1、运算符
1.1算术运算符
1.2比较运算符
>>> a = 10 >>> b = 20 >>> a > b False >>> a < b True >>> a == b False >>> a != b True >>> a <= b True >>> a >= b False >>> a = 'tajzhang' >>> b = 'python' >>> a > b True >>> a = 5 >>> b = '5' >>> a > b Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#13>", line 1, in <module> a > b TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'int' and 'str'
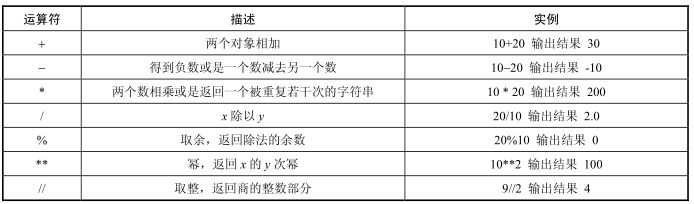
1.3逻辑运算符
1)布尔类型 True False
>>> a = " " >>> bool(a) True >>> b = "" >>> bool(b) False >>> bool("canglaoshi") True >>> bool([]) False >>> bool({}) False
2)布尔运算 and or not
and: 与
A and B:如果A的值是True,就计算B,并将B的结果返回作为最终结果。如果B的结果是False,那么A and B的最终结果就是False;如果B的结果是True,那么A and B的最终结果就是True。如果A的值是False 那么久不计算B了,直接返回A and B的结果为False
or: 或
如果A为True 返回True ,最终结果为True ,否则返回B的值为最终结果
not: 非
无论面对什么,否要否定它
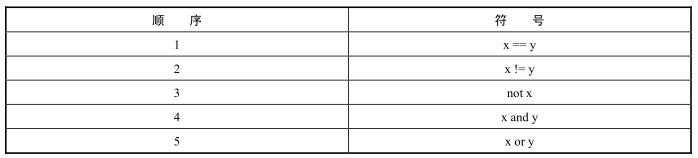
1.4 复杂的布尔表达式
遇到复杂表达式,最好的方法是使用括号 ()
计算优先级
2、简单语句
语句分类:
循环语句:容许一些语句反复运行次数
条件语句:容许仅当默写条件成立时才运行某个模块
无条件分支语句:容许运行顺序转移到程序的其他部分之中,包括跳转(如某些语言中的goto)等
循环、条件和无条件分支都是控制流程
2.1import
引入模块方法,python中常用,引用方法有如下几种:
>>> import math >>> math.pow(3,2) #可读性较好,不同模块同函数名不会产生冲突 9.0 >>> from math import pow #比较适合引入模块较少的时候,多模块时可读性会下降 >>> pow(3,2) 9.0 >>> from math import pow as pingfang #将每个模块引入的函数重命名 >>> pingfang(3,2) 9.0 >>> from math import pow,e,pi #引入多个函数 >>> pow(e,pi) 23.140692632779263 >>> from math import * #引入所有函数,可读性低,适合使用程序使用频繁 >>> pow(3,2) 9.0 >>> sqrt(9) 3.0
2.2赋值语句
>>> x,y,z = 1,"python",["hello",'world'] >>> x 1 >>> y 'python' >>> z ['hello', 'world'] >>> a = 'www.baidu.com','python' >>> a ('www.baidu.com', 'python') >>> type(a) <class 'tuple'>
>>> x = 9 >>> x += 1 >>> x 10 >>> m = "py" >>> m += "th" >>> m 'pyth' >>> m += "on" >>> m 'python'