import numpy as np import matplotlib as mpl mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["SimHei"] import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error import xgboost as xgb
def notEmpty(s): return s != ''
names = ['CRIM','ZN', 'INDUS','CHAS','NOX','RM','AGE','DIS','RAD','TAX','PTRATIO','B','LSTAT'] path = "datas/boston_housing.data" ## 由于数据文件格式不统一,所以读取的时候,先按照一行一个字段属性读取数据,然后再按照每行数据进行处理 fd = pd.read_csv(path, header=None) data = np.empty((len(fd), 14)) for i, d in enumerate(fd.values): d = map(float, filter(notEmpty, d[0].split(' '))) data[i] = list(d) x, y = np.split(data, (13,), axis=1) y = y.ravel() print ("样本数据量:%d, 特征个数:%d" % x.shape) print ("target样本数据量:%d" % y.shape[0])
样本数据量:506, 特征个数:13 target样本数据量:506
# 查看数据信息 X_DF = pd.DataFrame(x) X_DF.info() X_DF.describe().T X_DF.head()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 506 entries, 0 to 505 Data columns (total 13 columns): 0 506 non-null float64 1 506 non-null float64 2 506 non-null float64 3 506 non-null float64 4 506 non-null float64 5 506 non-null float64 6 506 non-null float64 7 506 non-null float64 8 506 non-null float64 9 506 non-null float64 10 506 non-null float64 11 506 non-null float64 12 506 non-null float64 dtypes: float64(13) memory usage: 51.5 KB

#数据的分割, x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.8, random_state=14) print ("训练数据集样本数目:%d, 测试数据集样本数目:%d" % (x_train.shape[0], x_test.shape[0]))
训练数据集样本数目:404, 测试数据集样本数目:102
# XGBoost将数据转换为XGBoost可用的数据类型 dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(x_train, label=y_train) dtest = xgb.DMatrix(x_test)
# XGBoost模型构建 # 1. 参数构建 params = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':1, 'silent':1, 'objective':'reg:linear'} num_round = 2 # 2. 模型训练 bst = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_round) # 3. 模型保存 bst.save_model('xgb.model')
# XGBoost模型预测 y_pred = bst.predict(dtest) print(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
24.869737956719252
# 4. 加载模型 bst2 = xgb.Booster() bst2.load_model('xgb.model') # 5 使用加载模型预测 y_pred2 = bst2.predict(dtest) print(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred2))
24.869737956719252
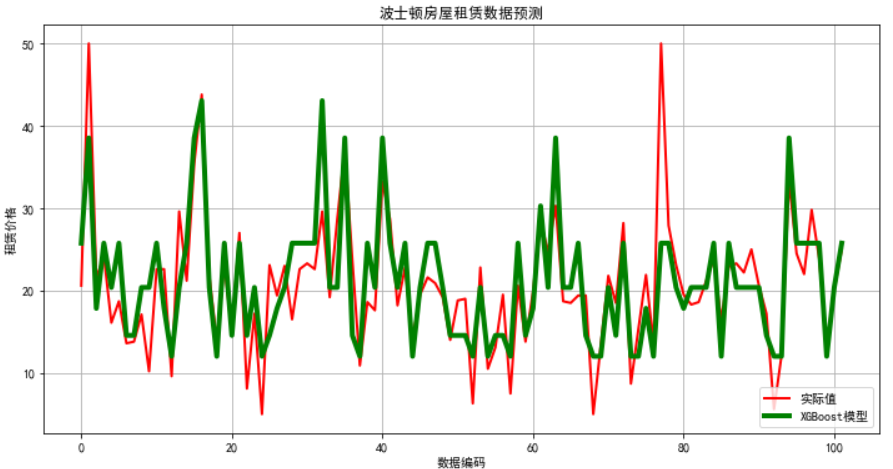
# 画图 ## 7. 画图 plt.figure(figsize=(12,6), facecolor='w') ln_x_test = range(len(x_test)) plt.plot(ln_x_test, y_test, 'r-', lw=2, label=u'实际值') plt.plot(ln_x_test, y_pred, 'g-', lw=4, label=u'XGBoost模型') plt.xlabel(u'数据编码') plt.ylabel(u'租赁价格') plt.legend(loc = 'lower right') plt.grid(True) plt.title(u'波士顿房屋租赁数据预测') plt.show()
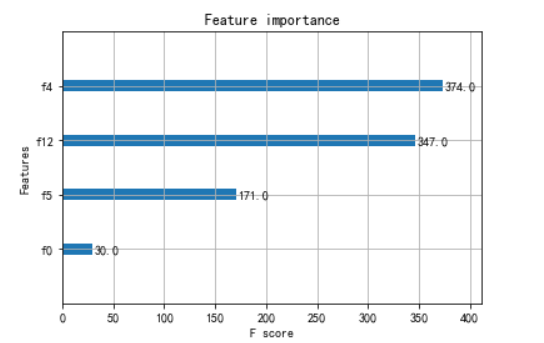
from xgboost import plot_importance from matplotlib import pyplot # 找出最重要的特征 plot_importance(bst,importance_type = 'cover') pyplot.show()