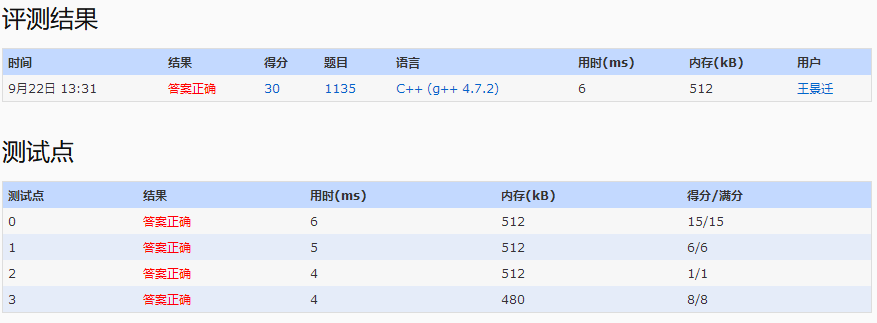
已知先序序列,判断对应的二叉排序树是否为红黑树。序列中负数表示红色结点,正数表示黑色结点。该序列负数取绝对值后再排序得到的是中序序列。根据红黑树的性质判断它是否符合红黑树的要求。考察了根据先序序列和中序序列建树和DFS。

1 //#include "stdafx.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 struct treeNode { // tree node struct 8 int key, lchild, rchild, flag; // key, left child, right child, color flag 9 }tree[31]; 10 11 struct intNode { // int node 12 int key, flag; // key, color flag 13 }pre[31]; // the array of the preorder traversal sequence 14 15 int treeRoot, flag, blackNodeCount, in[31]; // the index of tree root node, whether it is a red-black tree, the number of black nodes, the array of the inorder traversal sequence 16 17 void init(int m) { // initialize 18 int i; 19 for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { // every node has no child 20 tree[i].lchild = tree[i].rchild = -1; 21 } 22 23 flag = 1; // at first, it is a red-black tree 24 treeRoot = blackNodeCount = 0; // the initial index of tree root node is zero and the initial number of black nodes is zero 25 26 sort(in, in + m); // sort in array to get the inorder traversal sequence 27 } 28 29 int buildTree(int a1, int a2, int b1, int b2) { // build a tree according to the preorder traversal sequence and inorder 30 // initialize the current root node of the subtree 31 int root = treeRoot++; 32 int key = pre[a1].key; 33 tree[root].key = key; 34 tree[root].flag = pre[a1].flag; 35 36 int i; 37 for (i = b1; i <= b2; i++) { // seek the index of root node in the inorder traversal sequence 38 if (in[i] == key) { 39 break; 40 } 41 } 42 43 if (i > b1) { // if left subtree exists 44 tree[root].lchild = buildTree(a1 + 1, a1 + i - b1, b1, i - 1); 45 } 46 if (i < b2) { // if right subtree exists 47 tree[root].rchild = buildTree(a1 + i - b1 + 1, a2, i + 1, b2); 48 } 49 50 return root; // return the current root node of the subtree 51 } 52 53 void dfs(int cur, int count) { // traverse all nodes based on depth first 54 if (flag == 0) { // if it is not a red-black tree 55 return; 56 } 57 58 if (cur == -1) { // if it is a leaf node 59 if (count != blackNodeCount) { // judge whether black nodes is legal 60 if (blackNodeCount == 0) { 61 blackNodeCount = count; 62 } else { 63 flag = 0; 64 } 65 } 66 67 return; 68 } 69 70 int l = tree[cur].lchild; 71 int r = tree[cur].rchild; 72 73 if (tree[cur].flag == 0) { // If a node is red, then both its children are black. 74 if (l != -1 && tree[l].flag == 0) { 75 flag = 0; 76 return; 77 } else if (r != -1 && tree[r].flag == 0) { 78 flag = 0; 79 return; 80 } 81 } else { 82 count++; 83 } 84 85 // recursion 86 dfs(l, count); 87 dfs(r, count); 88 } 89 90 int judgeRBTree() { 91 if (tree[0].flag == 0) { // The root is black. 92 return 0; 93 } 94 95 // traverse 96 dfs(0, 0); 97 return flag; 98 } 99 100 int main() { 101 int n; 102 scanf("%d", &n); 103 104 int m, i; 105 while (n--) { 106 scanf("%d", &m); 107 for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { 108 scanf("%d", &pre[i].key); 109 110 // save the information of color 111 if (pre[i].key < 0) { 112 pre[i].key = - pre[i].key; 113 pre[i].flag = 0; 114 } else { 115 pre[i].flag = 1; 116 } 117 118 in[i] = pre[i].key; 119 } 120 121 init(m); // initialization 122 buildTree(0, m - 1, 0, m - 1); // build a tree 123 124 if (judgeRBTree() == 1) { 125 printf("Yes "); 126 } else { 127 printf("No "); 128 } 129 } 130 131 system("pause"); 132 return 0; 133 }