1 .三种非递归遍历(栈)
所要遍历的树是:
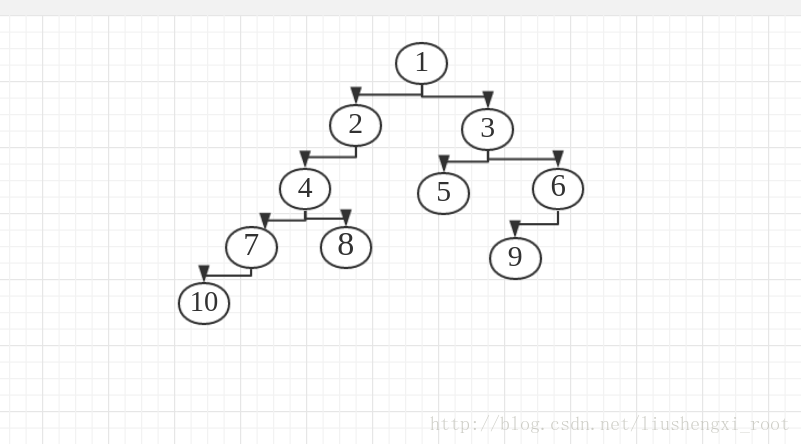
先序 + 中序
思路:就拿先序遍历为例来说吧。
1.访问根节点,根节点入栈,进入左子树。
2.访问左子树的根节点,根节点入栈,进入下一层左子树。
3.重复直到当前节点为空。即到达了最**左下方**的节点
4.如果栈不为空,就从栈顶取出节点,进入其右子树
5.直到当前节点和栈都为空时,结束。(栈为空就是所有的入栈的节点的右子树都访问过了。当前节点为空就代表所有的节点都访问过了)
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node {
char data ;
struct Node * Lchild ;
struct Node * Rchild ;
}BiNode ,*BiTree ;
typedef struct temp{
BiTree ptr;
struct temp *next ;
}SeqStack;
void CreteBitree(BiTree *root)
{
char ch ;
cin >> ch ;
if( ch == '#' )
*root= NULL;
else {
*root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Lchild);
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Rchild);
}
}
void InitSeqStack(SeqStack **S)
{
*S = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
(*S)->next = NULL ;
}
void Push(SeqStack *S,BiTree p)
{
SeqStack *temp ;
temp = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
temp-> ptr = p;
temp->next = S->next ;
S->next = temp ;
}
void Pop(SeqStack *S ,BiTree *p)
{
SeqStack *t ;
t= S->next ;
*p = t->ptr ;
S->next = t->next ;
free(t);
}
int IsEmpty(SeqStack *S)
{
if(S->next == NULL )
return 1;
else return 0;
}
void InOrder(BiTree root)
{
SeqStack *S;
BiTree p ;
InitSeqStack(&S);
p = root ;
while(p != NULL || !IsEmpty(S) )
{
while(p != NULL )
{
Push(S,p);
p=p->Lchild;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S))
{
Pop(S,&p);
cout << p->data ;
p=p->Rchild ;
}
}
cout << endl ;
}
void PreOrder(BiTree root)
{
SeqStack *S;
BiTree p ;
InitSeqStack(&S);
p = root ;
while(p != NULL || !IsEmpty(S) )
{
while(p != NULL )
{
cout << p->data ;
Push(S,p);
p=p->Lchild;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S))
{
Pop(S,&p);
p=p->Rchild ;
}
}
cout << endl ;
}
int main(void)
{
BiTree root;
cout << "Please input the string :" << endl ;
CreteBitree(&root);
cout << "非递归!!!先序:" << endl ;
PreOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "非递归!!!中序:" << endl ;
InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
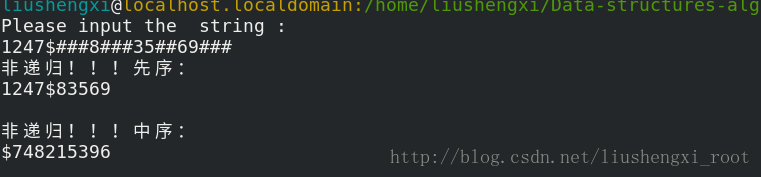
运行截图:
后序
思路:后序的遍历要比前面的两种复杂一些。因为在前面我们的思路就是进左子树,然后从左子树返回,退栈,进右子树。而在后序中,我们是必须先访问完左右子树才能退栈,访问根节点。那么我们如何知道是从哪个子树返回的呐?其实也很简单的啦。就设置一个标记(tag),左为0,右为1。如果tag==1就退栈返回,如果不为1,就修改它的tag==1,继续压回去,往右子树走就行了
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node {
char data ;
struct Node * Lchild ;
struct Node * Rchild ;
}BiNode ;
typedef struct temp{
BiNode *ptr;
int tag ;
struct temp *next ;
}SeqStack;
void CreteBitree(BiNode **root)
{
char ch ;
cin >> ch ;
if( ch == '#' )
*root= NULL;
else {
*root = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Lchild);
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Rchild);
}
}
void InitSeqStack(SeqStack **S)
{
*S = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
(*S)->next = NULL ;
}
void Push(SeqStack *S,SeqStack p)
{
SeqStack *temp ;
temp=(SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
temp->tag = p.tag ;
temp->ptr = p.ptr ;
temp->next = S->next ;
S->next = temp ;
}
SeqStack Pop(SeqStack *S ,SeqStack p)
{
SeqStack *t ;
t= S->next ;
p.ptr = t->ptr ;
p.tag = t->tag ;
S->next = t->next ;
free(t);
return p ;
}
int IsEmpty(SeqStack *S)
{
if(S->next == NULL )
return 1;
else return 0;
}
void PostOrder_with_stack(BiNode *root)
{
SeqStack *S;
SeqStack p ;
InitSeqStack(&S);
p.ptr = root ;
while(p.ptr != NULL || !IsEmpty(S) )
{
while(p.ptr != NULL )
{
p.tag= 0 ;
Push(S,p);
p.ptr=p.ptr->Lchild;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S))
{
p=Pop(S,p);
if(p.tag == 0 ){
p.tag = 1;
Push(S,p);
p.ptr=p.ptr->Rchild;
}
else{
cout << p.ptr->data ;
p.ptr = NULL ;
}
}
}
cout << endl ;
}
int main(void)
{
BiNode *root;
cout << "Please input the string :" << endl ;
CreteBitree(&root);
cout << "非递归!!!后序遍历:" << endl;
PostOrder_with_stack(root);
return 0;
}
运行截图:

总结:三种不同的遍历过程的搜索路径是相同的,不同的仅是三次经过节点时哪一次访问节点。但无论那次经过节点访问时,在第一次经过节点时,都需要保留其节点信息。以便返回时,找到其右子树或者该节点。
2.层次遍历(队列+BFS)
思路:先访问的节点的其孩子也将先访问,后访问的节点的其孩子也将后访问,先进先出与队列的形式相同哦
1.队头节点出队,并访问出队节点
2.出队节点的左右孩子依次入队
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node {
char data ;
struct Node * Lchild ;
struct Node * Rchild ;
}BiNode ;
typedef struct t1{
BiNode *ptr ;
struct t1 *next ;
}Queue;
typedef struct t2{
Queue *front;
Queue *rear;
}LinkList_Queue;
void CreteBitree(BiNode **root)
{
char ch ;
cin >> ch ;
if( ch == '#' )
*root= NULL;
else {
*root = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Lchild);
CreteBitree(&(*root)->Rchild);
}
}
void InitQueue(LinkList_Queue **Q)
{
*Q =(LinkList_Queue *)malloc(sizeof(LinkList_Queue)) ;
(*Q)->front = (*Q)->rear = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
(*Q)->front->next = NULL;
}
void InQueue(LinkList_Queue *Q ,BiNode *p)
{
Queue *temp ;
temp = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
temp->ptr = p ;
temp->next = Q->rear->next ;
Q->rear->next = temp ;
Q->rear = temp ;
}
void OutQueue(LinkList_Queue *Q,BiNode **p)
{
Queue *temp ;
temp = Q->front->next;
(*p) = Q->front->next->ptr ;
Q->front->next = temp->next ;
if(Q->front->next == NULL )
Q->front = Q->rear ;
}
int IsEmpyt(LinkList_Queue *Q)
{
if(Q->front == Q->rear )
return 1;
else return 0;
}
void LevelOrder(BiNode *root)
{
LinkList_Queue *Q;
BiNode *p;
InitQueue(&Q);
InQueue(Q,root);
while( !IsEmpyt(Q))
{
OutQueue(Q,&p);
cout << p->data << " ";
if(p->Lchild != NULL )
InQueue(Q,p->Lchild);
if(p->Rchild != NULL)
InQueue(Q,p->Rchild);
}
cout << endl ;
}
int main(void)
{
BiNode *root;
cout << "Please input the string :" << endl ;
CreteBitree(&root);
cout << "层次遍历:" << endl ;
LevelOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

PS:如果不懂的童鞋,就看下面的参考学习中的视频(是我找到的很好的视频哦),看完就会了,耶!



