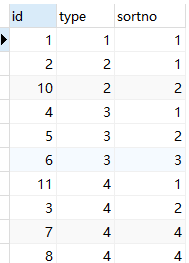
数据准备
-- mysql语法
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `test_group_type`;
CREATE TABLE `test_group_type` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`type` int(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '分类',
`sortno` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '分类排序',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('1', '1', '1');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('2', '2', '1');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('3', '2', '2');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('4', '3', '1');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('5', '3', '2');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('6', '3', '3');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('7', '4', '4');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('8', '4', '3');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('9', '4', '1');
INSERT INTO `test_group_type` VALUES ('10', '4', '2');
需求说明
取每个分类的前3条数据。
实现
SELECT * from test_group_type p
where (select count(1) from test_group_type r where r.type = p.type and r.id < p.id) < 3
ORDER BY p.type, p.id
r.id < p.id 或 r.id > p.id, 区别是: 取前, 还是取后。
r.id < p.id结果:

r.id > p.id结果:

sql解释:
核心是select count(1) from test_group_type r where r.type = p.type and r.id < p.id。
首先, 理解select count(1) from test_group_type r where r.type = p.type, 统计与当前行类型相同的一共有多少行。
然后r.id < p.id, 只统计当前行之前的数据(因为表结构的id是自增)。
比如id=7, 实际就是 select count(1) from test_group_type r where r.type = 4 and r.id < 7, 结果是0, 并且0 < 3, true。
所以id=7的行被选中。
类推,id=10, 结果是3 < 3, false, 所以不满足。
扩展
以上是建立在id有序自增长的基础上,如果想要自定义排序要怎么写?
如果理解了前面的sql, 那么只需要改变count的筛选。
比如,取type=4根据sortno排序的前3条。
SELECT * from test_group_type p
where p.type = 4
and (select count(1) from test_group_type r where r.type = p.type and r.sortno < p.sortno) < 3
ORDER BY p.type, p.id
结果:
r.sortno < p.sortno:  r.sortno > p.sortno:
r.sortno > p.sortno: 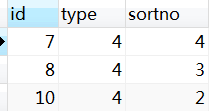
方式二 (2017-11-28): mysql动态sql实现 特别: 并未测试大量数据下的性能, 但感觉效率不高
上面方式如果是根据sortno排序有bug. 比如数据结构如下:

取每组前4条,排序规则order by sortno, id. 理想结果是(type=4): 11, 3, 7, 8
如果用方式一得到的结果: (因为sortno存在相同, 且sortno不足4条)
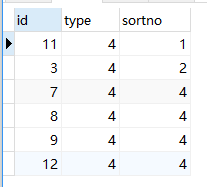
于是另外一种方式是: 利用动态sql先对每行数据进行组内排序, 再取rownum <= 4
SELECT t1.*
, case when @type = t1.type then @row:=@row+1 else @row:=1 END rownum
, @type:=t1.type rowtype
from test_group_type t1
ORDER BY t1.type, t1.sortno, t1.id
结果:
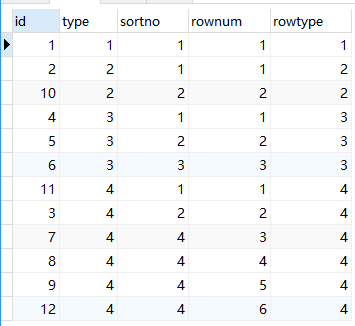
sql解释:
1、首先要明确sql执行顺序select * from的*是最后执行的;
2、所以以上sql在order by后, 再追加组内排序号rownum。
@type是变量, @type:=t1.type即把每行的type赋值给变量。
当@type不等于当前行type时(即改行是该type的第一行),所以rownum=1;
当@type等于当前行type时,rownum递增;
-- 完整sql
SELECT tt.id, tt.type, tt.sortno from(
SELECT t1.*
, case when @type = t1.type then @row:=@row+1 else @row:=1 END rownum
, @type:=t1.type rowtype
from test_group_type t1
ORDER BY t1.type, t1.sortno, t1.id
) tt where tt.rownum <= 4;