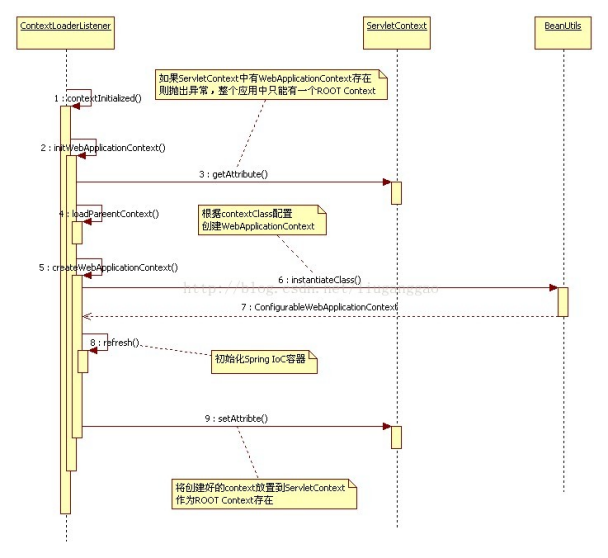
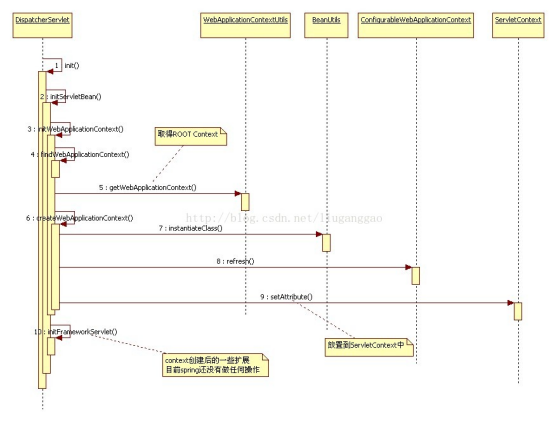
先来看一下ContextServletListener的代码
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener { public ContextLoaderListener() { } public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) { super(context); } /** 这个方法就是用来初始化web application context的
服务器启动时,检测到此监听类,系统会调用此方法。 */ @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); } /** 服务器关闭时,这个方法调用,用来销毁容器
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
初始化方法contextInitialized里调用了父类ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法
下面我们看下initWebApplicationContext方法的代码
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) { /** webApplicationContext只能存在一个,若重复会抛出IllegalStateException异常 从servletContext中获取ApplicationContext容器;如果已经存在,则提示初始化容器失败,检查web.xml文件中是否定义有多个容器加载器 ServletContext接口的简述:public interface ServletContext 定义了一系列方法用于与相应的servlet容器通信,比如:获得文件的MIME类型,分派请求,或者是向日志文件写日志等。 每一个web-app只能有一个ServletContext,web-app可以是一个放置有web application 文件的文件夹,也可以是一个.war的文件。 ServletContext对象包含在ServletConfig对象之中,ServletConfig对象在servlet初始化时提供servlet对象。 */ if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " + "check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); } Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that // it is available on ServletContext shutdown. if (this.context == null) { //若WebApplicationContext容器为空,则创建一个WebApplicationContext容器 this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } //判断是否是可配置的对象,若可配置则进行一系列配置 if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> // determine parent for root web application context, if any. ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); } //配置完成后,进行配置和刷新WebApplicationContext configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } } //把容器放入到servletContext中 servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) { currentContext = this.context; } else if (ccl != null) { currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]"); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", err); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err); throw err; } }
从上面的代码可以看出,我们创建好的applicationContext容器会放在servletContext中。servletContext是什么 呢?
在web容器中,通过ServletContext为Spring的IOC容器提供宿主环境,对应的建立起一个IOC容器的体系。其中,首先需要建立的是根上下文,这个上下文持有的对象可以有业务对象,数据存取对象,资源,事物管理器等各种中间层对象。在这个上下文的基础上,和web MVC相关还会有一个上下文来保存控制器之类的MVC对象,这样就构成了一个层次化的上下文结构。
真正创建ApplicationContext的方法是在createWebApplicationContext方法中完成的。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) { // 首先决定要创建的applicationContext容器的类 Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc); // 如果获取到的类不是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型的,则创建容器失败,所以这里创建的容器必须是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型的 if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]"); } //通过BeanUtils的instantiateClass方法创建 return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
determineContextClass()方法获取了要创建的容器类
protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) throws ApplicationContextException { // 从web.xml中获取需要初始化的容器的类名 String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM); // 如果获取到的类名不为空,则创建该容器的Class对象 if (contextClassName != null) { try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } // 否则创建默认的容器的Class对象,即:org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext // 在创建ContextLoader时,defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);这句代码已经准备好默认的容器类 else { contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName()); try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } }
该方法首先判断从web.xml文件的初始化参数CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM(的定义为public static final String CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM = "contextClass";)获取的的类名是否存在,如果存在,则容器的Class;否则返回默认的Class。如何获取默认的容器Class,注意看创建contextLoader时的代码注释就知道了。
由此看来,spring不仅有默认的applicationContext的容器类,还允许我们自定义applicationContext容器类,不过Spring不建义我们自定义applicationContext容器类。
在通过createWebApplicationContext()方法创建WebApplicationContext容器之后,会调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法为容器初始化配置文件中定义的bean类,它的实现过程还没搞清楚,下一章节再来做解释(=_=)。
最后放上前辈的两张图,帮助大家更容易理解此配置的实现原理。