一个点在射线上匀速向外运动,同时射线以w的速度转动,点的轨迹就被称为阿基米德螺旋线或等速螺线。
1.公式
阿基米德螺旋线的极坐标公式可以表示为:
其中a为起始点与极坐标中心的距离,主要负责旋转整个螺线(增加a顺时针旋转);
b为控制螺线间的螺距,,b越大变化越快螺线越密;
的范围控制了螺线的大小,越大螺线的范围越大。
在直角坐标系下,利用极坐标系到直角坐标的公式,其公式可以被改写为:
此外还可以利用角速度和线速度的概念来控制螺线的形状,生成其他螺旋线:
上式为关于t的参数方程,其中v为线速度、w为角速度,t为点运动的时间。可以通过上式子得到等角速度、等线速度等各类螺旋
2.程序
首先我们来画出极坐标系下的阿基米德螺线。
%matlab 程序
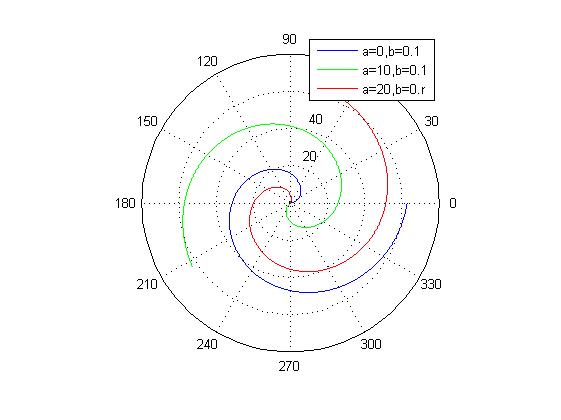
%不同a和b造成螺线的变化
theta = 0:0.01*pi:20*pi;
r1 = 0 + 0.1*theta;
r2 = 10 + 0.1*theta;
r3 = 20 + 0.1*theta;
polar(r1,theta,'b');hold on;
polar(r2,theta,'g')
polar(r3,theta,'r')
legend('a=0,b=0.1','a=10,b=0.1','a=20,b=0.r')
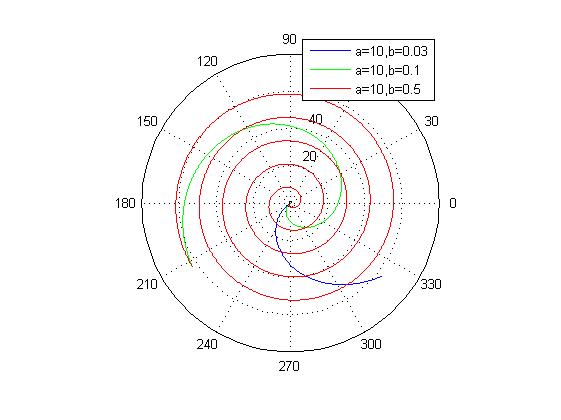
随后变化b来观察螺距的变化:
theta = 0:0.01*pi:20*pi;
r4 = 10 + 0.03*theta;
r5 = 10 + 0.1*theta;
r6 = 10 + 0.5*theta;
polar(r4,theta,'b');hold on;
polar(r5,theta,'g')
polar(r6,theta,'r')
legend('a=10,b=0.03','a=10,b=0.1','a=10,b=0.5')
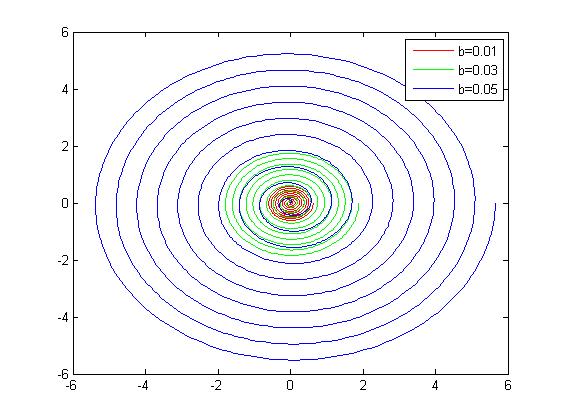
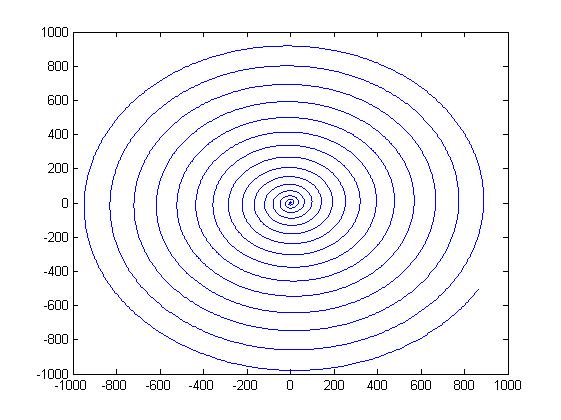
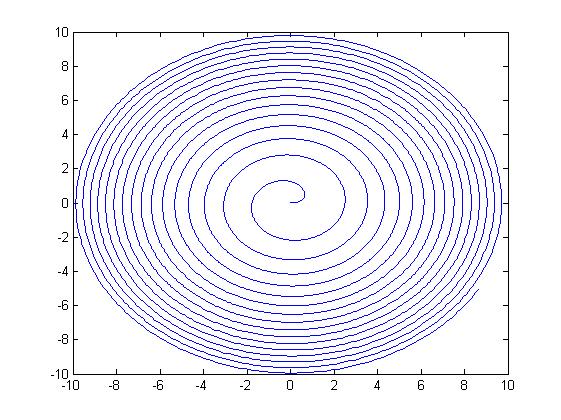
随后在直角坐标系中画出螺线:
theta = 0:0.01*pi:20*pi;
r7 = 0 + 0.01*theta;
x = r7.*cos(theta);
y = r7.*sin(theta);
%初始点是0,螺距为0.01
%在直角坐标系下b控制着螺线间距,b越大螺线间距越大
plot(x,y,'r')
hold on;
r8 = 0 + 0.03*theta;
x = r8.*cos(theta);
y = r8.*sin(theta);
plot(x,y,'g')
r9 = 0 + 0.09*theta;
x = r9.*cos(theta);
y = r9.*sin(theta);
plot(x,y,'b')
legend('b=0.01','b=0.03','b=0.05')
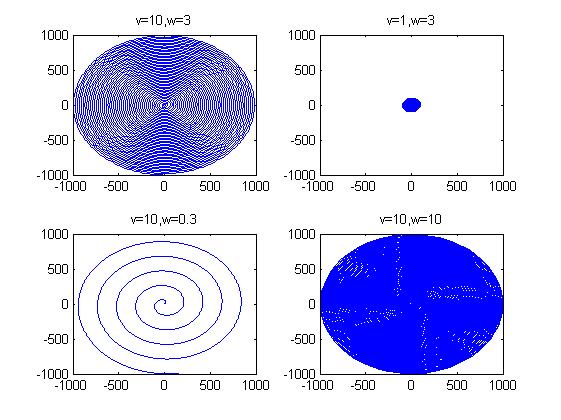
另外可以通过引入速度的概念控制螺线的形状:
t = 0:0.01:100;
v = 10; %线速度控制了大小,越大走得越快螺线形状越大
w = 3 ; %角速度控制了疏密,越小越稀疏,单位时间内旋转少。
x = v*t.*cos(w*t);
y = v*t.*sin(w*t);
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(x,y)
title('v=10,w=3')
axis([-1000 1000 -1000 1000])
v = 1; %线速度变小,图形变小
w = 3 ;
x = v*t.*cos(w*t);
y = v*t.*sin(w*t);
subplot(2,2,2)
plot(x,y)
title('v=1,w=3')
axis([-1000 1000 -1000 1000])
v = 10;
w = 0.3 ; %角速度变小,图形变疏
x = v*t.*cos(w*t);
y = v*t.*sin(w*t);
subplot(2,2,3)
plot(x,y)
title('v=10,w=0.3')
axis([-1000 1000 -1000 1000])
v = 10; %变大
w = 10 ; %变密
x = v*t.*cos(w*t);
y = v*t.*sin(w*t);
subplot(2,2,4)
plot(x,y)
title('v=10,w=10')
axis([-1000 1000 -1000 1000])
或者将w变化或者v变化:
%向外渐开线
t = 0:0.01:100;
v = 0:0.001:10; %线速度逐渐加快
w = 1 ; %
x = v.*t.*cos(w*t);
y = v.*t.*sin(w*t);
plot(x,y)
%渐密线
t = 0:0.01:100;
v = 0.1;
w = 0:0.0001:1; ; %角速度逐渐加大变密. tips:一定要注意区分坐标系,以及角速度与b的关系
x = v.*t.*cos(w.*t);
y = v.*t.*sin(w.*t);
plot(x,y)
ref
https://baike.baidu.com/item/阿基米德螺线/6174118?fr=aladdin
http://muchong.com/html/201106/3290808.html
https://blog.csdn.net/menghuanxiy/article/details/81348393
http://blog.sina.cn/dpool/blog/s/blog_62c180b20102wx3n.html
pic from pexels.com
