You've got array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n], consisting of n integers. Count the number of ways to split all the elements of the array into three contiguous parts so that the sum of elements in each part is the same.
More formally, you need to find the number of such pairs of indices i, j (2 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n - 1), that 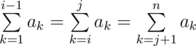 .
.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5·105), showing how many numbers are in the array. The second line contains n integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (|a[i]| ≤ 109) — the elements of array a.
Output
Print a single integer — the number of ways to split the array into three parts with the same sum.
用两个数组ki[i],kj[j]分别记录满足1-ki,kj-n的和是sum/3的点,然后遍历时判断这两个点是不是相邻的,如果相邻就不算

#include <cstdio> #include <cctype> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; LL n; LL a[500004]; LL ki[500004],kj[500004]; int main() { // freopen("test.in","r",stdin); cin >> n; LL sum = 0; for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin >> a[i]; sum += a[i]; } if (sum % 3 != 0){ cout << 0; return 0; } LL res = sum / 3,totalnum = 0; LL nowsum = 0,totali = 0,totalj = 0; for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){ nowsum += a[i]; if (nowsum == res){ totali ++; ki[totali] = i; } } nowsum = 0; for (int i=n;i>=1;i--){ nowsum += a[i]; if (nowsum == res){ totalj ++; kj[totalj] = i; } } sort(kj+1,kj+1+totalj); int now = 1; for (int i=1;i<=totali;i++){ while (now <= totalj && kj[now] <= ki[i] + 1){ now ++; } if (now > totalj) break; totalnum += totalj - now + 1; } cout << totalnum; return 0; }
