网络编程(java.net)
一、网络要素
1、IP地址:InetAddress
192.168.1.255(192.168.1网段的广播地址)
2、端口号
0--65535
0-1024
3、传输协议
UDP
将数据及源和目的封装成数据包中,不需要建立连接
数据包大小限制在64K内
因无连接,不可靠协议
不需要建立连接,速度快
TCP
建立连接,形成传输数据的通道
在连接中进行大数据量传输
通过三次握手完成连接,是可靠协议
必须建立连接,效率稍低
二、UDP协议实例
DatagramSocket:用来发送和接收数据包的套接字
网络通信:发送端
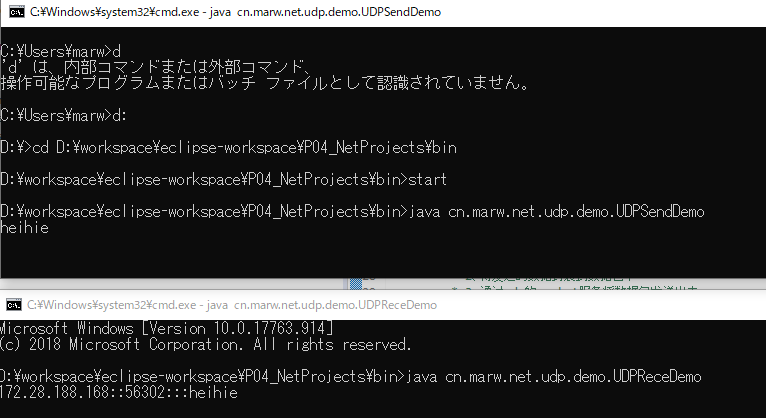
1 public class UDPSendDemo { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 * @throws IOException 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 /* 9 * 创建UDP传输的发送端 思路: 10 * 1、建立udp的socket服务 11 * 2、将发送的数据封装到数据包中 12 * 3、通过udp的socket服务将数据包发送出去 13 * 4、关闭socket服务 14 */ 15 // 1、 16 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(); 17 // 2、 18 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 19 String line=null; 20 while ((line=br.readLine())!=null) { 21 byte[] buff = line.getBytes(); 22 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buff, buff.length, InetAddress.getByName("172.28.188.168"), 10000); 23 ds.send(dp); 24 } 25 26 ds.close(); 27 28 } 29 30 }
二、网络通信:接收端
1 public class UDPReceDemo { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 * @throws IOException 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 /* 9 * 建立UDP接收端的思路 10 * 1、建立udp socket服务 11 * 2、创建数据包,用于存储接收到的数据。方便用数据包对象的方法解析这些数据 12 * 3、使用socket服务的receive方法将接收的数据存储到数据包中。 13 * 4、通过数据包的方法解析数据包的数据 14 * 5、关闭资源 15 */ 16 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000); 17 while (true) { 18 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 19 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); 20 // 使用接收方法将数据存储到数据包中 21 ds.receive(dp);// 阻塞式 22 23 // 4、通过数据包对象的方法,解析其中的数据,比如地址,端口,数据内容 24 25 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 26 int port = dp.getPort(); 27 String str = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 28 System.out.println(ip + "::" + port + ":::" + str); 29 // ds.close(); 30 } 31 } 32 33 }
结果:
实例二、多线程
思路:多线程任务:有发送数据任务和接收数据任务,准备两个类分别用于发送和接收
发送类
1 public class Send implements Runnable { 2 private DatagramSocket ds; 3 4 Send(DatagramSocket ds) { 5 this.ds = ds; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 try { 11 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 12 String line = null; 13 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 14 byte[] buff = line.getBytes(); 15 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buff, buff.length, InetAddress.getByName("172.28.188.168"), 16 10000); 17 ds.send(dp); 18 19 if("886".equals(line)) 20 break; 21 } 22 ds.close(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 29 }
接收类
1 public class Rece implements Runnable { 2 private DatagramSocket ds; 3 4 Rece(DatagramSocket ds) { 5 this.ds = ds; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 try { 11 while (true) { 12 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 13 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); 14 // 使用接收方法将数据存储到数据包中 15 16 ds.receive(dp);// 阻塞式 17 18 // 4、通过数据包对象的方法,解析其中的数据,比如地址,端口,数据内容 19 20 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 21 // int port = dp.getPort(); 22 String str = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 23 System.out.println(ip + "::" + str); 24 if("886".equals(str)) 25 System.out.println(ip + "退出"); 26 } 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 }
主函数
1 public class ChatDemo { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 * @throws IOException 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 DatagramSocket rece=new DatagramSocket(10000); 9 DatagramSocket send=new DatagramSocket(); 10 new Thread(new Rece(rece)).start(); 11 new Thread(new Send(send)).start(); 12 } 13 14 }
结果:
