在前面,我们已经讲解了很多算子用来检测边缘,其中用得最多的canny算子边缘检测。本篇我们讲解一些其它方法来检测轮廓。
一 查找轮廓(find_contours)
measure模块中的find_contours()函数,可用来检测二值图像的边缘轮廓。
函数原型为:
skimage.measure.find_contours(array, level)
- array: 一个二值数组图像
- level: 在图像中查找轮廓的级别值
- 返回轮廓列表集合,可用for循环取出每一条轮廓。
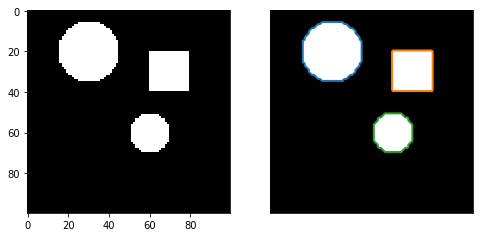
例1:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import measure,draw
#生成二值测试图像
img=np.zeros([100,100])
img[20:40,60:80]=1 #矩形
rr,cc=draw.circle(60,60,10) #小圆
rr1,cc1=draw.circle(20,30,15) #大圆
img[rr,cc]=1
img[rr1,cc1]=1
#检测所有图形的轮廓
contours = measure.find_contours(img, 0.5)
#绘制轮廓
fig, (ax0,ax1) = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(8,8))
ax0.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
ax1.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
for n, contour in enumerate(contours):#enumerate 函数用于遍历序列中的元素以及它们的下标
ax1.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2)
ax1.axis('image')
ax1.set_xticks([])
ax1.set_yticks([])#xticks和yticks: 为x,y轴的主刻度和次刻度设置颜色、大小、方向,以及标签大小。
plt.show()
结果如下图所示:
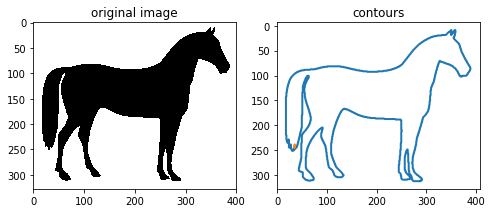
例2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import measure,data,color
#生成二值测试图像
img=color.rgb2gray(data.horse())
#检测所有图形的轮廓
contours = measure.find_contours(img, 0.5)
#绘制轮廓
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(8,8))
ax0, ax1= axes.ravel()#将多维数组降位一维
ax0.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray)
ax0.set_title('original image')
rows,cols=img.shape
ax1.axis([0,rows,cols,0])
for n, contour in enumerate(contours):
ax1.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2)
ax1.axis('image')
ax1.set_title('contours')
plt.show()
结果如下图所示:
二 逼近多边形曲线
逼近多边形曲线有两个函数:
- subdivide_polygon()
- approximate_polygon()
subdivide_polygon()采用B样条(B-Splines)来细分多边形的曲线,该曲线通常在凸包线的内部。
函数格式为:
skimage.measure.subdivide_polygon(coords, degree=2, preserve_ends=False)
- coords: 坐标点序列。
- degree: B样条的度数,默认为2
- preserve_ends: 如果曲线为非闭合曲线,是否保存开始和结束点坐标,默认为false
- 返回细分为的坐标点序列。
approximate_polygon()是基于Douglas-Peucker算法的一种近似曲线模拟。它根据指定的容忍值来近似一条多边形曲线链,该曲线也在凸包线的内部。
函数格式为:
skimage.measure.approximate_polygon(coords, tolerance)
- coords: 坐标点序列
- tolerance: 容忍值
- 返回近似的多边形曲线坐标序列。
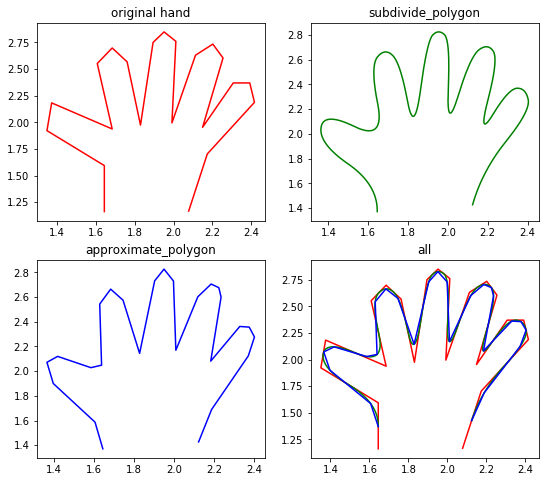
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import measure
#生成二值测试图像
hand = np.array([[1.64516129, 1.16145833],
[1.64516129, 1.59375],
[1.35080645, 1.921875],
[1.375, 2.18229167],
[1.68548387, 1.9375],
[1.60887097, 2.55208333],
[1.68548387, 2.69791667],
[1.76209677, 2.56770833],
[1.83064516, 1.97395833],
[1.89516129, 2.75],
[1.9516129, 2.84895833],
[2.01209677, 2.76041667],
[1.99193548, 1.99479167],
[2.11290323, 2.63020833],
[2.2016129, 2.734375],
[2.25403226, 2.60416667],
[2.14919355, 1.953125],
[2.30645161, 2.36979167],
[2.39112903, 2.36979167],
[2.41532258, 2.1875],
[2.1733871, 1.703125],
[2.07782258, 1.16666667]])
#检测所有图形的轮廓
new_hand = hand.copy()
for _ in range(5):
new_hand =measure.subdivide_polygon(new_hand, degree=2)
# approximate subdivided polygon with Douglas-Peucker algorithm
appr_hand =measure.approximate_polygon(new_hand, tolerance=0.02)
print("Number of coordinates:", len(hand), len(new_hand), len(appr_hand))
fig, axes= plt.subplots(2,2, figsize=(9, 8))
ax0,ax1,ax2,ax3=axes.ravel()
ax0.plot(hand[:, 0], hand[:, 1],'r')
ax0.set_title('original hand')
ax1.plot(new_hand[:, 0], new_hand[:, 1],'g')
ax1.set_title('subdivide_polygon')
ax2.plot(appr_hand[:, 0], appr_hand[:, 1],'b')
ax2.set_title('approximate_polygon')
ax3.plot(hand[:, 0], hand[:, 1],'r')
ax3.plot(new_hand[:, 0], new_hand[:, 1],'g')
ax3.plot(appr_hand[:, 0], appr_hand[:, 1],'b')
ax3.set_title('all')
结果如下图所示: