结合Autowired和Service注解
public interface IUser { void say(); } @Service public class Student implements IUser { @Override public void say() { System.out.println("I'm a student"); } } @Component @Order(value = 3) public class Entry implements CommandLineRunner { public Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Entry.class); @Autowired IUser user; @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { user.say(); } }
如果要在构造函数中就需要访问注入的变量,那么Autowired的位置就要放到构造函数上
@Component @Order(value = 3) public class TestService { private final IUser user; @Autowired public void TestService (IUser user) { user.say(); } }
自定义注入的扫描范围
要注意Springboot扫描包的时候默认是从启动类(一般是Application)目录开始往下扫描,也就意味着如果Bean不在Application目录的下层,是不会被扫描到的。
这种情况会提示:
Description: Field xxx in xxxxxx required a bean of type 'xxxxxx' that could not be found. Action: Consider defining a bean of type 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxx' in your configuration.
不过这也不是无法改变的,我们手动指定扫描范围即可:
@SpringBootApplication @ComponentScan(basePackages={"springbootdemo.basic","anotherspringbootdemo.basic"}) public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
范围列表中不要忘记添加原来的目录,及启动类的包范围。
另外,这个ComponentScan不是必须放到启动类上,只要可以被扫描到即可。
通过Configuration的方式
通过Configuration也可以实现“跨域”的注入方式(即package不在一个范围内)
/** * Springboot会扫描标有Configuration注解的类 * 该类中标有Bean注解的方法,返回值会被作为被注入项 * 至于这个Bean的注入项,在方法里面return就是。 */ @Configuration public class TestConfig{ @Bean public IUser user(){ return new Teacher(); } //有依赖关系的Bean也很简单 //这个IDepartment依赖IUser @Bean public IDepartment(){ return new Development(user()); } } /*调用*/ public class TestClass{ @Autowired IUser user; public void run(String... args) throws Exception { user.say(); } }
上面的Configuration虽然解决了“跨域”注入,但Configuration注解还是要求放到调用的项目中。
很多时候当我们需要依赖一个第三方jar包,并想要实现自动注入的时候,我们并不想再去手动写Configuration,毕竟如果多个地方引用这个jar包,每一处都需要这样处理。
能不能一劳永逸呢?
使用Springboot中的框架时,例如使用ES,我们发现虽然并没有声明ElasticSearchTemplate,但是却可以直接使用
这里有一篇不错的讲解 https://www.jianshu.com/p/346cac67bfcc
假设第三方项目是ProjectA,应用方是ProjectB
现在ProjectA有 类TestTemplate
package ProjectA; public class TestTemplate{ public void test() { System.out.println("GO TEST"); } }
ProjectB需要注入并使用TestTemplate,当然肯定要先添加maven的依赖(忽略),调用逻辑
package ProjectB; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import springbootdemo.common.TestTemplate; @Component public class Entry implements CommandLineRunner { @Autowired private TestTemplate aa; @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { aa.test(); } }
这时候运行ProjectB的话肯定是会报错的,因为找不到TestTemplate的注入结果,即使在TestTemplate上添加注解也是一样。
我们直接给出一个简单的解决方案
①在ProjectA中新建一个自动配置类 TestAutoConfiguration
package ProjectA; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class TestAutoConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public TestTemplate testTemplate(){ return new TestTemplate(); } }
②在ProjectA的资源目录src/main/resources下创建目录META-INF/spring.factories
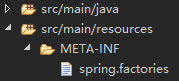
内容:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
ProjectA.TestAutoConfiguration
现在再执行,一切OK!