代理模式
代理(Proxy)模式,为其它对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在某些情况下一个对象不适合或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介作用。
代理模式UML类图
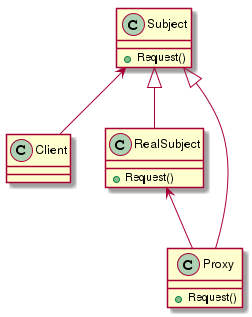
Subject类,定义了RealSubject和Proxy的公共接口,这样就在任何使用RealSubject的地方都可以使用Proxy。
RealSubject类,定义了Proxy所代表的的真实实体。
Proxy类,保存一个引用使得代理可以访问实体,并提供一个与Subject的接口相同的接口,这样代理就可以用来代替实体。
Client,通过Proxy类间接的和RealSubject进行通信。
代理模式的优缺点
优点:
1.在客户端和目标对象之间起到一个中介的作用,这样可以对目标对象起到一个保护作用。
缺点:
1.在客户和目标对象之间增加了一个抽象层,这可能会影响到处理速度。
适用场景:
1.远程代理,也就是为一个对象在不同的地址空间提供局部代表。这样可以隐藏一个对象存在于不同地址空间的事实。
2.虚拟代理,是根据需要创建开销很大的对象。通过它来存放实例化需要很长时间的真实对象。
3.安全代理,用来控制真实对象的访问权限。
4.智能指引,是指当调用真实的对象时,代理处理另外一些事。例如只能指针。
代码示例
学习《大话设计模式》的最后一章了,设计模式之路才刚刚开始。依然是使用该书中A委托B追求C的例子吧。
1.Subject类

#ifndef SUBJECT_H_ #define SUBJECT_H_ //这个虚基类,是代理和真实对象所共有的方法 //这这个例子中,代理和真实对象都具有送花、送洋娃娃的能力 class Subject { public: virtual void giveDolls() = 0; virtual void giveFlowers() = 0; virtual void giveChocolate() = 0; Subject() = default; virtual ~Subject() = default; }; #endif
2.RealSubject类

#ifndef PURSUIT_H_ #define PURSUIT_H_ //这个类是真实的对象(目标类) #include "Subject.h" #include <string> #include <iostream> class Pursuit : public Subject { private: std::string m_strGirlsName; //被追求女孩的名字 public: void giveDolls() override; void giveFlowers() override; void giveChocolate() override; Pursuit(const std::string strGirlsName) : m_strGirlsName(strGirlsName){}; Pursuit() = default; ~Pursuit() = default; }; #endif #include "Pursuit.h" void Pursuit::giveDolls() { std::cout << m_strGirlsName << ".Give you Dolls." << std::endl; } void Pursuit::giveFlowers() { std::cout << m_strGirlsName << ".Give you Flowers." << std::endl; } void Pursuit::giveChocolate() { std::cout << m_strGirlsName << ".Give you Cholocate." << std::endl; }
3.Proxy类

#ifndef PROXY_H_ #define PROXY_H_ #include "Pursuit.h" class Proxy : public Subject { private: Pursuit m_Pursuit; public: void giveDolls() override; void giveFlowers() override; void giveChocolate() override; Proxy(const std::string strGirlsName) : m_Pursuit(Pursuit(strGirlsName)){}; ~Proxy() = default; }; #endif #include "Proxy.h" void Proxy::giveDolls() { m_Pursuit.giveDolls(); } void Proxy::giveFlowers() { m_Pursuit.giveFlowers(); } void Proxy::giveChocolate() { m_Pursuit.giveChocolate(); }
4.Client

#include "Proxy.h" using namespace std; int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { Proxy daili("Yang yang"); daili.giveDolls(); daili.giveFlowers(); daili.giveChocolate(); return (1); }
