与StringIndexer相对应,IndexToString的作用是把标签索引的一列重新映射回原有的字符型标签。
其主要使用场景一般都是和StringIndexer配合,先用StringIndexer将标签转化成标签索引,进行模
型训练,然后在预测标签的时候再把标签索引转化成原有的字符标签。当然,你也可以另外定义其他
的标签。
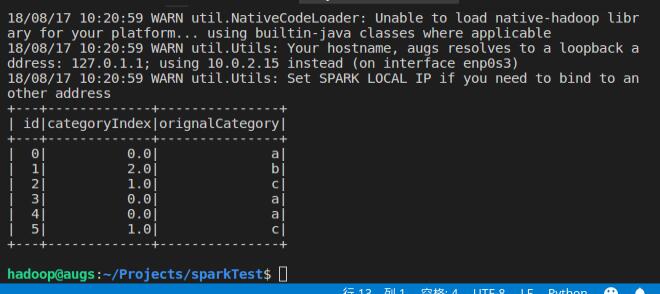
首先,和StringIndexer的实验相同,我们用StringIndexer读取数据集中的“category”列,把字符
型标签转化成标签索引,然后输出到“categoryIndex”列上,构建出新的DataFrame。
#导入相关的类库
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.ml.feature import IndexToString, StringIndexer
#创建SparkSession对象,配置spark
spark= SparkSession.builder.master('local').appName('IndexToStringDemo').getOrCreate()
#创建一个简单的DataFrame训练集
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[(0, "a"), (1, "b"),
(2, "c"), (3, "a"),
(4, "a"), (5, "c")],
["id", "category"])
#创建StringIndexer对象,设置输入输出对象
indexer = StringIndexer(inputCol='category', outputCol='categoryIndex')
#利用fit方法生成训练模型
model = indexer.fit(df)
#利用生成的模型对DataFrame进行转换
indexed = model.transform(df)
#创建IndexToString对象,设置输入输出参数,获得原有数据集的字符型标签,然后再输出到“originalCategory”
#列上。最后,通过输出“originalCategory”列,可以看到数据集中原有的字符标签。
converter = IndexToString(inputCol='categoryIndex',outputCol='orignalCategory')
converter =converter.transform(indexed)
converter.select("id","categoryIndex","orignalCategory").show()