题意:求一个无向图的最小生成树,如果有多个最优解,输出"Not Unique!"
题解:
考虑kruskal碰到权值相同的边:
假设点3通过边(1,3)连入当前所维护的并查集s。
然后有一条边(下图蓝色的边)满足:
1.长度等于(1,3)
2.一端连到3,一端连入S。
那么该边可以替换掉(1,3)。产生另一颗最小生成树。
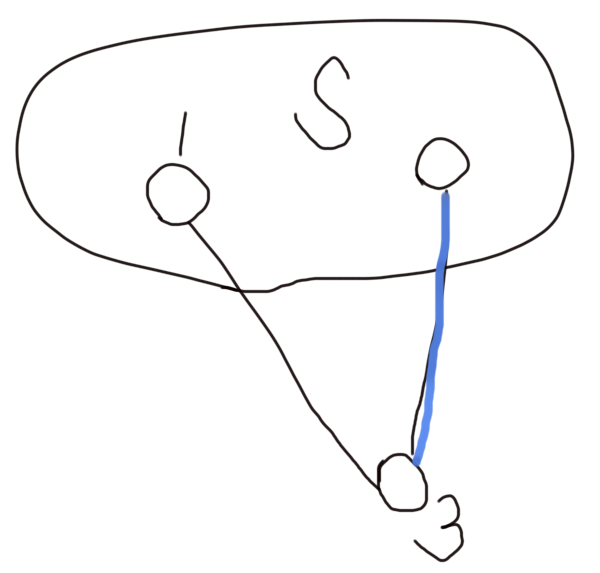
关于如何判断该边一端连3,一端连入S,
用set来记录S中的点,find判断点是否在集合内。(发现kruskal可以用set写啊)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include<stdio.h> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string.h> #include<set> using namespace std; const int maxn = 3e4;;set<int> s; struct edge { int to, from, w; edge(int to=0, int from=0, int w=0) :to(to), from(from), w(w) {} }e[maxn]; bool cmp(edge a, edge b) { return a.w < b.w; } int f[maxn]; int find(int x) { return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]); } void un(int x, int y) { int u = find(x), v= find(y); f[u] = v; } bool same(int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); } int main() { int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int x, y, z; cin >> x >> y >> z; e[num++] = edge(x, y, z); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)f[i] = i; sort(e, e + m,cmp); int lastw = -1, lastto = -1, lastfrom = -1,lastv = -1; int res=0, flag=0; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { if (same(e[i].to, e[i].from)) { if (e[i].w == lastw) { if (e[i].to == lastv && (s.find(e[i].from) != s.end())) { flag = 1; break; } if (e[i].from == lastv && (s.find(e[i].to) != s.end())) { flag = 1; break; } } continue; } un(e[i].to, e[i].from);
res += e[i].w; if (s.find(e[i].to) == s.end()) lastv = e[i].to; else lastv = e[i].from; s.insert(e[i].to); s.insert(e[i].from); } if (flag)cout << "Not Unique!"; else cout << res; cout << endl; } }
队友的玄学代码(改)可以不断记录上一条被选择的边,每次选边时判断一下入度出度关系;
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include<stdio.h> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 3e4;; char s[maxn], str[maxn]; int len1, len2, p[maxn], ans; struct edge { int to, from, w; edge(int to=0, int from=0, int w=0) :to(to), from(from), w(w) {} }e[maxn]; bool cmp(edge a, edge b) { return a.w < b.w; } int f[maxn]; int find(int x) { return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]); } void un(int x, int y) { int u = find(x), v= find(y); f[u] = v; } bool same(int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); } int main() { int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int x, y, z; cin >> x >> y >> z; e[num++] = edge(x, y, z); e[num++] = edge(y, x, z); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)f[i] = i; sort(e, e + 2*m,cmp); int lastw=-1, lastto=-1, lastfrom=-1; int res=0, flag=0; for (int i = 0; i < m*2; i++) { if (same(e[i].to, e[i].from)) { if (e[i].w == lastw) { if ((e[i].from == lastto)&&(e[i].to!=lastfrom)) { flag = 1; break; } if ((e[i].to == lastfrom) && (e[i].from != lastto)) { flag = 1; break; } } continue; } un(e[i].to, e[i].from); res += e[i].w; lastto = e[i].to; lastw = e[i].w; lastfrom = e[i].from; } if (flag)cout << "Not Unique!"; else cout << res; cout << endl; } }