一道神奇的BFS
前置芝士
具体做法
数据范围非常大,直接BFS肯定是一片黑色(指TLE,MLE),直接贪心又有可能会出一些莫名其妙的问题,所以,大范围贪心,小范围BFS的思路就出现了(不要问我是怎么出现的).
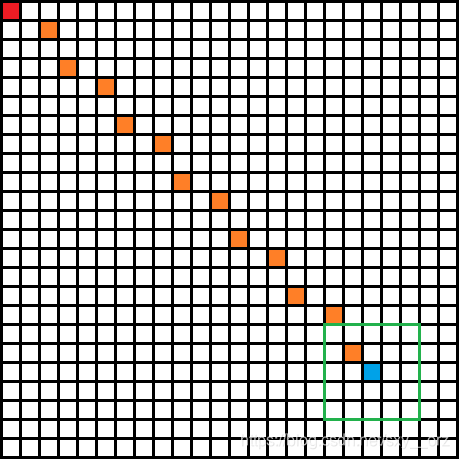
如这样一张图,要从红点到蓝点,可以先顺着橙色点的路径到绿色的框中(框的大小和形状可以自由调整),到框中以后就可以BFS了,BFS时坐标很大,所以可以用map(set)来判断这个点是否走过.
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rap(i,first,last) for(int i=first;i<=last;++i)
using namespace std;
const int maxN=500;
const int move_x[9]={233,1,1,-1,-1,2,2,-2,-2};
const int move_y[9]={233,2,-2,2,-2,1,-1,1,-1};
map<pair<int,int>,int>visit;//
int fx,fy,lx,ly;
int dis(int x,int y,int x1,int y1)//我比较喜欢正方形
{
return max(abs(x-x1),abs(y-y1));
}
struct Que//定义一个结构体
{
int x,y,sp;
}que[maxN*maxN];
void write(int answer)//输出answer
{
printf("%d",answer);
exit(0);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&fx,&fy,&lx,&ly);
lx=abs(fx-lx);//将这两个点的位置更改一下,但相对位置不变,方便处理
ly=abs(fy-ly);
fx=0;
fy=0;
int answer=0;
while(dis(fx,fy,lx,ly)>=100)//在BFS的范围外贪心
{
if(abs(lx-fx)>abs(ly-fy))
{
if(lx>fx)
fx+=2;
else
fx-=2;
if(ly>fy)
fy++;
else
fy--;
}
else
{
if(lx>fx)
fx++;
else
fx--;
if(ly>fy)
fy+=2;
else
fy-=2;
}
answer++;
}
que[1].x=fx;
que[1].y=fy;
que[1].sp=0;
visit[make_pair(fx,fy)]=1;//visit去重
int head=0,tail=1;
while(++head<=tail)//BFS的部分
{
if(que[head].x==lx&&que[head].y==ly)write(que[head].sp+answer);//到终点就输出answer
rap(i,1,8)
if(dis(lx,ly,que[head].x+move_x[i],que[head].y+move_y[i])<=100)//注意不能超出范围
if(!visit[make_pair(que[head].x+move_x[i],que[head].y+move_y[i])])//如果没有走过就走
{
que[++tail].x=que[head].x+move_x[i];
que[tail].y=que[head].y+move_y[i];
que[tail].sp=que[head].sp+1;
visit[make_pair(que[tail].x,que[tail].y)]=1;
}
}
return 0;
}