DZY Loves Chemistry
DZY loves chemistry, and he enjoys mixing chemicals.
DZY has n chemicals, and m pairs of them will react. He wants to pour these chemicals into a test tube, and he needs to pour them in one by one, in any order.
Let's consider the danger of a test tube. Danger of an empty test tube is 1. And every time when DZY pours a chemical, if there are already one or more chemicals in the test tube that can react with it, the danger of the test tube will be multiplied by 2. Otherwise the danger remains as it is.
Find the maximum possible danger after pouring all the chemicals one by one in optimal order.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and m 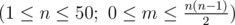 .
.
Each of the next m lines contains two space-separated integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi < yi ≤ n). These integers mean that the chemical xi will react with the chemical yi. Each pair of chemicals will appear at most once in the input.
Consider all the chemicals numbered from 1 to n in some order.
Print a single integer — the maximum possible danger.
1 0
1
2 1
1 2
2
3 2
1 2
2 3
4
In the first sample, there's only one way to pour, and the danger won't increase.
In the second sample, no matter we pour the 1st chemical first, or pour the 2nd chemical first, the answer is always 2.
In the third sample, there are four ways to achieve the maximum possible danger: 2-1-3, 2-3-1, 1-2-3 and 3-2-1 (that is the numbers of the chemicals in order of pouring).
写题的时候估计脑袋被驴踢了,就是依次把化学物品倒入试管,如果有反应的危险值*2,如果没有反应的危险值就不变
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cmath> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 #define N 55 8 9 int f[N]; 10 11 int found(int a) 12 { 13 if(f[a] != a) 14 f[a] = found(f[a]); 15 return f[a]; 16 } 17 18 int main() 19 { 20 int n, m, a, b; 21 22 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) 23 { 24 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 25 f[i] = i; 26 int x = n; 27 28 while(m--) 29 { 30 scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); 31 int na = found(a), nb = found(b); 32 f[na] = nb; 33 } 34 35 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 36 { 37 if(f[i] == i) // 如果根节点是他自己,和别人没关系,放进去就不反应,就少乘一个2,有几颗树,就有几个根节点放进去的时候是不反应的 38 x--; 39 } 40 long long ans = pow(2, x); 41 42 printf("%lld ", ans); 43 } 44 return 0; 45 }