原文:https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/103291318
问题描述:
输入:abdca 返回:abdc
方法一:
暴力解析:遍历出给定字符串的所有子串,判断其中是否有重复字符,没有则记录长度,与下一次也无重复字符的子串比较长度,最长的即为所求。
代码:
public static String noDuplicate(String str) { if(str==null||str.length()==0){ return null; } Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(); String result = ""; System.out.println("length:" + str.length()); for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j <= str.length(); j++) { String s = str.substring(i, j); set.add(s); } } int max = 0; Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { LinkedHashSet<String> setchar = new LinkedHashSet<>(); String st = iterator.next().toString(); for (int a = 0; a < st.length(); a++) { setchar.add(String.valueOf(st.charAt(a))); } if(setchar.size()==st.length()){ int len = st.length(); if(max<len){ max = Math.max(max, len); result = st; } } } System.out.println(max); return result; }
暴力法的时间复杂度为:n2+n2===>2n2 即O(n2)
时间复杂度排序:
Ο(1)<Ο(log2n)<Ο(n)<Ο(nlog2n)<Ο(n2)<Ο(n3)<…<Ο(2n)<Ο(n!)
方法二:
滑动窗口:保证窗口中都是不重复的子串实现 _有回溯
public static String getMaxsubHuisu(String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0) { return null; } int start = 0;//滑动窗口的开始值 int maxlen = 0; int len = 0; int startMaxIndex = 0;//最长子串的开始值 Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//存储窗口内字符跟位置 int i; for (i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); Integer value = map.get(ch); if (map.containsKey(ch)) {//map中包含字符,则出现重复字符 start = value + 1;//下一次开始的位置是,存在map中重复字符的下一个位置 len = 0;//重新开始新的窗口,len置为0 map = new HashMap<>();//map置空 i=value;//下次从重复的值开始回溯 } else { map.put(ch, i);//不存在重复的,就存入map len++;//每次进来长度自增1 if (len > maxlen) {//如果当前的窗口长度>最长字符串则,更新最长串,跟最长子串开始位置 maxlen = len; startMaxIndex = start; } } } return s.substring(startMaxIndex, (startMaxIndex + maxlen));\截取字符串,substring为左闭右开 }
实现 _无回溯
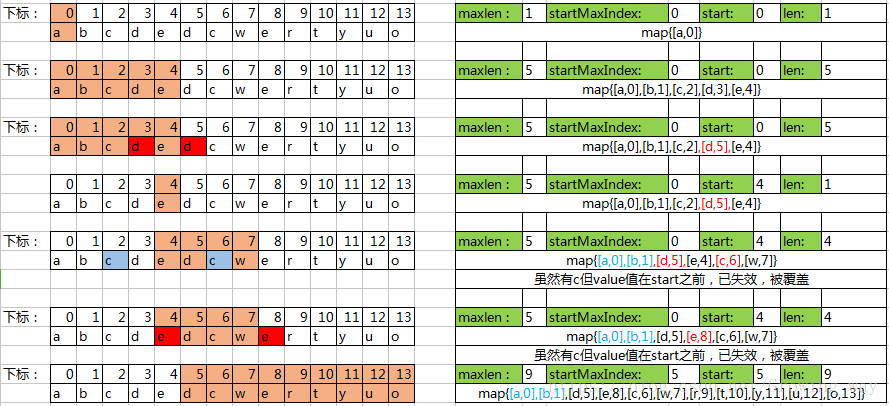
public static String getMaxsub(String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0) { return null; } int start = 0;//滑动窗口的开始值 int maxlen = 0; int len = 0; int startMaxIndex = 0;//最长子串的开始值 Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int i; for (i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); Integer value = map.get(ch); if (value != null && value >= start) {//map中存在在字符,且字符的位置在窗口范围内,即字符有效 start = value + 1;//下次开始的位置为,重复字符的下一个位置 len = i - value;//长度为当前的遍历字符的位置-重复字符的位置 } else { len++;//若不存在,则字符+1 if (len > maxlen) {//若当前窗口的长度>最长子串的位置,则更新最长子串的长度跟最长子串的起始位置 maxlen = len; startMaxIndex = start; } } map.put(ch, i);//无论存在不存在重复字符,都要把遍历的 字符存入map中,重复的则覆盖 } return s.substring(startMaxIndex, (startMaxIndex + maxlen)); }
无回溯_具体过程示意图
时间复杂度
有回溯:最好情况无回溯,时间复杂度O(n),最坏情况,每次都回溯O(2n),平均值为O(3/2 *n)
无回溯:O(n)
在特别长的字符串情况下,会有差异
小结:
1.第一步对输入的值做判断,不可忘;
2. 滑动窗口法的思路很重要,先用一个窗口限定字符,每次判断字符是否重复,记录位置,最长子串开始位置跟长度,为之后截取字符串做准备
3. 要想明白过程,出现重复字符的时候需要做的,不出现重复时候需要做的:
出现重复的 时候:更新窗口位置,当前窗口的长度。
不出现重复的时候:当前长度自增,判断更新最长子串长度与起始位置,存字符。
边界值出错的时候,要重缕思路,不能只是去试,要看思路边界上哪里有问题