Masha wants to open her own bakery and bake muffins in one of the n cities numbered from 1 to n. There are m bidirectional roads, each of whose connects some pair of cities.
To bake muffins in her bakery, Masha needs to establish flour supply from some storage. There are only k storages, located in different cities numbered a1, a2, ..., ak.
Unforunately the law of the country Masha lives in prohibits opening bakery in any of the cities which has storage located in it. She can open it only in one of another n - k cities, and, of course, flour delivery should be paid — for every kilometer of path between storage and bakery Masha should pay 1 ruble.
Formally, Masha will pay x roubles, if she will open the bakery in some city b (ai ≠ b for every 1 ≤ i ≤ k) and choose a storage in some city s (s = aj for some 1 ≤ j ≤ k) and b and s are connected by some path of roads of summary length x (if there are more than one path, Masha is able to choose which of them should be used).
Masha is very thrifty and rational. She is interested in a city, where she can open her bakery (and choose one of k storages and one of the paths between city with bakery and city with storage) and pay minimum possible amount of rubles for flour delivery. Please help Masha find this amount.
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of cities in country Masha lives in, the number of roads between them and the number of flour storages respectively.
Then m lines follow. Each of them contains three integers u, v and l (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, 1 ≤ l ≤ 109, u ≠ v) meaning that there is a road between cities u and v of length of l kilometers .
If k > 0, then the last line of the input contains k distinct integers a1, a2, ..., ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ n) — the number of cities having flour storage located in. If k = 0 then this line is not presented in the input.
Print the minimum possible amount of rubles Masha should pay for flour delivery in the only line.
If the bakery can not be opened (while satisfying conditions) in any of the n cities, print - 1 in the only line.
5 4 2
1 2 5
1 2 3
2 3 4
1 4 10
1 5
3
3 1 1
1 2 3
3
-1
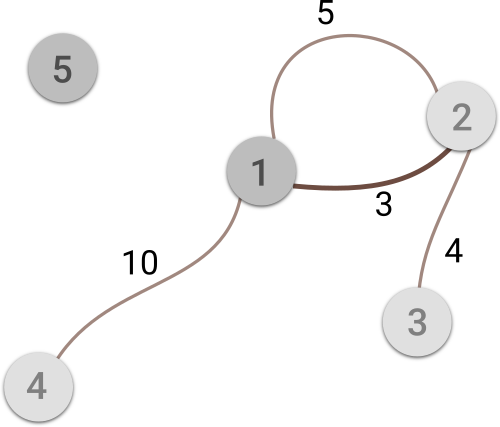
Image illustrates the first sample case. Cities with storage located in and the road representing the answer are darkened.
题意:看懂题意就行了,有一些面粉厂,从其他的点到其中一个面粉厂最短路。
分析:
暴力扫边的题,活生生的被我建图成了迪杰斯特拉。其实也是仿照了网络流的姿势。
CF721C