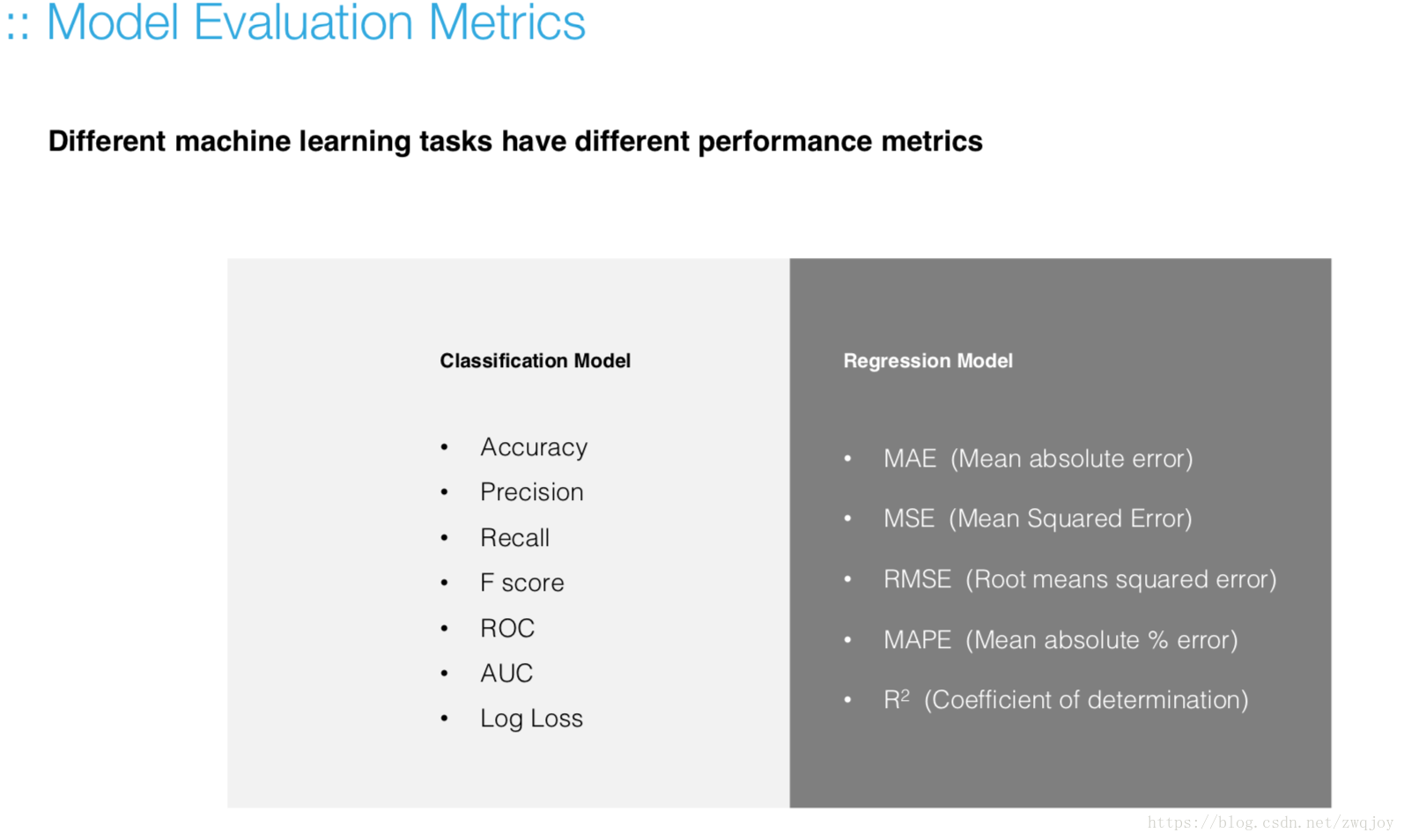
六. Model Evaluation
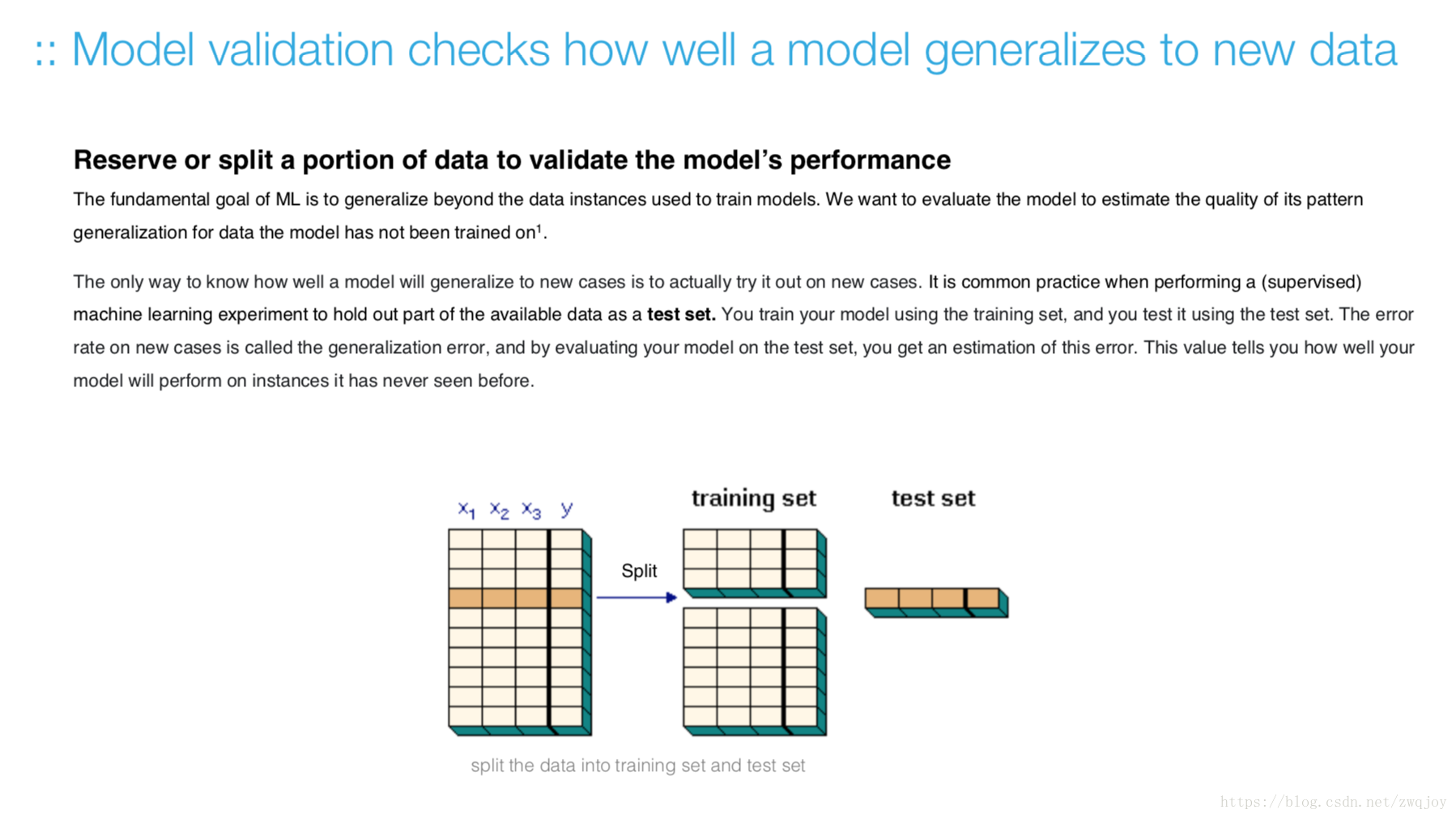
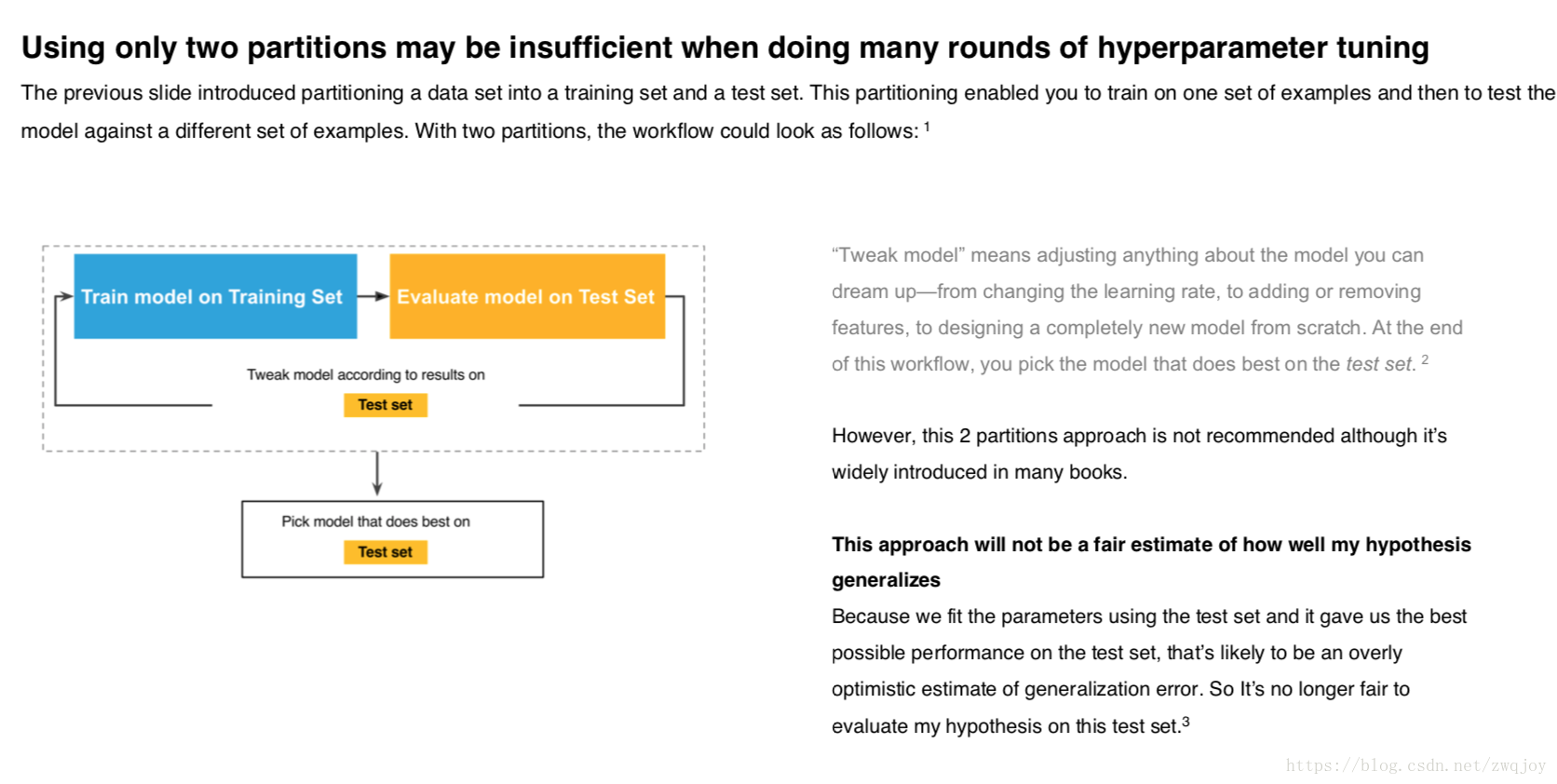
Hold-out validation strategy
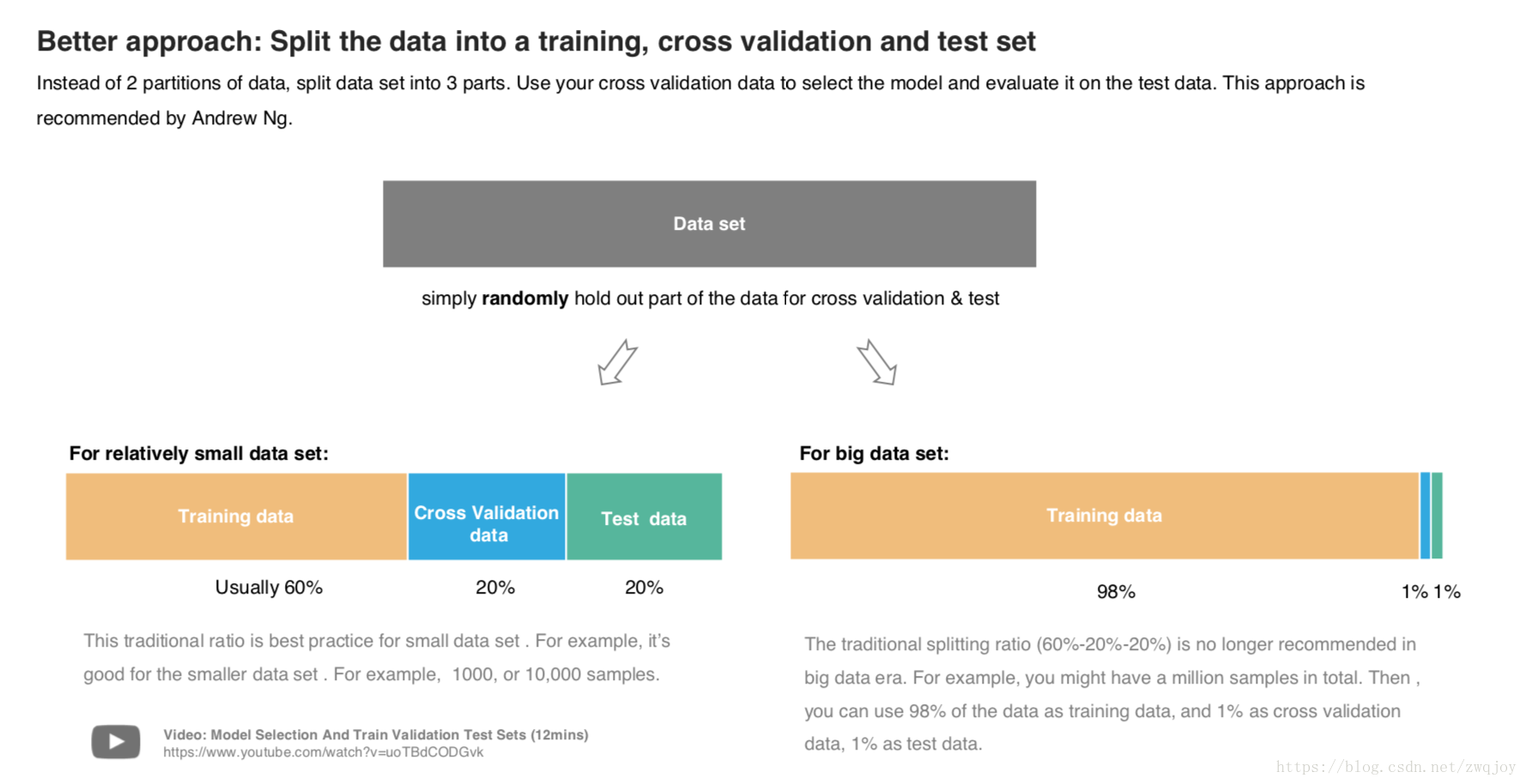
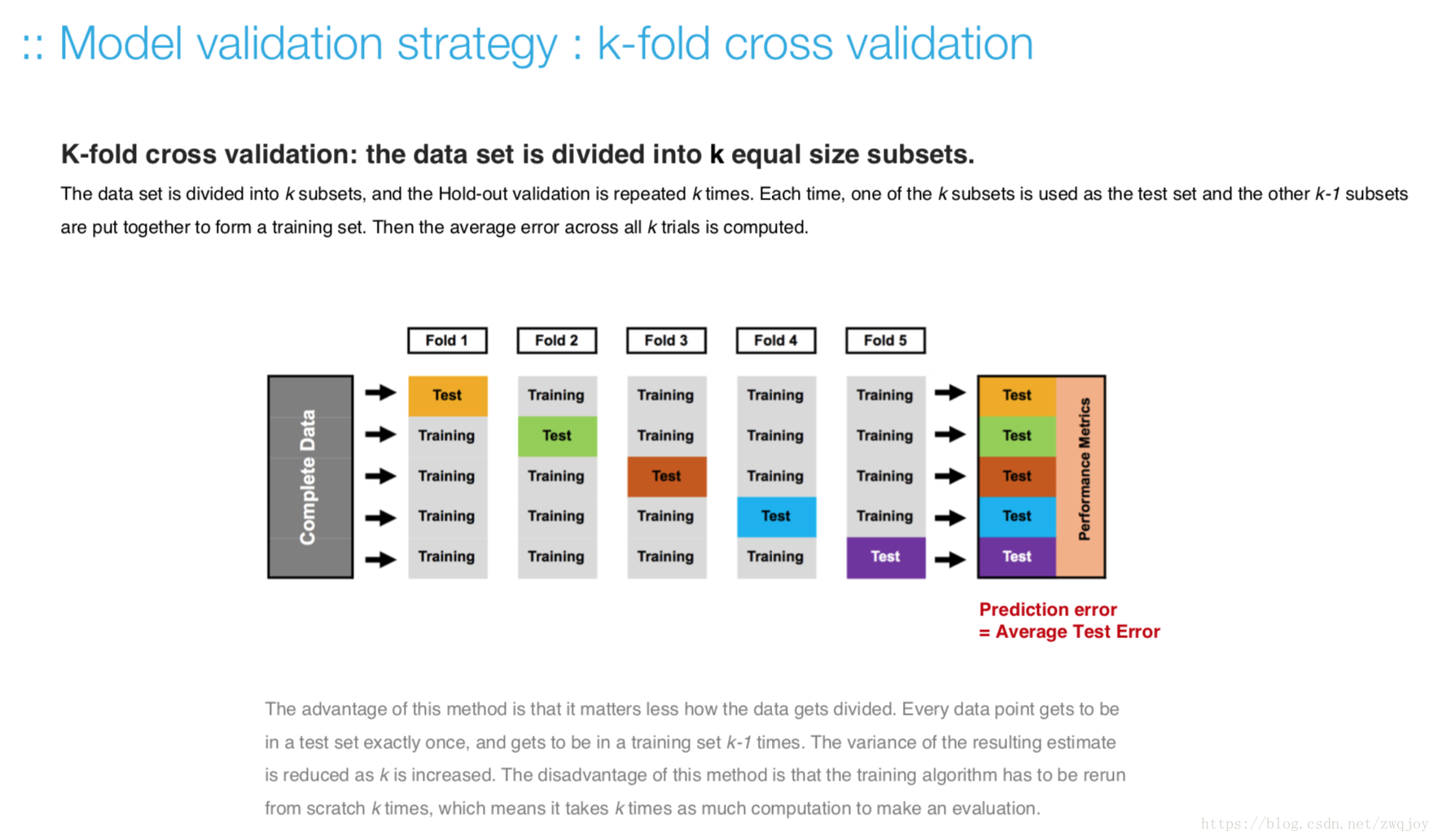
k-fold cross validation strategy
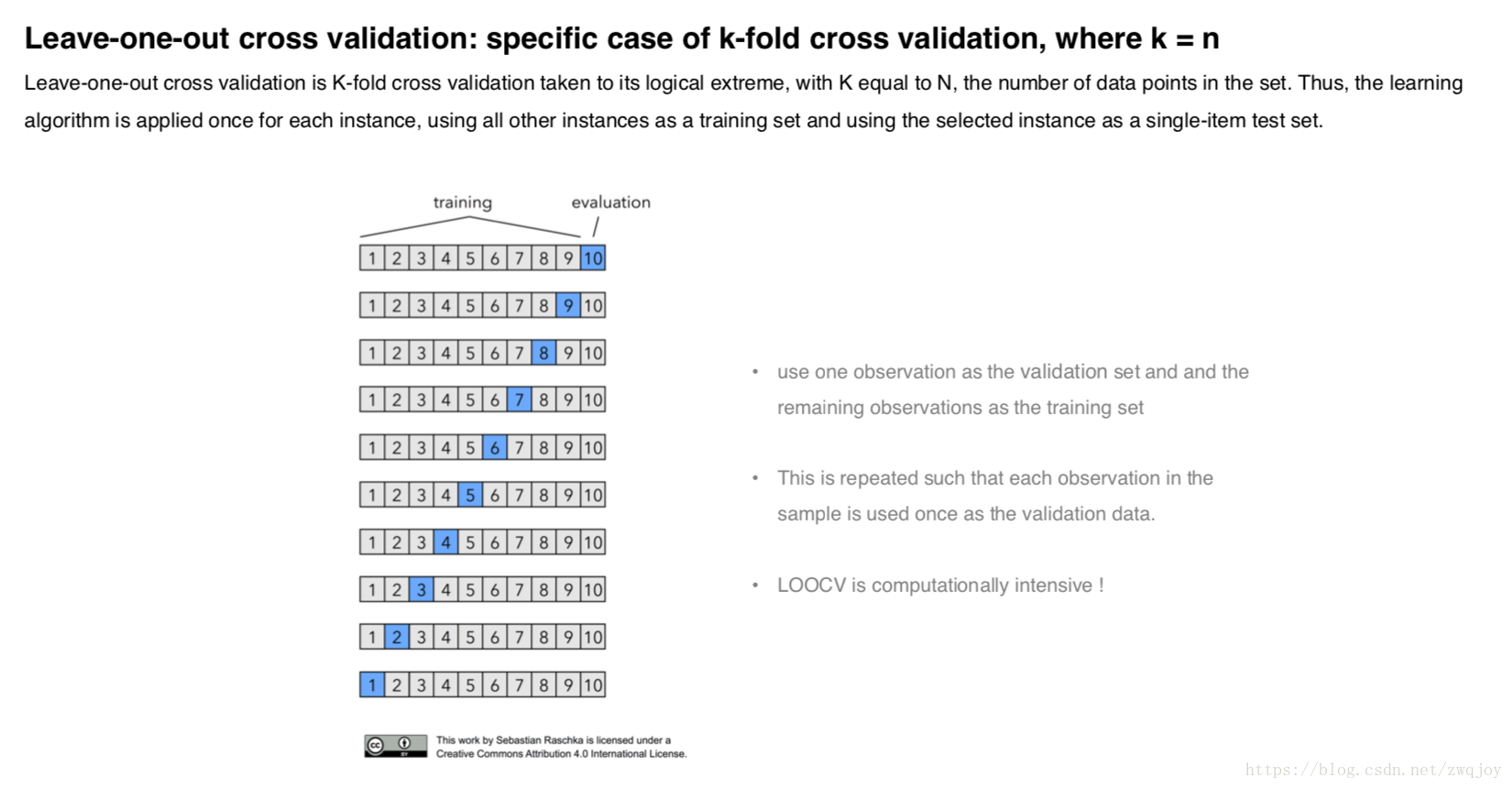
leave-one-out cross validation strategy
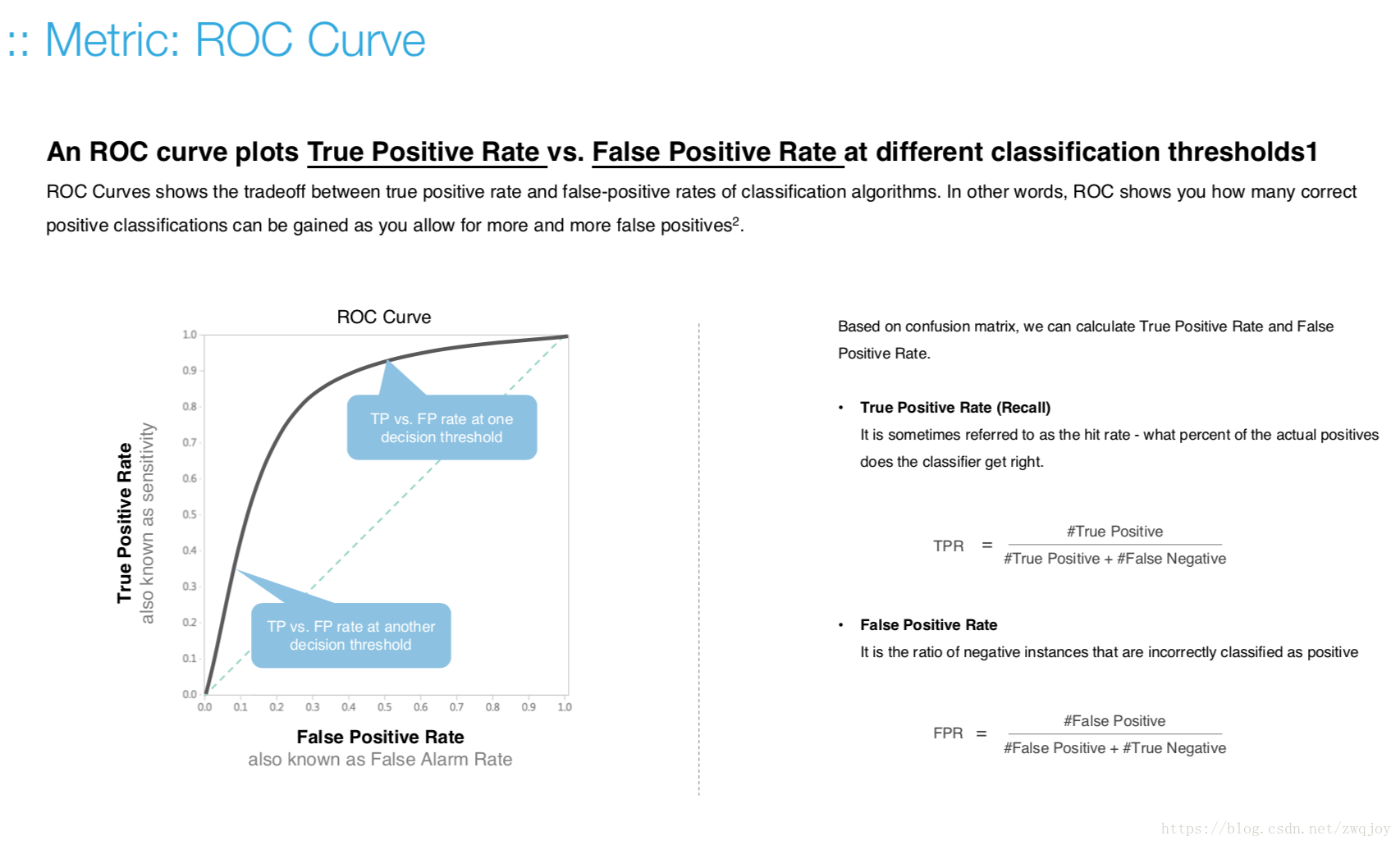
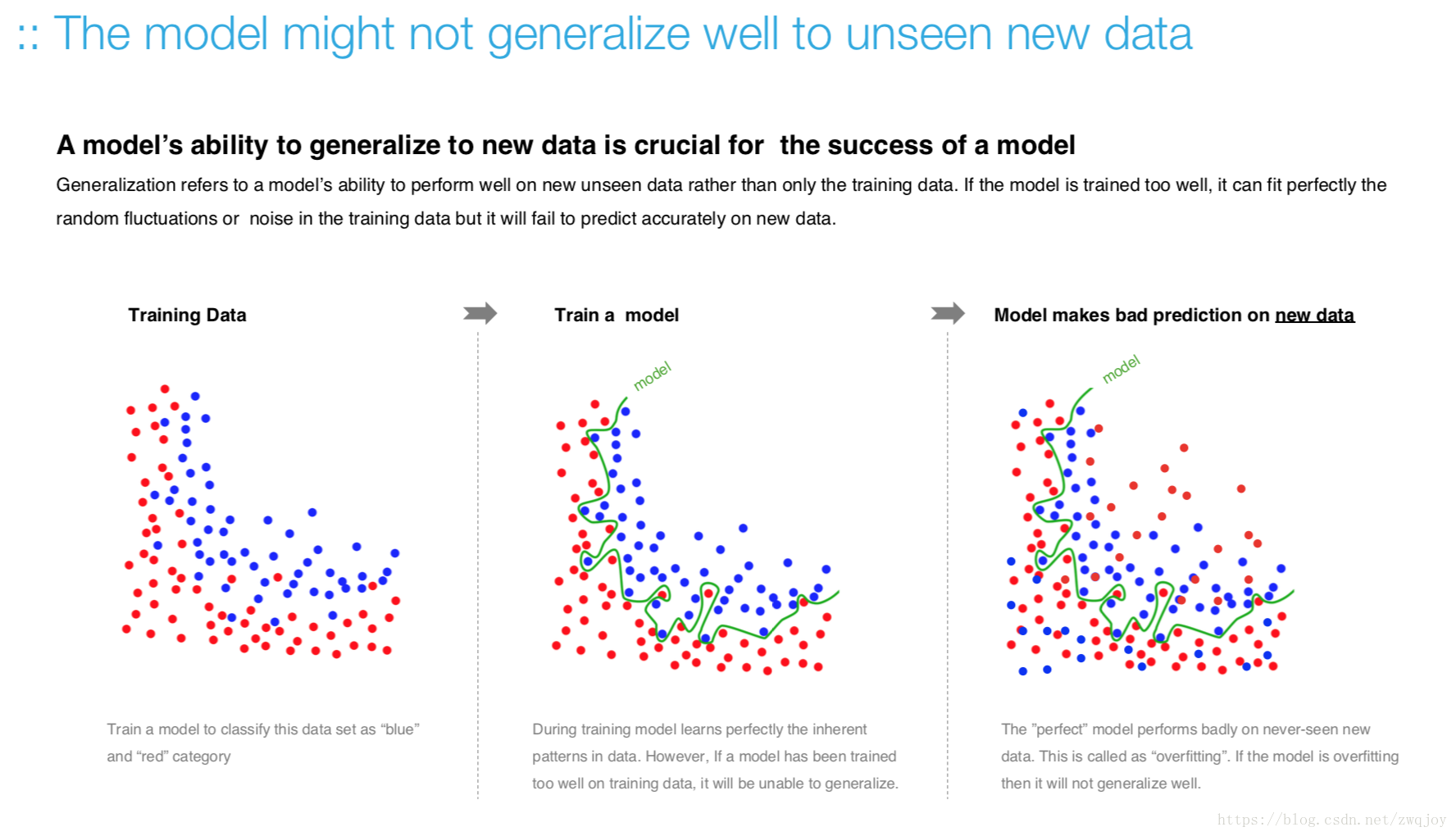
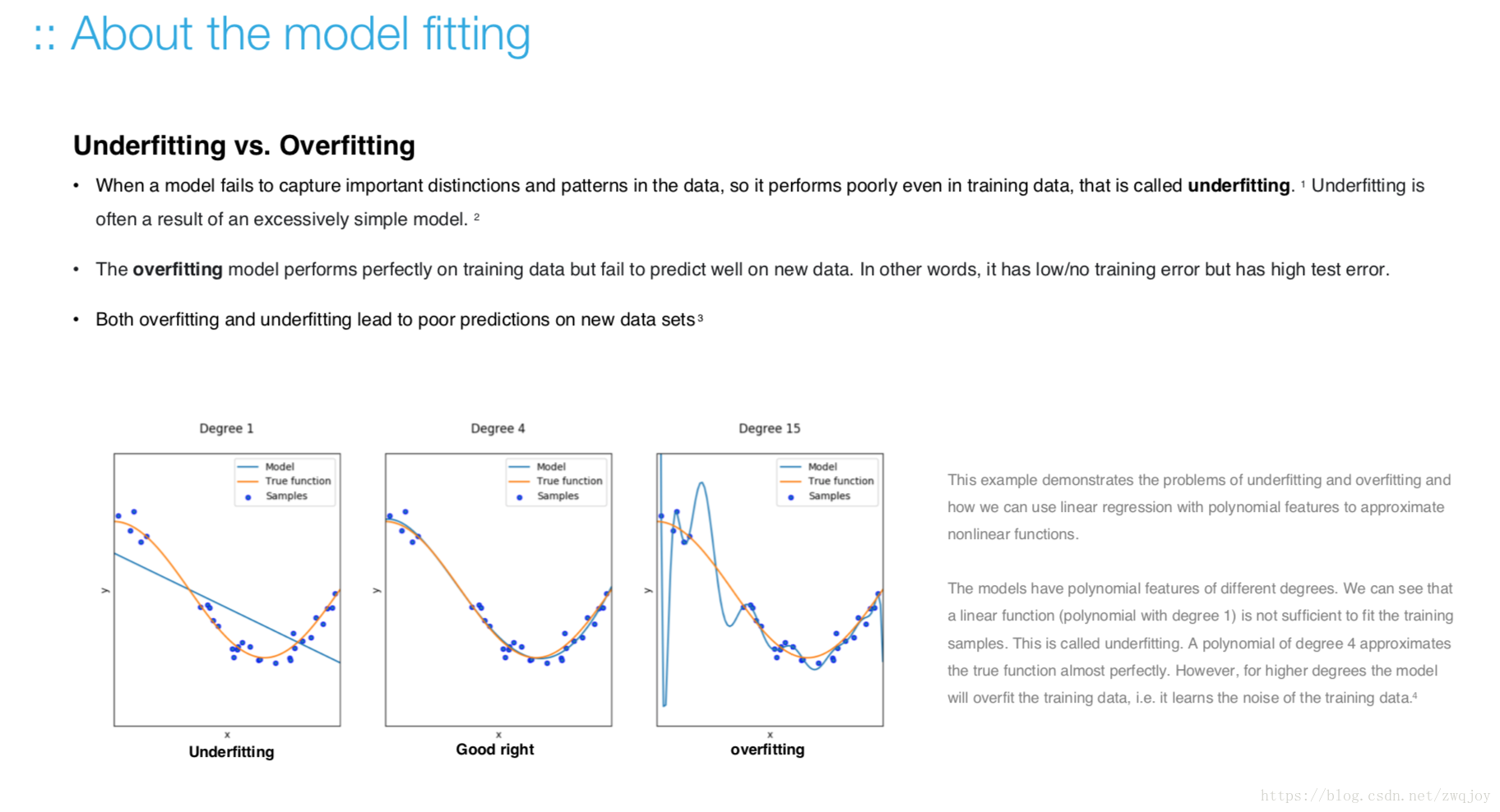
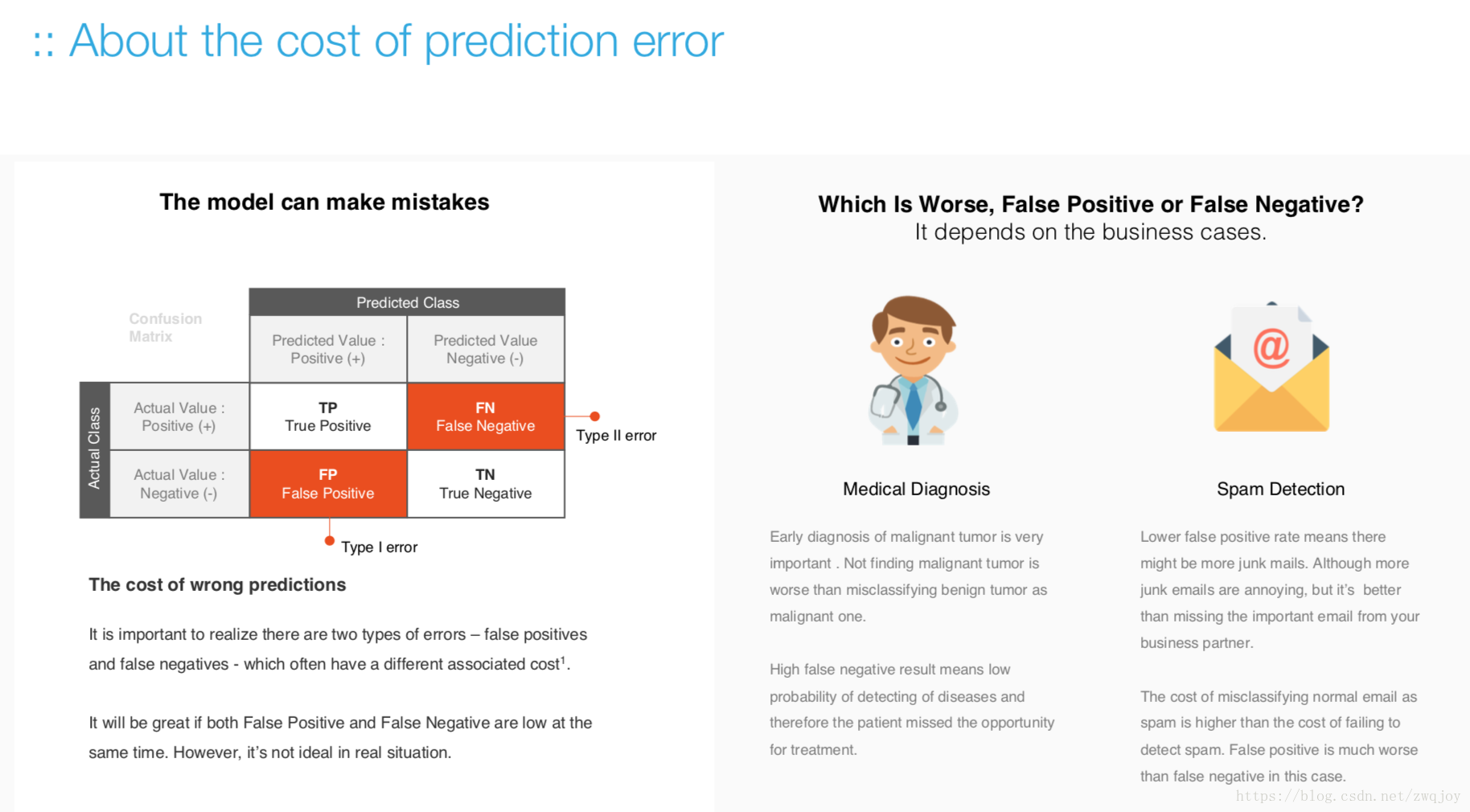
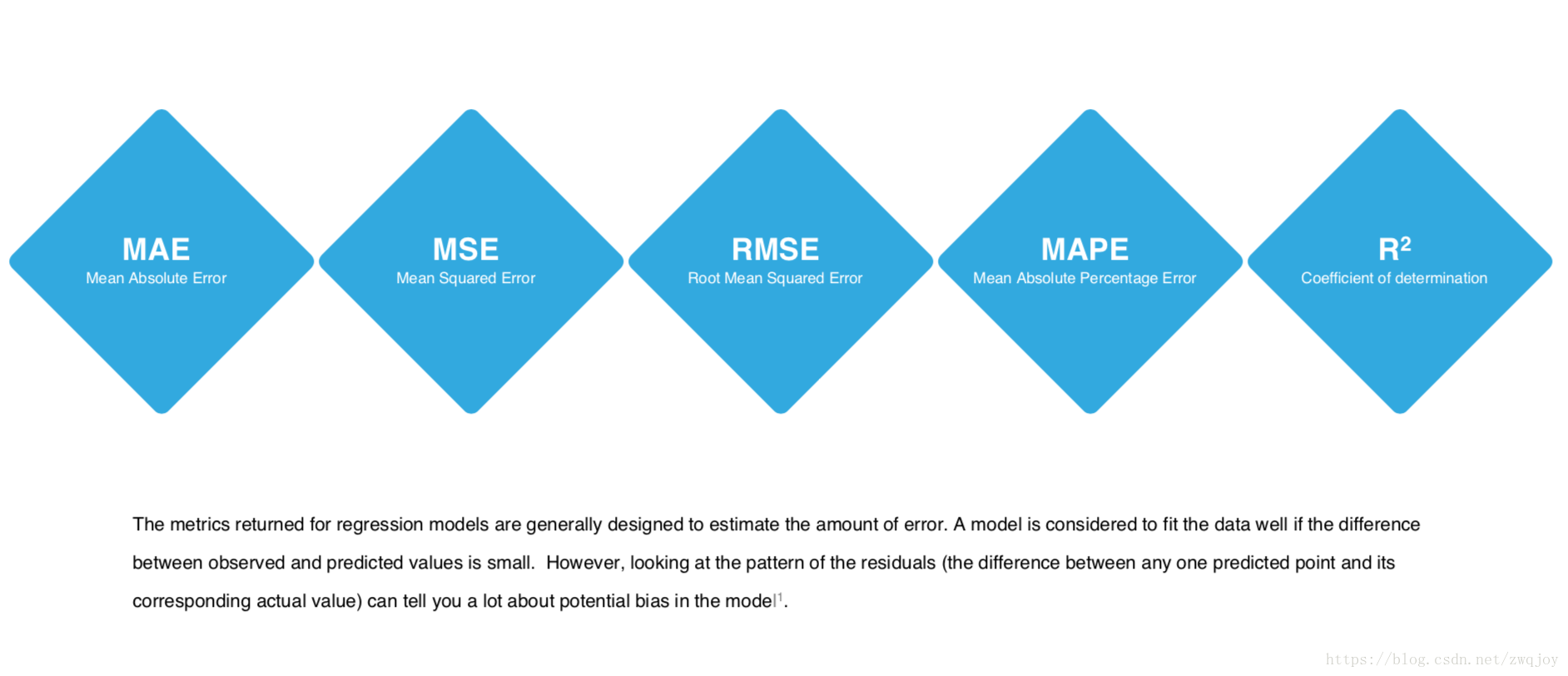
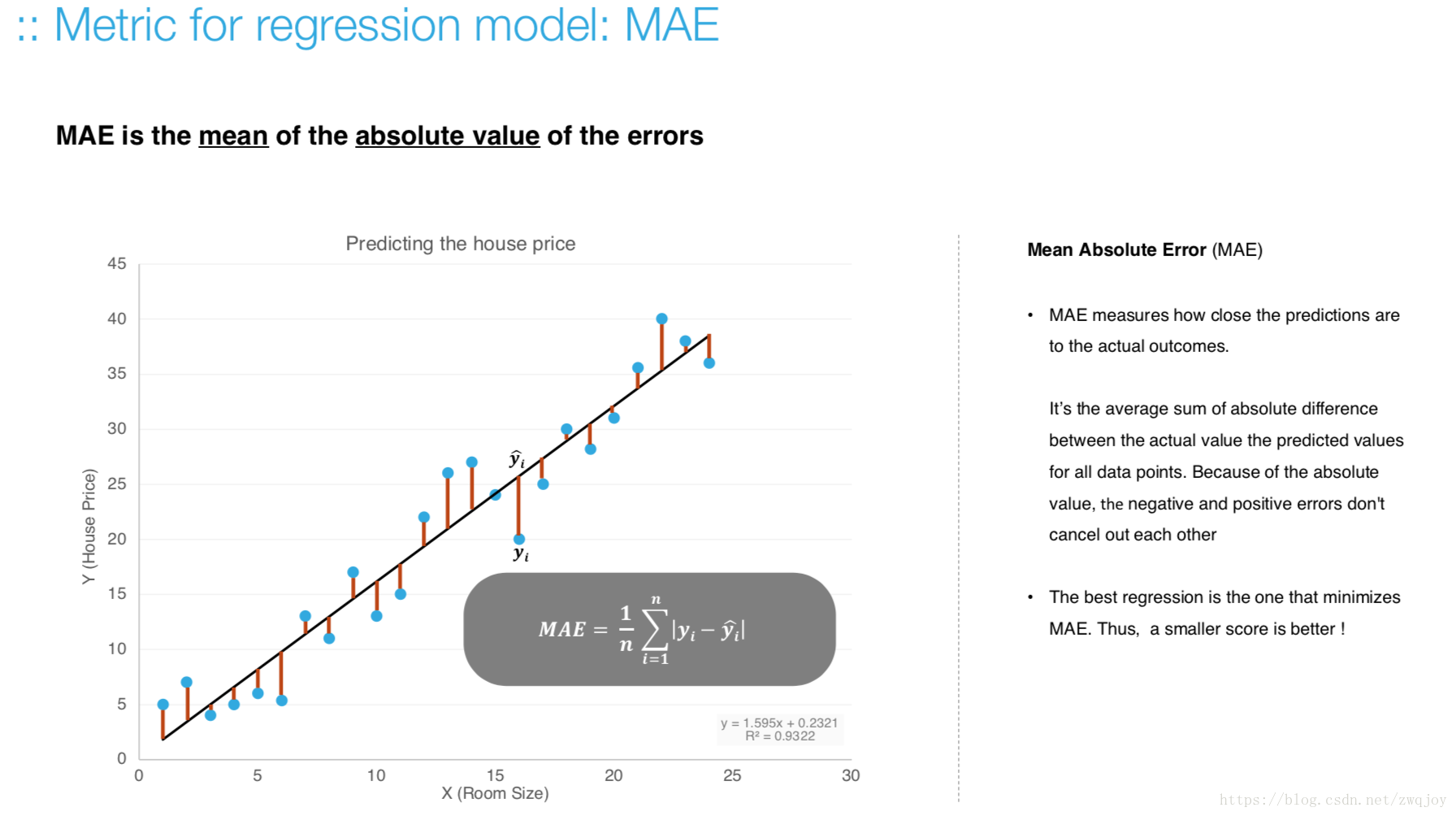
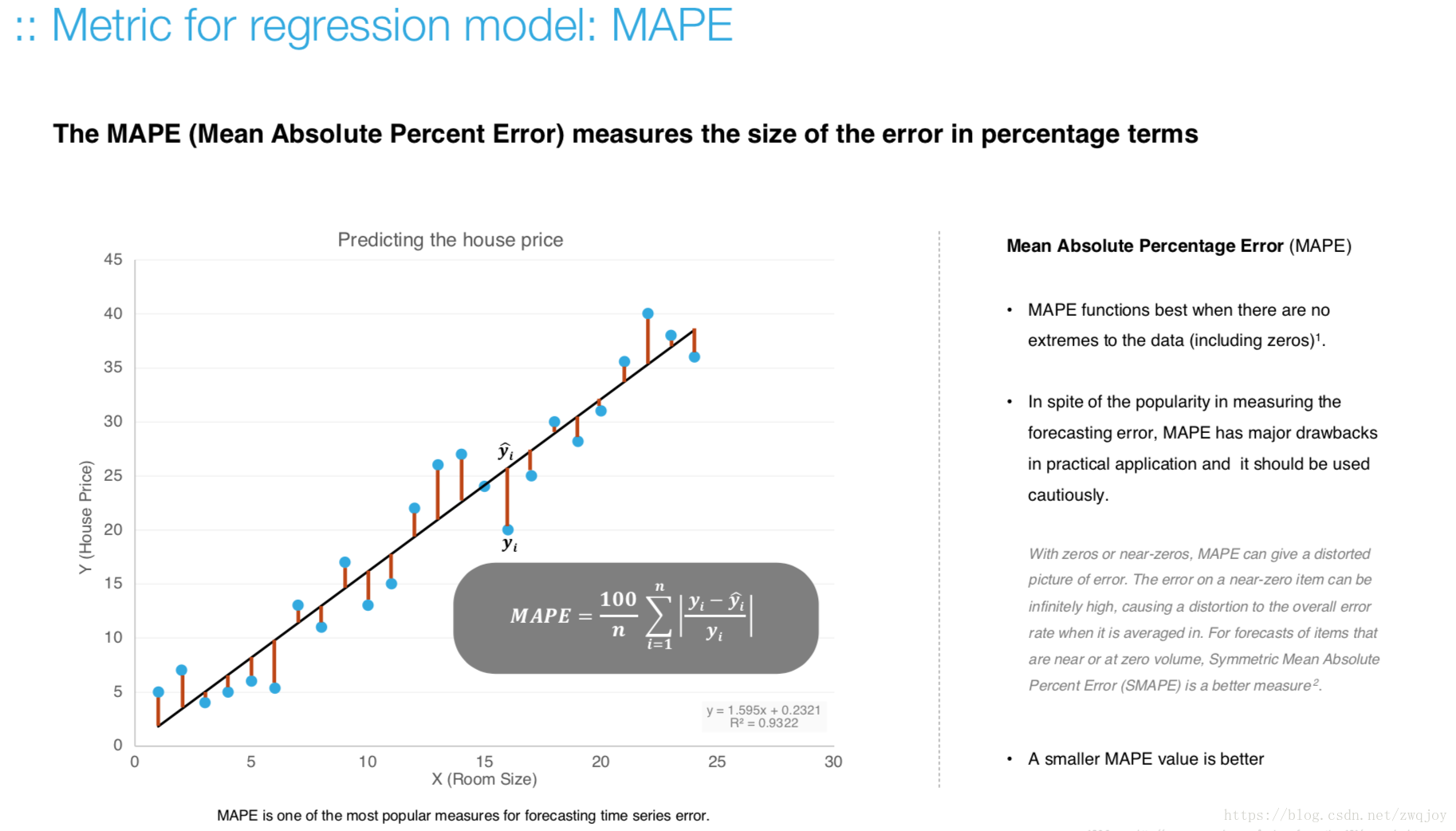
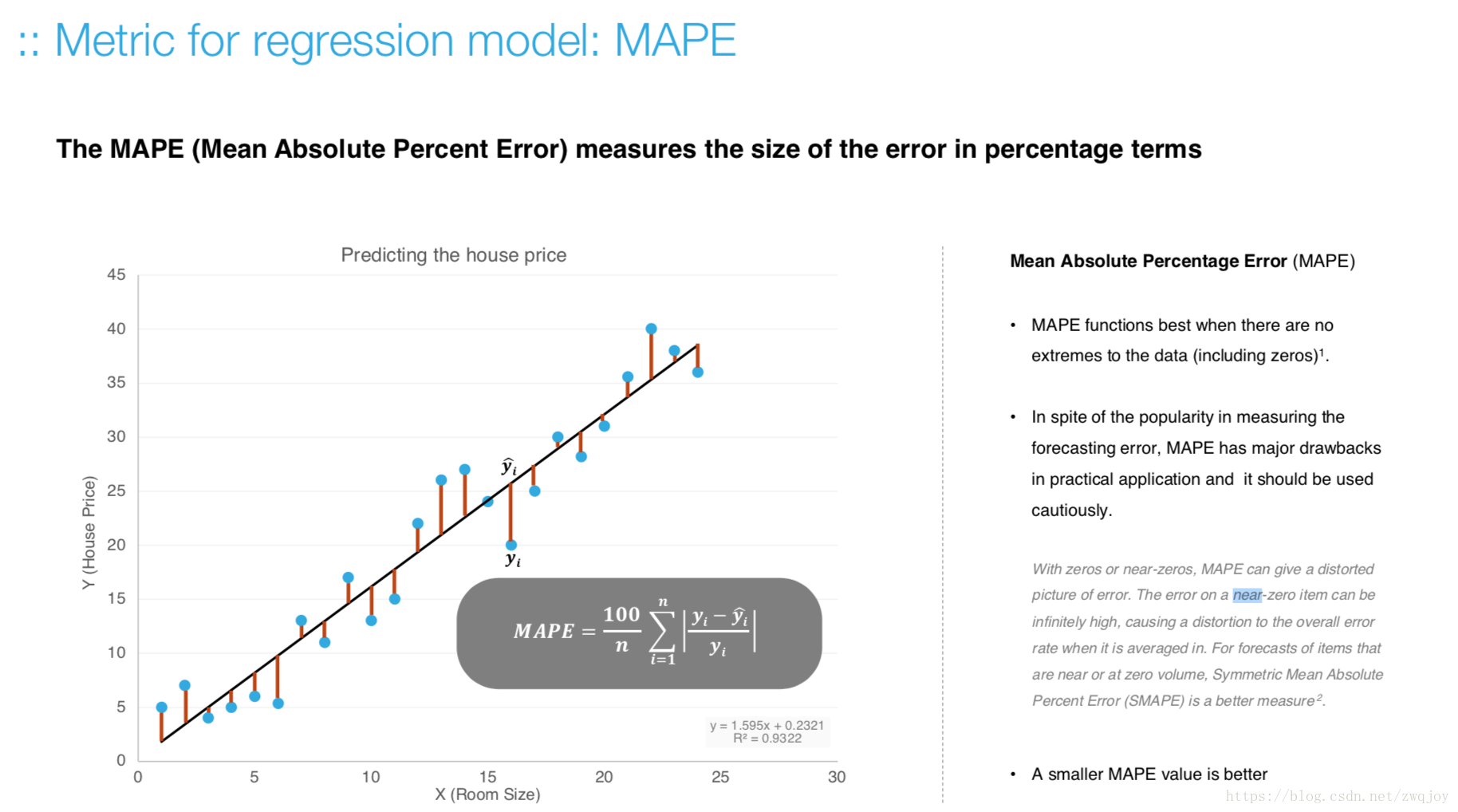
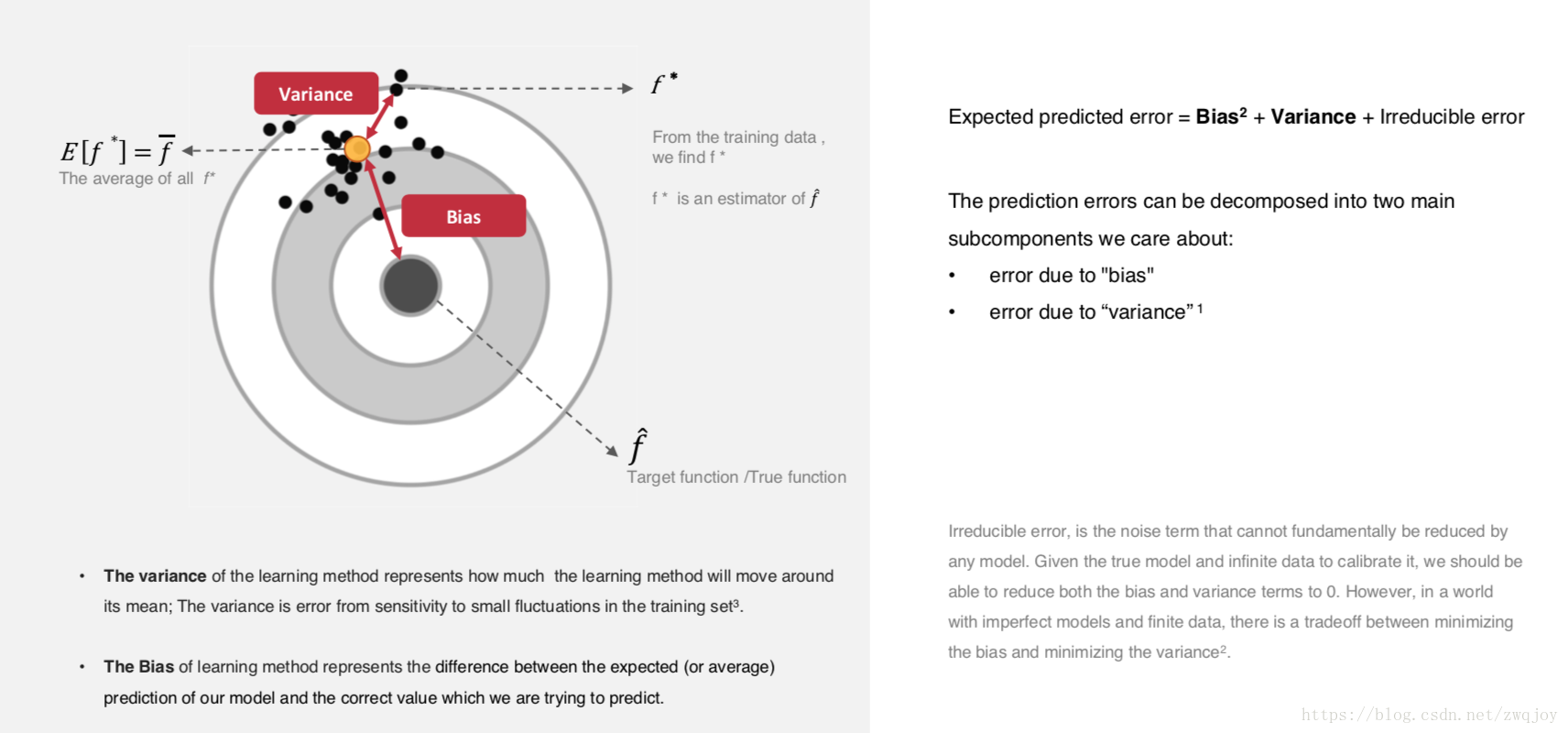
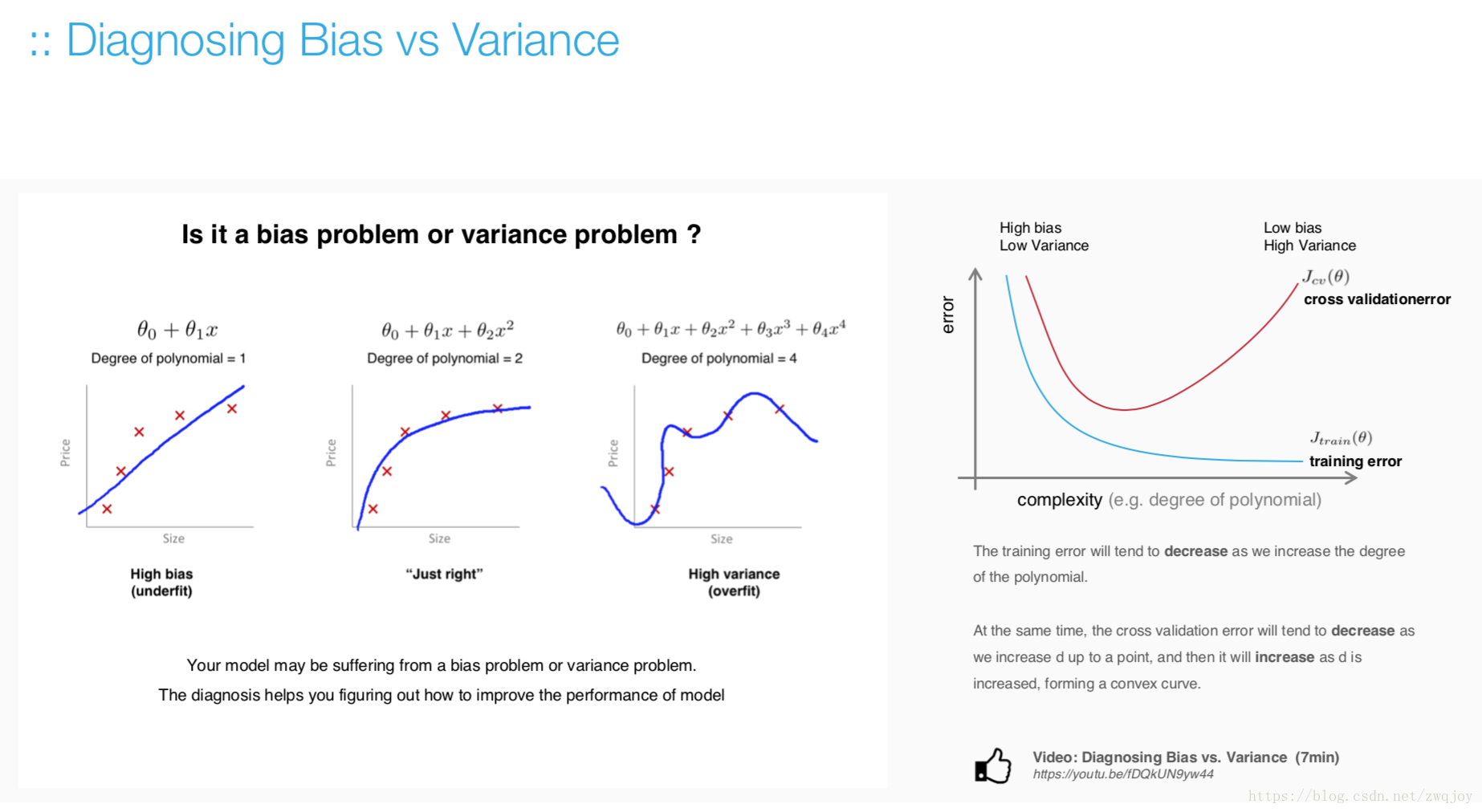
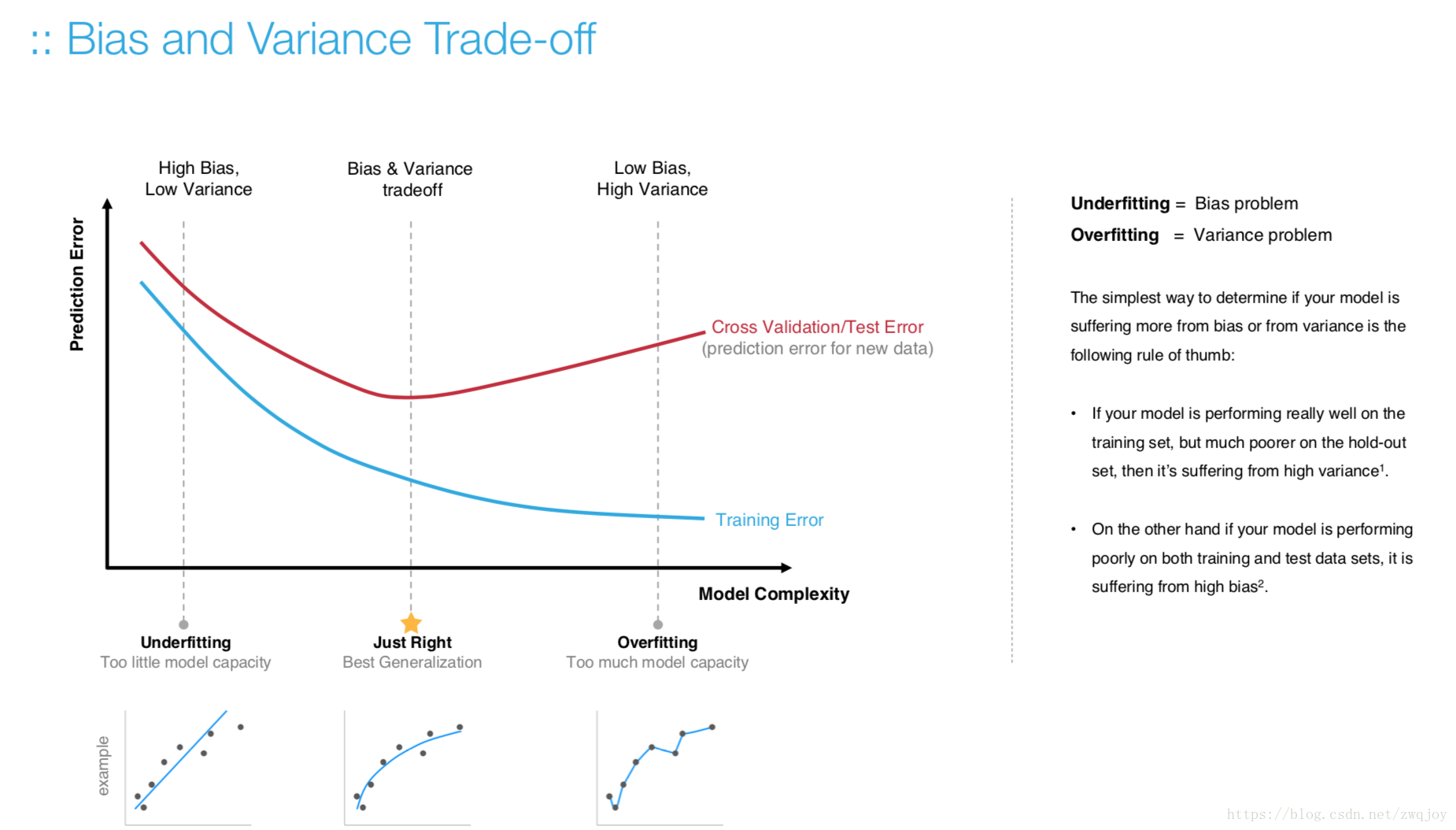
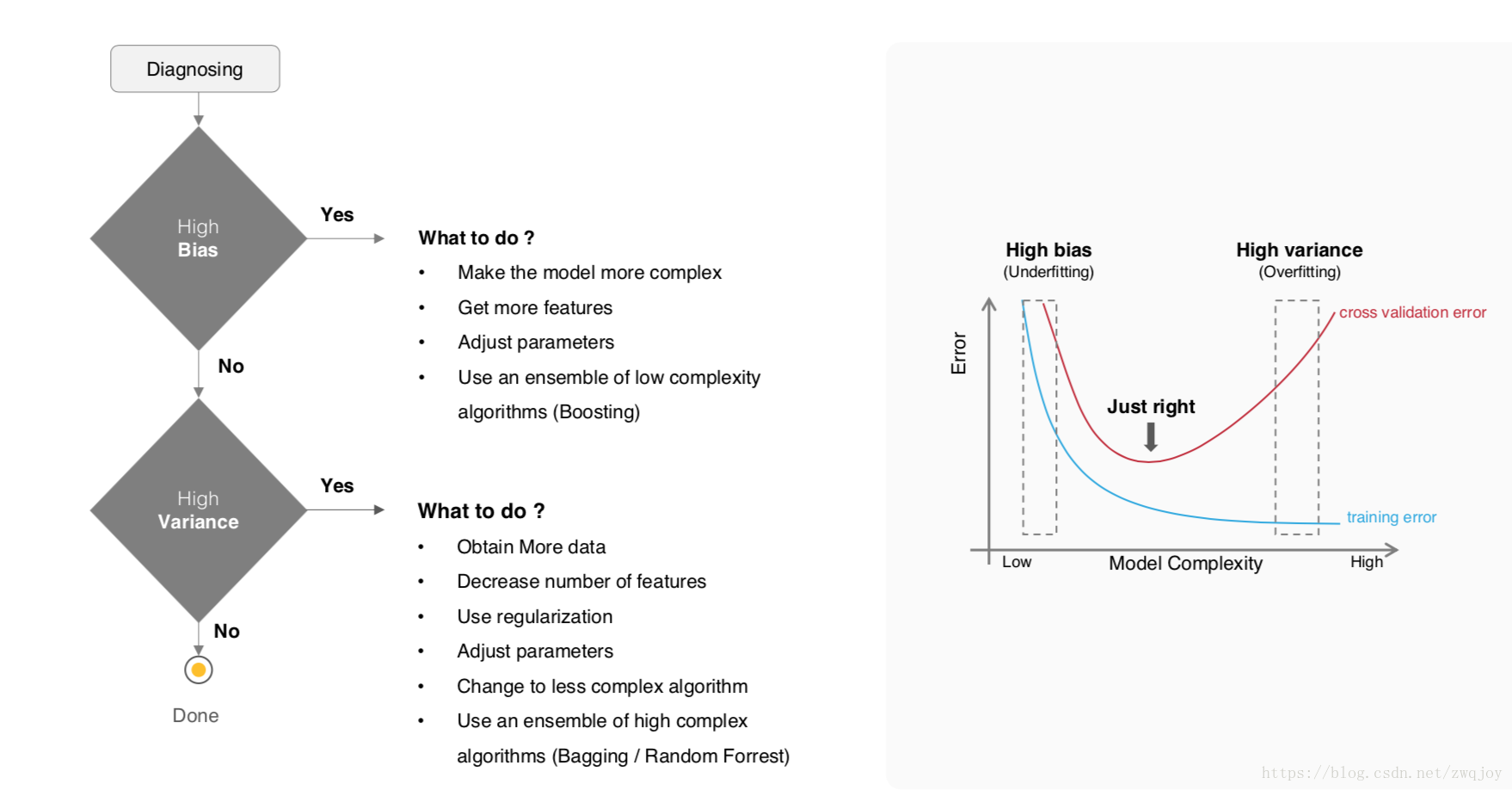
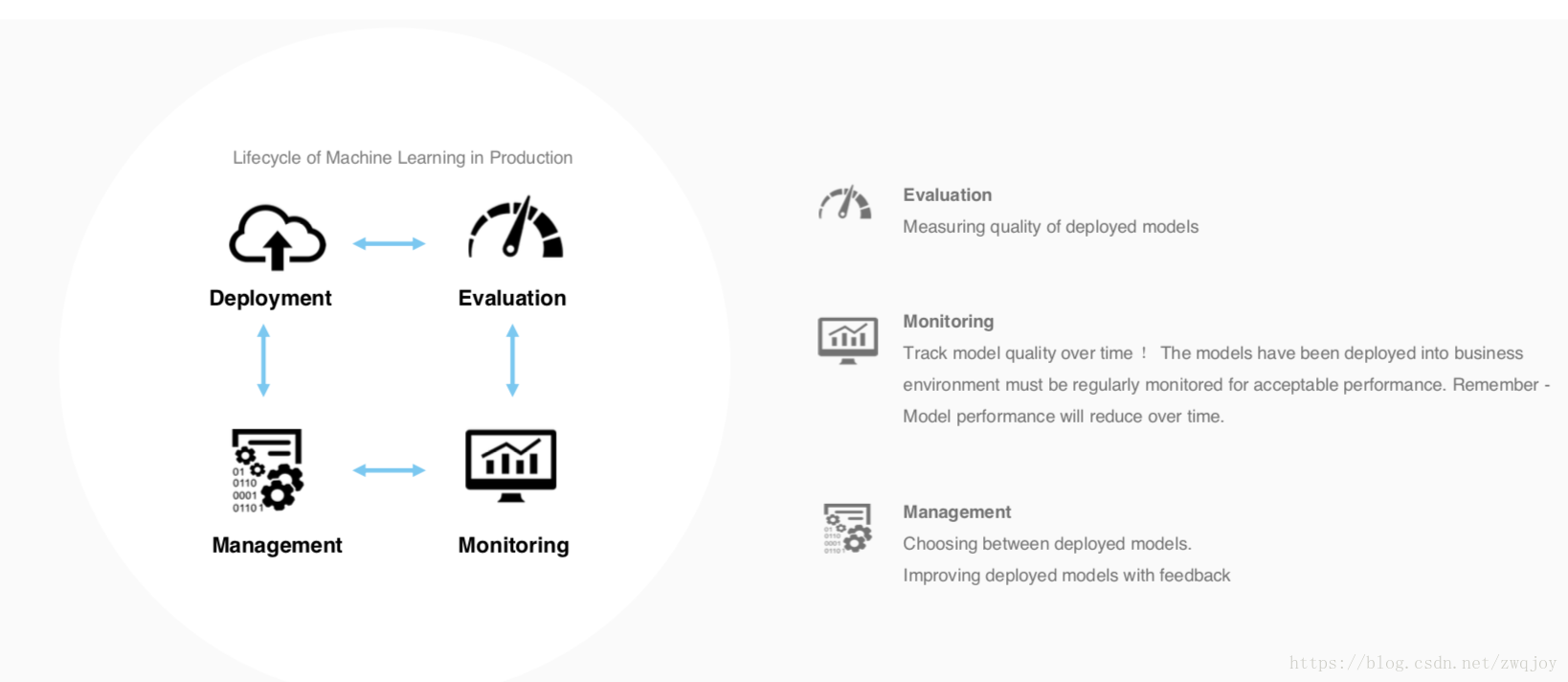
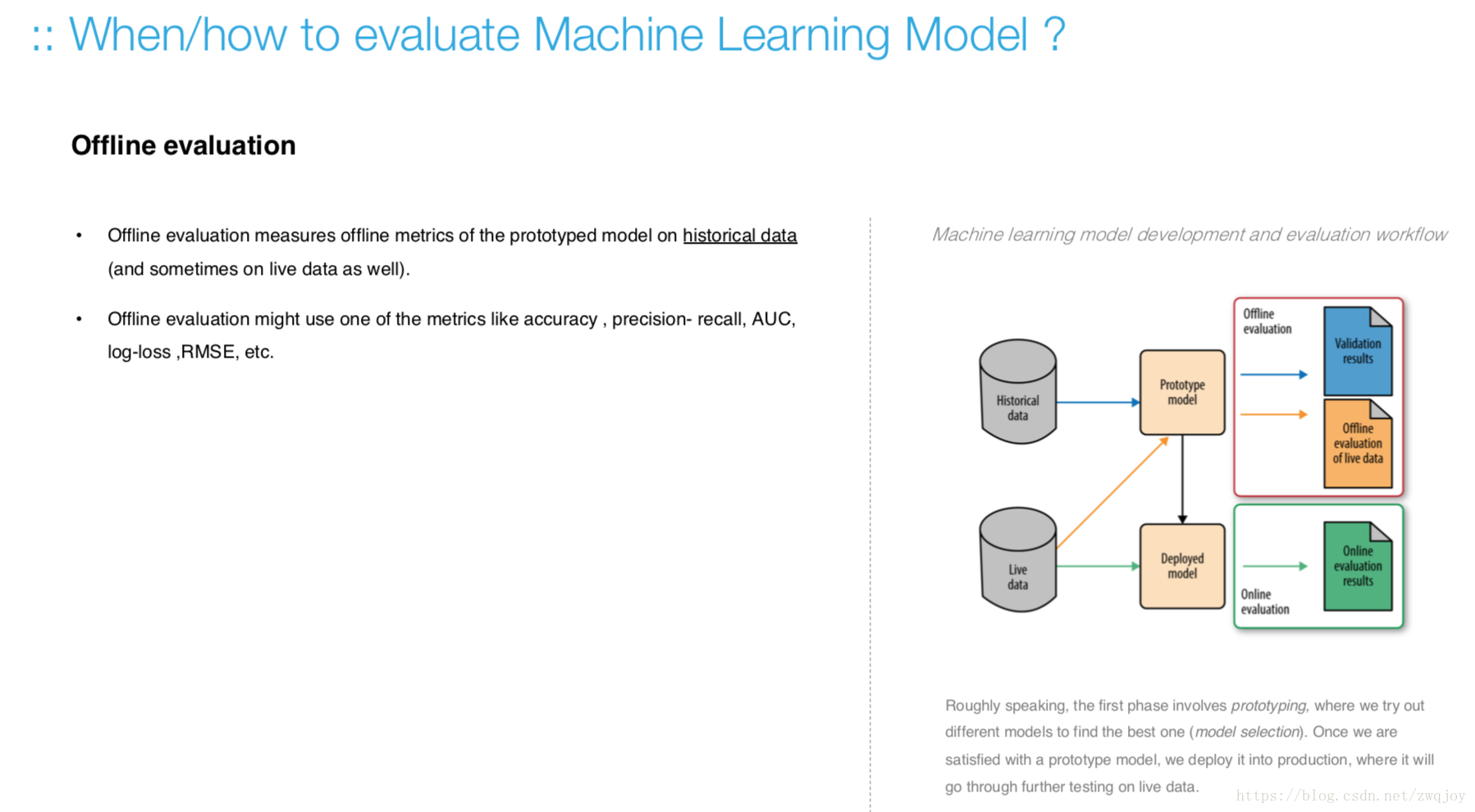
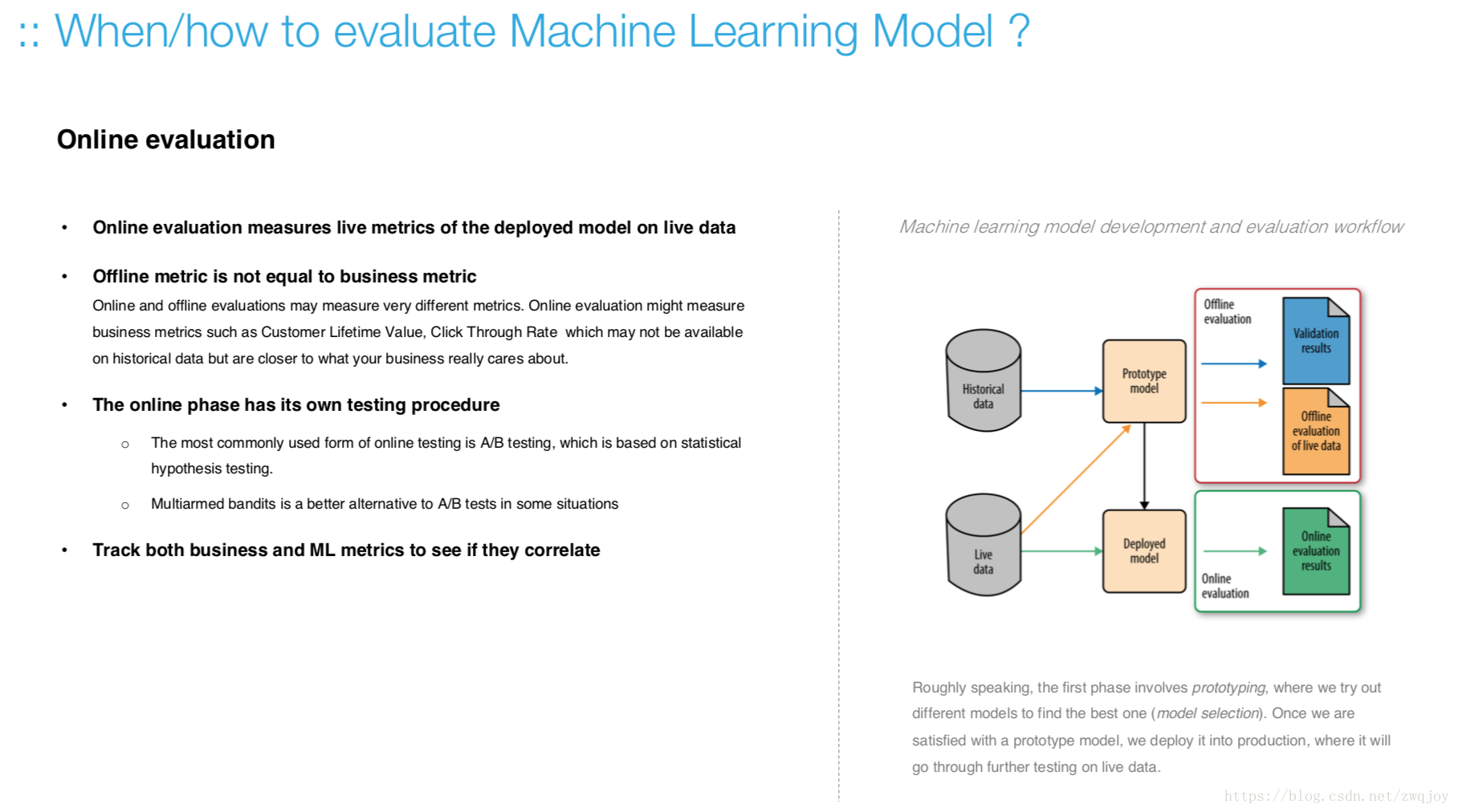
Model evaluation measures the quality of the machine learning model and determines how well our machine learning model will generalize to predict the target on new and future data.
Because future instances have unknown target values, you need to check the accuracy metric of the ML model on data for which you already know the target answer, and use this assessment as a proxy for predictive accuracy on future data 1.
Evaluate your trained model by using validation/test dataset. You compare the results of your model's predictions to the target values in the evaluation data and use statistical techniques appropriate to your model to gauge your success.
Because future instances have unknown target values, you need to check the accuracy metric of the ML model on data for which you already know the target answer, and use this assessment as a proxy for predictive accuracy on future data 1.
Evaluate your trained model by using validation/test dataset. You compare the results of your model's predictions to the target values in the evaluation data and use statistical techniques appropriate to your model to gauge your success.
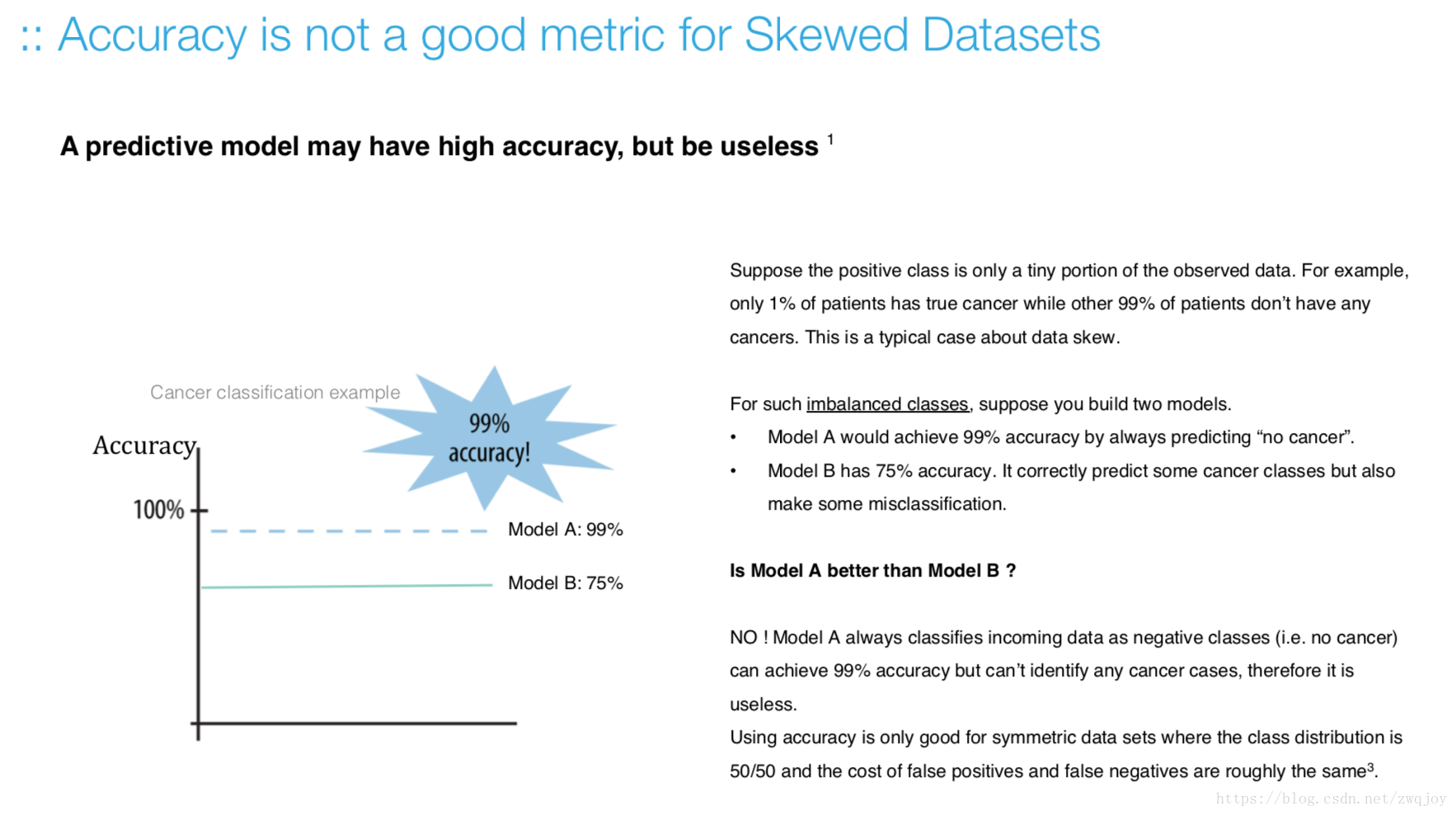
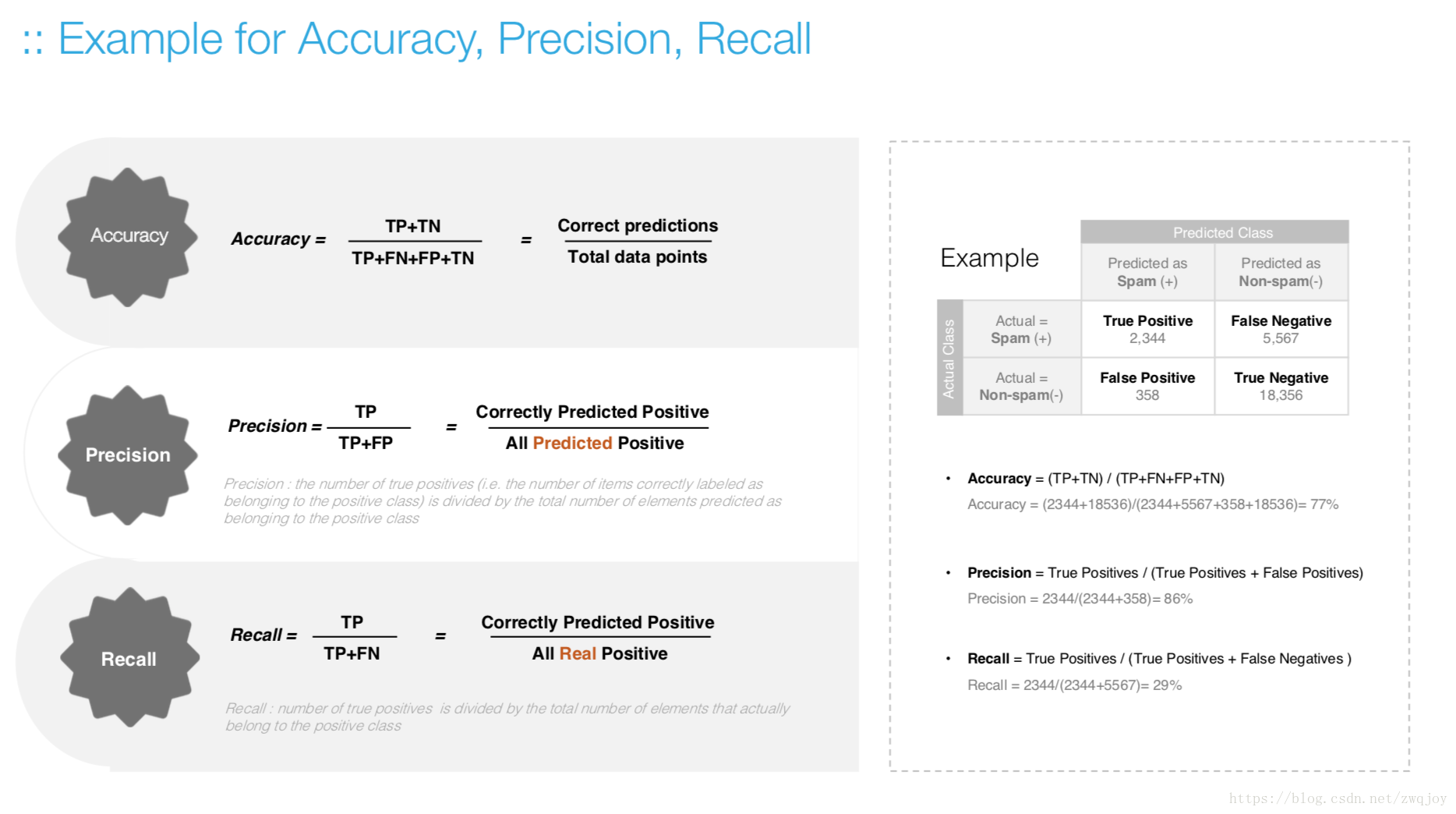
What’s the accuracy
Accuracy measures the ratio of correct predictions to the total number of cases evaluated

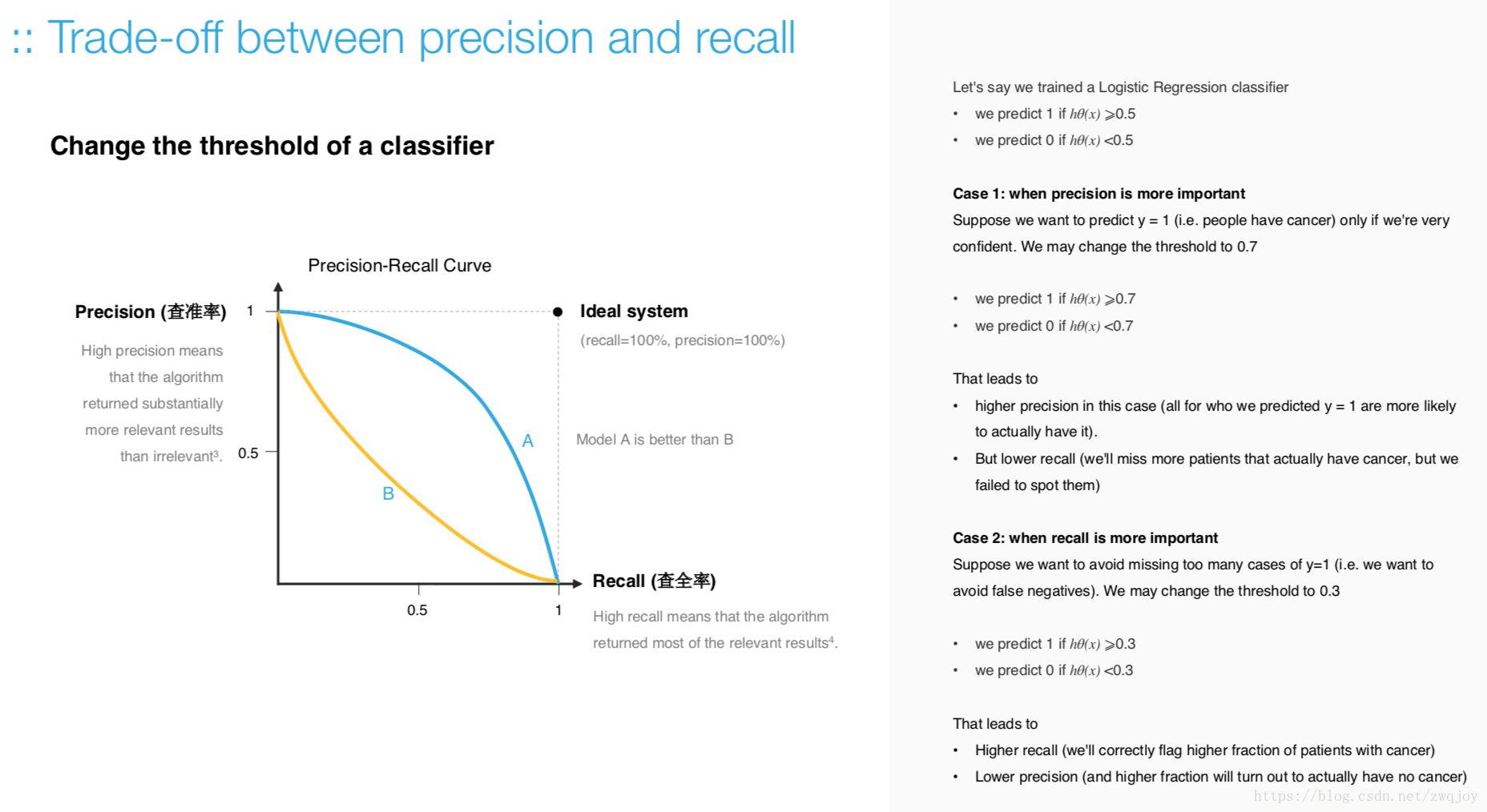
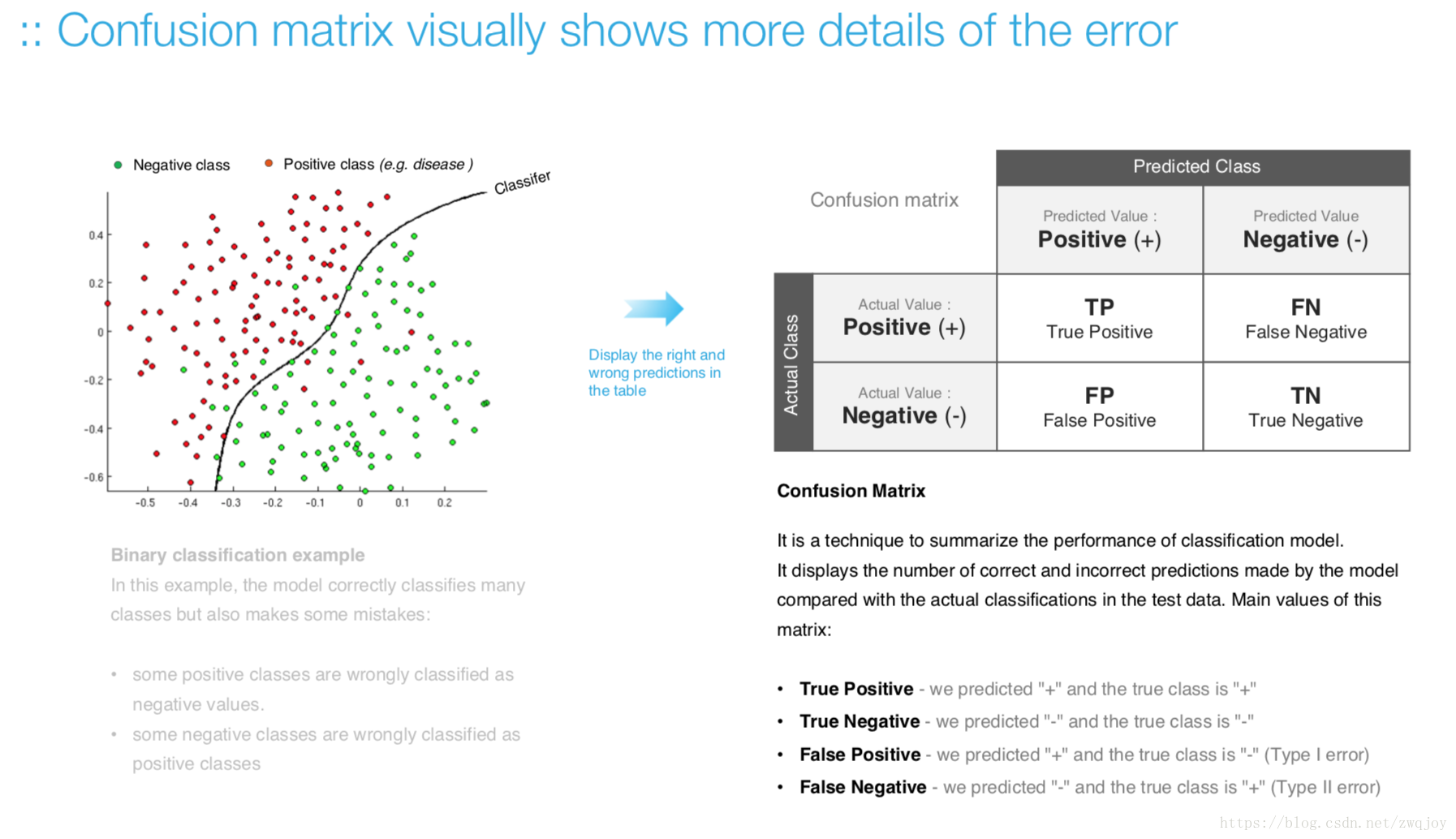
Increasing precision reduces recall, and vice versa. This is called the precision/recall tradeoff
- Within any one model, you can decide to emphasize either precision or recall.
- You can influence precision and recall by changing the threshold of the model.