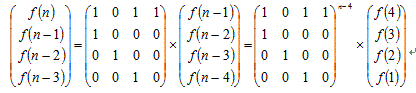Problem Description
Queues and Priority Queues are data structures which are known to most computer scientists. The Queue occurs often in our daily life. There are many people lined up at the lunch time.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue. Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
Input
Input a length L (0 <= L <= 10 6) and M.
Output
Output K mod M(1 <= M <= 30) where K is the number of E-queues with length L.
Sample Input
3 8 4 7 4 8
Sample Output
6 2 1
Source
题意:
n个人排队,f表示女,m表示男,包含子串‘fmf’和‘fff’的序列为O队列,否则为E队列,有多少个序列为E队列。
分析:
矩阵快速幂入门题。
用f(n)表示n个人满足条件的结果,那么如果最后一个人是m的话,那么前n-1个满足条件即可,就是f(n-1);
如果最后一个是f那么这个还无法推出结果,那么往前再考虑一位:那么后三位可能是:mmf, fmf, mff, fff,其中fff和fmf不满足题意所以我们不考虑,但是如果是
mmf的话那么前n-3可以找满足条件的即:f(n-3);如果是mff的话,再往前考虑一位的话只有mmff满足条件即:f(n-4)
所以f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4),递推会跪,可用矩阵快速幂
构造一个矩阵:

1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<cmath> 6 #include<math.h> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<queue> 9 #include<set> 10 #include<bitset> 11 #include<map> 12 #include<vector> 13 #include<stdlib.h> 14 #include <stack> 15 using namespace std; 16 #define PI acos(-1.0) 17 #define max(a,b) (a) > (b) ? (a) : (b) 18 #define min(a,b) (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b) 19 #define ll long long 20 #define eps 1e-10 21 #define MOD 1000000007 22 #define N 1000006 23 #define inf 1e12 24 int L,M; 25 struct Matrix{ 26 int mp[4][4]; 27 }; 28 Matrix Mul(Matrix a,Matrix b){ 29 Matrix res; 30 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 31 for(int j=0;j<4;j++){ 32 res.mp[i][j]=0; 33 for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ 34 res.mp[i][j]=(res.mp[i][j]+(a.mp[i][k]*b.mp[k][j])%M+M)%M; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 return res; 39 } 40 Matrix fastm(Matrix a,int b){ 41 Matrix res; 42 memset(res.mp,0,sizeof(res.mp)); 43 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 44 res.mp[i][i]=1; 45 } 46 while(b){ 47 if(b&1){ 48 res=Mul(res,a); 49 } 50 a=Mul(a,a); 51 b>>=1; 52 } 53 return res; 54 } 55 int main() 56 { 57 while(scanf("%d%d",&L,&M)==2){ 58 59 if(L==1){ 60 printf("%d ",2%M); 61 continue; 62 } 63 if(L==2){ 64 printf("%d ",2%M); 65 continue; 66 } 67 if(L==3){ 68 printf("%d ",6%M); 69 continue; 70 } 71 if(L==4){ 72 printf("%d ",9%M); 73 continue; 74 } 75 76 Matrix tmp; 77 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 78 for(int j=0;j<4;j++){ 79 tmp.mp[i][j]=0; 80 } 81 } 82 83 tmp.mp[0][0]=1; 84 tmp.mp[0][2]=1; 85 tmp.mp[0][3]=1; 86 tmp.mp[1][0]=1; 87 tmp.mp[2][1]=1; 88 tmp.mp[3][2]=1; 89 Matrix cnt=fastm(tmp,L-4); 90 91 92 Matrix g; 93 g.mp[0][0]=9; 94 g.mp[1][0]=6; 95 g.mp[2][0]=4; 96 g.mp[3][0]=2; 97 cnt=Mul(cnt,g); 98 printf("%d ",cnt.mp[0][0]%M); 99 } 100 101 return 0; 102 }