A. String Similarity
题目链接
题目大意
给定一个长度为 2 * n - 1 的字符串要 S
要求构造一个字符串 W 使得 W 与 S[1,n] , S[2,n+1] , ... , S[n,2*n-1] 相似
相似的定义 :如果一个字符串 A 与 一个字符串 B 至少有一个位置的字符相同 , 则 A、B相似
解题思路
令 W[i] 与 S[i , i + n - 1] 的第 i 位相同即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
int T = 1 , n;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
string s , t = "";
cin >> n >> s ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i += 2) t += s[i];
cout << t << '
';
}
return 0;
}
B. RPG Protagonist
题目链接
题目大意
你有一个容量为 P 的背包 , 你的伙伴有个容量为 F 的背包
现有 x 件物品 A , y 件物品 B , 物品 A 的体积为 S , 物品 B 的体积为 W
问你和你的伙伴最多能拿多少件物品
解题思路
枚举你拿物品 A 的数量 , 那么你还可以拿的 B 的数量也确定了
对于同伴优先拿体积小的物品即最优 , 枚举完输出最大值即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
int p , f , x , y , s , w , ans = 0;
cin >> p >> f >> x >> y >> s >> w;
if(s > w) swap(s , w) , swap(x , y);
for(int i = 0 ; i <= x ; i ++)
{
if(i * s > p) break;
int j = min(y, (p - (i * s)) / w), k = min(x - i, f / s), l = min(y - j, (f - (s * k)) / w);
ans = max(ans, i + j + k + l);
}
cout << ans << '
';
}
return 0;
}
C. Binary String Reconstruction
题目链接
题目大意
字符串 w、s 只包含 01
给定一个 x , 若 w[i] = 1 , 则 s[i - x] 、s[i + x] = 1
现给出 s , 求 w
解题思路
对于 S[i] = 0 , W[i + x] 、W[i - x] 必定也为 0
然后对于 S[i] = 1 , 判断 W[i + x] 或 W[i - x] 是否可以为 1
若 S[i] = 1 , 且 W[i + X] 、W[i - X] 都必须为 0 , 则无法构造出 W
若对于所有的 S[i] 都可满足 W[i + X] 或 W[i - X] 可以为 1 , 则构造成功 , 输出 W
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
char s[N] , w[N];
int n , x , flag;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
cin >> s + 1 >> x;
n = strlen(s + 1) , flag = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) w[i] = '#';
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) if(s[i] == '0')
{
if(i - x >= 1) w[i - x] = '0';
if(i + x <= n) w[i + x] = '0';
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) if(s[i] == '1')
{
if(i - x >= 1)
{
if(w[i - x] == '#' || w[i - x] == '1') {w[i - x] = '1' ; continue ;}
}
if(i + x <= n)
{
if(w[i + x] == '#' || w[i + x] == '1') {w[i + x] = '1' ; continue ;}
}
flag = 1 ; break ;
}
if(flag) cout << -1 << '
';
else
{
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
{
if(w[i] == '#') cout << 1;
else cout << w[i];
}
cout << '
';
}
}
return 0;
}
D. Zigzags
题目链接
题目大意
给定一个长度为 n 的数组 A
问满足 1 <= I < J < K < L <= n , 且 aI = aK , aJ = aL 的四元组 (I , J , K , L) 有多少个
解题思路
简单分析一下 , 在看到 N <= 3000 时 , 首先可以想到的是枚举四元组的其中两个
那么就有以下六种方案
- 枚举 I J
- 枚举 I K
- 枚举 I L
- 枚举 J K
- 枚举 J L
- 枚举 L K
再根据 aI = aK , aJ = aL可以得到以下:
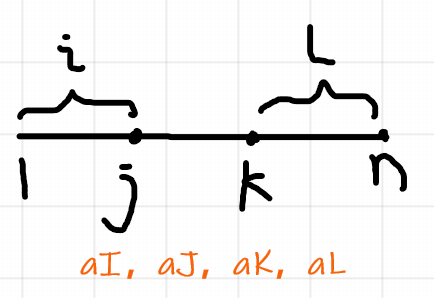
①、若我们选择枚举 I J , 则我们可以得到 aI、aJ、aK、aL,以及控制 I、J的大小关系 , 但是这样 K、L的区间就重了 , 因此我们还需要多枚举一个 K or L
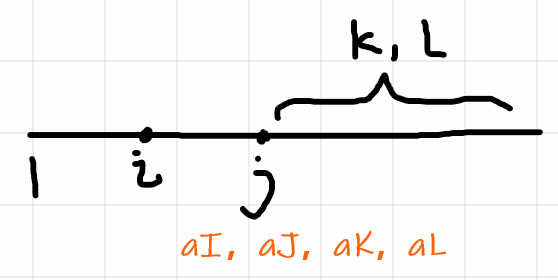
②、若我们枚举 I K , 则我们可以得到 aI、aK,以及控制 I、J、K、L的大小关系 , 但 aJ 和 aL 的值我们就无法得知了 , 因此我们还需要多枚举一个 J or L
③、若我们枚举 I L , 问题同方案①
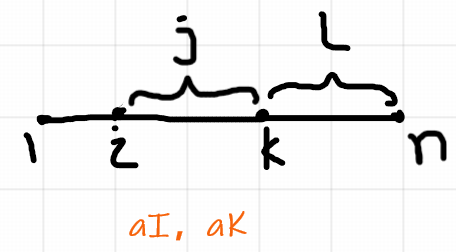
④、若我们枚举 J K , 则我们可以得到 aI、aJ、aK、aL,以及控制 I、J、K、L的大小关系 , 所有需要的信息都有了 , 因此我们枚举 J K即可
方案⑤、方案⑥的问题分别同 ②、①
因此我们枚举 J K , ans += 区间[1 , J - 1] 内 aK 的个数 * 区间[K +1 , n] 内 aL 的个数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 3e3 + 10;
int sum[N][N] , a[N] , n;
int get(int l , int r , int x){
return sum[r][x] - sum[l - 1][x];
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++) sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j];
sum[i][a[i]] ++ ;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int j = 2 ; j <= n - 2 ; j ++)
for(int k = j + 1 ; k <= n - 1 ; k ++) ans += get(1 , j - 1 , a[k]) * get(k + 1 , n , a[j]);
cout << ans << '
';
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++) sum[i][j] = 0;
}
return 0;
}
E. Clear the Multiset
题目链接
题目大意
给出了 N 个墙的高度,要求把这些墙都涂满。
每次可以刷一行或一列,问最少刷多少次可以将所有墙刷完。
解题思路
老原题了
要将区间 [L , R] 的墙刷完 , 可以执行若干次步骤
每次步骤有两种选则
1、选择一个区间横向不断刷直到改区间高度最低的墙被刷完
2、选择某面墙 , 竖着一次性把它刷完
因为 N <= 5000 , 所以很显然采用分治统计最优解
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3 + 10;
int n , a[N];
int get(int st , int ed)
{
int mi = 0x3f3f3f3f , res = 0;
for(int i = st ; i <= ed ; i ++) mi = min(a[i] , mi);
res += mi;
for(int i = st ; i <= ed ; i ++) a[i] -= mi;
int l = st , r = st;
while(l <= ed)
{
while(!a[l] && l <= ed) l ++ ;
if(l > ed) break ;
r = l + 1;
while(a[r] && r <= ed) r ++ ;
res += get(l , r - 1);
l = r;
}
return min(ed - st + 1 , res);
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> a[i];
cout << get(1 , n) << '
';
return 0;
}