剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和(dp)

求连续子数组的最大和,要最大,即加上后的值变大,所以我们用一个数组dp[]来记录该连续和,如果加上num[i]变大代表需要这个数,变小代表不需要这个数就不加,流程如下:
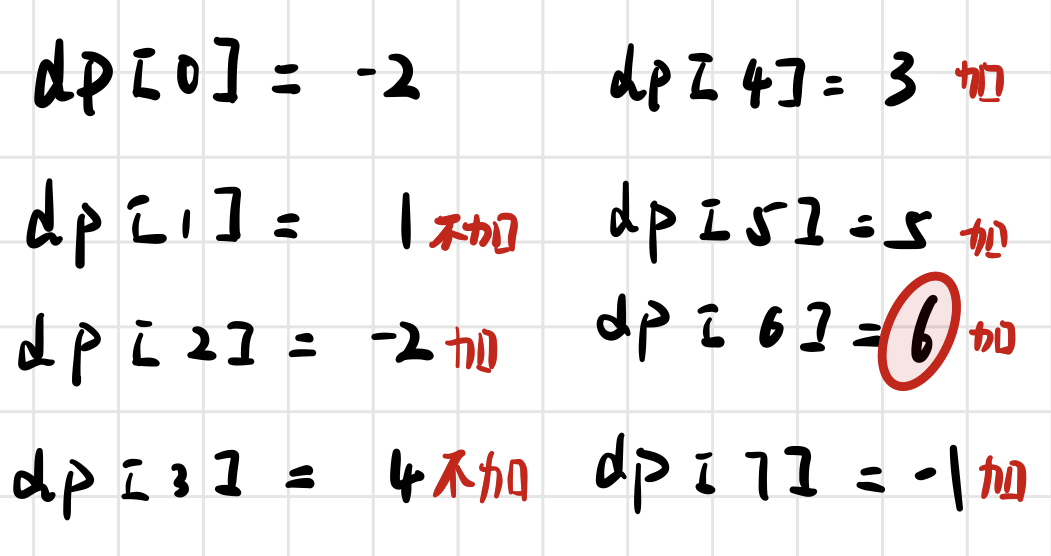
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>dp;
dp.resize(nums.size());
dp[0] = nums[0];
int res = nums[0];
for(int i = 1;i<nums.size();i++){
//如果当前前缀和加上该结点值变大就加上,否则不加
dp[i] = dp[i-1]+nums[i]>nums[i] ? dp[i-1]+nums[i] : nums[i];
res = res>dp[i] ? res : dp[i];//更新最大值
}
return res;
}
};
上面的代码的空间复杂度为O(n),还可以进一步优化
当数组很大时,使用滚动数组可以节约相当空间
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int currentMax = nums[0];
int res = nums[0];
for(int i = 1;i<nums.size();i++){
int preMax = currentMax;//将当前的最大值赋给preMax
//当前的最大值为
currentMax = currentMax+nums[i]>nums[i] ? currentMax+nums[i] : nums[i];
//判断是否更新结果最大值
res = res>currentMax ? res : currentMax;
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符

解法一:用一个map存对应关系
class Solution {
public:
vector<map<char,int>>v;
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
if(s.length()==0) return ' ';
map<char,int>m;
for(char ch:s){
if(m.find(ch)==m.end()){
//还未加入,则加入
m.insert(make_pair(ch,1));
// v.push_back(m);
}else{//在map中已经存在,则记数值++
m[ch]++;
}
}
char res = ' ';
for( char c:s ){
if(m[c]==1){
res = c;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};
高级写法
class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
unordered_map<char, bool> dic;
for(char c : s)//取出每一个字符
//如果c字符未找到,将true赋值给dic[c],如果找到了代表出现不止一次,将false赋值给dic[c]
dic[c] = dic.find(c) == dic.end();
for(char c : s)
if(dic[c]) return c;//找到第一个为true的c返回
return ' ';
}
};
方法二:有序哈希表

class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
vector<char> keys;
unordered_map<char, bool> dic;
for(char c : s) {
if(dic.find(c) == dic.end())
keys.push_back(c);
dic[c] = dic.find(c) == dic.end();
}
for(char c : keys) {
if(dic[c]) return c;
}
return ' ';
}
};
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
大佬的写法
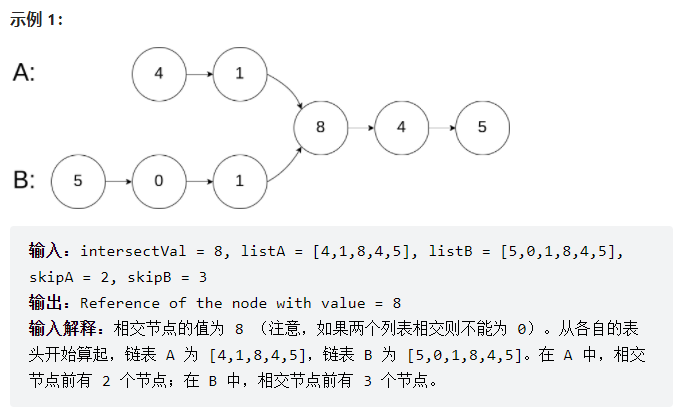
思路是这样的:因为两个要找到两个链表的第一个公共结点(一定存在),但是两个链表在公共结点之前的结点数目又不一样,所有让两个链表分别遍历自己和对方,则一定会一起走到相同结点。
两个链表长度分别为L1+C、L2+C, C为公共部分的长度, 第一个人走了L1+C步后,回到第二个人起点走L2步;第2个人走了L2+C步后,回到第一个人起点走L1步。 当两个人走的步数都为L1+L2+C时就走到了公共结点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode * node1 = headA;
ListNode * node2 = headB;
while(node1 != node2){
//判断1的路走完没有,走完就走2的路,同理2
node1 = node1!=NULL ? node1->next : headB;
node2 = node2!=NULL ? node2->next : headA;
}
return node1;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I

这道题,面试中一般是想考察你的二分查找
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int count = 0;
for(int num :nums){
if(num==target){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
};
二分写法:
二分的条件是该序列是有序排列的
这里的二分思想是这样的,1.去找traget的右边界,即第一个不为target的值
2.去找target-1的右边界,即第一个target出现的位置
3.然后将两个位置下标相减,得到最终结果
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
//return 右边界-左边界 就可以得到个数
return bin_search(nums,target) - bin_search(nums,target-1);
}
int bin_search(vector<int>&nums ,int target){
int low =0,high = nums.size()-1;
while(low <= high){
int mid = (low + high)/2;
if(nums[mid]<=target)
{
low = mid+1;
}else{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字

解法一:无脑解法
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = 0;
for(int num:nums){
if(num!=res){
break;
}
res ++;
}
return res;
}
};
解法二:二叉查找
思路:如果下标数等于mid代表左边的都已经有序了(因为如果不等于代表一定有缺失的值)此时向右边搜索,否则代表左边是无序的向右边搜索
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int low =0,high = nums.size()-1;
while(low<=high){
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(mid==nums[mid]){ //左边未出现缺失
low = mid+1;
}else{
high = mid-1;
}
}
return low;
}
};
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点

如上图按照右根左的遍历序列可以直接得到第K大的数
class Solution {
public:
int k,res;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
this->k = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return ; //边界条件
dfs(root->right); //向右遍历
if(k==0) return ;
if(--k==0) res = root->val;
dfs(root->left); //向左遍历
}
};
树的中序遍历(左根右)
中序遍历的结果为从小到大的排序,要找到第K大的数即为倒数第K个即v[count-k]
class Solution {
public:
int count=0,res,k;
vector<int>v;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
this->k = k;
dfs(root);
return v[count-k];
}
void dfs(TreeNode *root){
// 左根右
if(root==nullptr) return;
if(root->left) dfs(root->left);
v.push_back(root->val);
count++;
if(root->right) dfs(root->right);
}
};
剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法
考察异或,位运算这类的问题要对计算机组成原理有一定的了解,其实在底层乘法器和除法器都是依靠加法器和移位来实现的,而加法器的实现靠的是本位和和进位(Cin)来计算的

class Solution {
public:
int add(int a, int b) {
//因为不允许用+号,所以求出异或部分和进位部分依然不能用+ 号,所以只能循环到没有进位为止
while(b!=0)
{
//保存进位值,下次循环用
int c=(unsigned int)(a&b)<<1;//C++中负数不支持左移位,因为结果是不定的
//保存不进位值,下次循环用,
a^=b;
//如果还有进位,再循环,如果没有,则直接输出没有进位部分即可。
b=c;
}
return a;
}
};
剑指 Offer II 024. 反转链表
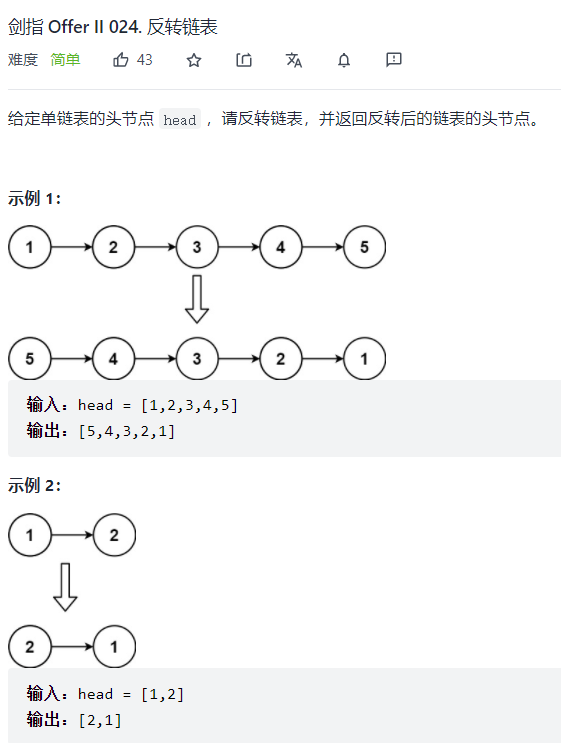
链表的原地逆置
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
// 链表的原地逆置
ListNode *p,*q = head;
p = head ->next;
head->next = NULL;
while(p){
q = p->next;
p->next = head;
head = p;
p = q;
}
return head;
}
};
面试题 01.02. 判定是否互为字符重排

就是两个串,判断B串是否为A串的重新排列,那只用判断B串中是否仅含A串的字母,和上面的剑指offer50类似用一个map解决
class Solution {
public:
bool CheckPermutation(string s1, string s2) {
//仅需要判断是不是A中的字符B中都有就可以了
map<char,int>m;
bool res = true;
for(char each:s1){
if(m.find(each)==m.end()){
m.insert(make_pair(each,1));
// m[each]++;
}else{
m[each]++;
}
}
for(char each:s2){
if(m.find(each)==m.end()||m[each]==0){
return false;
}else{
m[each]--;
}
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度

解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left); //左递归
int right = maxDepth(root->right); //右递归
return left>right ? left+1 :right+1; //返回条件,每次向上返回时,left和right各自加一
}
};
解法二:
注意,当用层次遍历需要记录层次数时,使用for(int i = q.size();i>0;i--)
class Solution {
int count = 0;
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q; //创建队列q
q.push(root); //将root推入队列q
while(!q.empty()){
for(int i = q.size(); i; i--){
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(node->left != NULL) q.push(node->left);
if(node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right);
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树

判断一颗树是不是平衡二叉树,可以用上面的解法一的思路,对每一个结点的左右都判断深度差,当所有结点左右子树深度差小于2时代表该树是一颗平衡二叉树
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root)>0 ? true :false;
}
int dfs(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return true;
int left = dfs(root->left);//向左遍历
if(left==-1) return -1;
int right = dfs(root->right);//向右遍历
if(right==-1) return -1;
return abs(left-right)<2 ? max(left,right)+1 :-1;//判断左右之差是否小于2
}
};
解法二:
/* 先序遍历+判断深度 (从左到右,自顶向下。因为对每个节点 都进行了dfs,所以会产生大量重复计算,时间复杂度较高)*/
class Solution {
private:
int dfs(TreeNode* root);
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if (nullptr == root) return true;
int left_deep = dfs(root->left); // 以该root为根节点的树 的左子树深度
int right_deep = dfs(root->right); // 以该root为根节点的树 的右子树深度
if (std::abs(left_deep - right_deep) > 1) return false; // 0<=左右子树的深度差<=1 才满足条件,否则返回false
return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); // 继续遍历该树的其它节点,并检查 以每个节点为root的子树 是否为平衡二叉树
}
};
int Solution::dfs(TreeNode* root) { // 以该root为根节点的树 的深度
if (nullptr == root) return 0;
return std::max(dfs(root->left), dfs(root->right)) + 1;
}
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数

仅两个数字仅出现一次,其余都出现两次,思路如下注释
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
int x = 0, y = 0, n = 0, m = 1;
// 以{4,1,4,6,3,3}为例
for(int num : nums) // 1. 遍历异或
n ^= num; //最终为1^6 = 0111= 7
while((n & m) == 0) // 2. 循环左移,计算 m
m <<= 1; //获取首位1 m=0001
// 再用这个首位1为分界线将其分为两组
// 为何?1 --> 0001
// 6 --> 0110
// 即找到他们有差别的那一位数字
// 那么我们再在nums中取数,1&m=0001一定不为0 6&m=0000一定为0
// 其他数字都出现两次,一定抵消,则结果一定为1和6
for(int num : nums) { // 3. 遍历 nums 分组
if(num & m) x ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m != 0
else y ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m == 0
}
return vector<int> {x, y}; // 5. 返回出现一次的数字
}
};
剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
没有复杂度要求,可以考虑计数这样是双O(n)
解法一:
利用map映射,该数字出现就计数
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size()==0) return 0;
// 法一:map映射
map<int,int>m;
// 1.是数字 2.是count数量
for(int num:nums){
if(m.find(num)!=m.end()) m[num]++;
else{
m.insert(make_pair(num,1));
}
}
int res;
for(pair<int,int>a:m){
if(a.second!=3){
res = a.first;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};
解法二:将每位上的二进制位数都统计一遍,然后再对3取余,则剩下的为所求的二进制位数
原理就是其余数字都出现3次,则转换为2进制后每一位都会出现3次,取余后相当于消去了出现3次的数,则剩下的为所求
// 位运算 + 遍历统计
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> vec(32); // 记录所有数字的各二进制位的 1的出现次数
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
unsigned int m = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 32; ++j) {
if ((m & nums[i]) != 0) ++vec[j]; // 如果第j位上为1,即(m & nums[i])!= 0,则对应vec[j]+1
m <<= 1;
}
}
unsigned int res = 0;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) { // 将vec各元素对3求余,结果为"只出现一次的数字"的各二进制位上的数。
res <<= 1;
res |= vec[i] % 3; // 恢复第i位的值到res(从高位到底位)
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字

题目中给的递增(有序)直接可以想到二分
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int>res;
if(nums.size()==0) return res;
int left = 0, right = nums.size()-1;
while(left<right){
if(nums[left]+nums[right]==target){//当找到和为S的数时
res.resize(2);
res[0] = nums[left];
res[1] = nums[right];
break;
}
if(nums[left]+nums[right]>target) right--;//大于S时范围大了向左收缩
else if(nums[left+nums[right]<target]) left++;
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
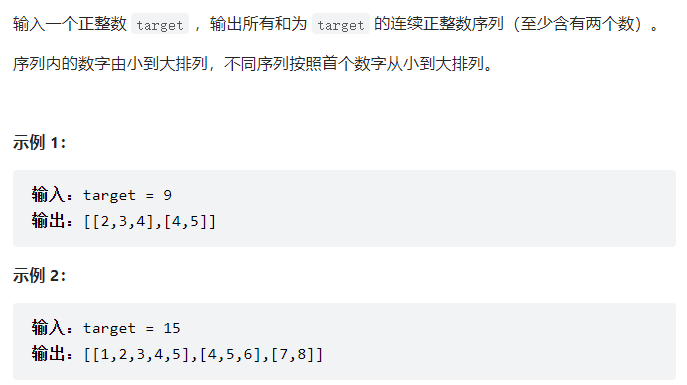
要输出所有和为S的,思路就是利用一个左边界和右边界,当小于目标值时左边界向右滑动,当大于目标值时,右边界向左滑动
滑动窗口
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
int i = 1; // 滑动窗口的左边界
int j = 1; // 滑动窗口的右边界
int sum = 0; // 滑动窗口中数字的和
vector<vector<int>> res;
while (i <= target / 2) {//左边界一定小于等于target的一半,不然一定大于target
if (sum < target) {
// 右边界向右移动
sum += j;
j++;
} else if (sum > target) {
// 左边界向右移动
sum -= i;
i++;
} else {
// 记录结果
vector<int> arr;
for (int k = i; k < j; k++) {
arr.push_back(k);
}
res.push_back(arr);
// 左边界向右移动
sum -= i;
i++;
}
}
return res;
}
};