三大认证
入口:dispatch():self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)#三大认证
# 认证模块 校验用户是否登陆,登陆用户,非法用户,游客
self.perform_authentication(request)
# 权限认证,校验用户是否拥有权限,校验对象是登陆用户和游客
self.check_permissions(request)
# 频率认证,访问接口的次数在设定的时间范围内是否过快
# ,配置访问频率,每次访问都要缓存访问次数,超过一定的次数后需要等待时间。
self.check_throttles(request)
class APIView(View):
# The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
# 三大认证的默认设置
# 配置视图类的认证
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
# 配置视图类的频率
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
# 配置视图类的权限
我们在settings.py中寻找认证和权限的配置
然后在我们自己的settings中进行注册,如过自己不重写的话,也可以不用在自己的settings中进行配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 渲染模块
'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': ['rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer'],
# 异常模块
# 'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler',
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'utils.exception.exception_handler',
# 认证配置
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],
# 权限配置
# 认证配置,权限配置是捆绑的,一起出现
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
],
}
认证模块的工作原理
- 继承BaseAuthentication类,重写了authenticate方法
- 认证规则(authenticate方法实现体):
- 没有携带认证信息,直接返回None = >游客
- 由认证信息,校验失败,抛异常 =》 合法用户
- 由认证信息校验出user对象,合法用户
源码
class BasicAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
"""
HTTP Basic authentication against username/password.
"""
www_authenticate_realm = 'api'
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Returns a `User` if a correct username and password have been supplied
using HTTP Basic authentication. Otherwise returns `None`.
"""
auth = get_authorization_header(request).split()
# print(auth)
if not auth or auth[0].lower() != b'basic':
return None
if len(auth) == 1:
msg = _('Invalid basic header. No credentials provided.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
elif len(auth) > 2:
msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials string should not contain spaces.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
try:
auth_parts = base64.b64decode(auth[1]).decode(HTTP_HEADER_ENCODING).partition(':')
except (TypeError, UnicodeDecodeError, binascii.Error):
msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials not correctly base64 encoded.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
userid, password = auth_parts[0], auth_parts[2]
return self.authenticate_credentials(userid, password, request)
def authenticate_credentials(self, userid, password, request=None):
"""
Authenticate the userid and password against username and password
with optional request for context.
"""
credentials = {
get_user_model().USERNAME_FIELD: userid,
'password': password
}
user = authenticate(request=request, **credentials)
if user is None:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('Invalid username/password.'))
if not user.is_active:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('User inactive or deleted.'))
return (user, None)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
return 'Basic realm="%s"' % self.www_authenticate_realm
权限认证模块的工作原理
- 继承BasePermission类,重写 了has_permission方法
- 权限规则(has_permission方法实现体):
- 返回True,代表由权限
- 返回Flase,代表五权限
源码
class AllowAny(BasePermission):
"""
Allow any access.
This isn't strictly required, since you could use an empty
permission_classes list, but it's useful because it makes the intention
more explicit.
"""
def has_permission(self, request, view):
return True # 认证通过,如果给源码改成False,那么就不会由权限
# 必须认证通过的
class IsAuthenticated(BasePermission):
"""
Allows access only to authenticated users.
"""
def has_permission(self, request, view):
return bool(request.user and request.user.is_authenticated)
自定义认证与权限类
实际开发,系统和第三方提供的认证与权限类已经够用了,特别特殊的需求才需要自定义
自定义认证类
"""
认证模块工作原理
1)继承BaseAuthentication类,重写authenticate方法
2)认证规则(authenticate方法实现体):
没有携带认证信息,直接返回None => 游客
有认证信息,校验失败,抛异常 => 非法用户
有认证信息,校验出User对象 => 合法用户
"""
""" 认证类的认证核心规则
def authenticate(self, request):
token = get_token(request)
try:
user = get_user(token) # 校验算法
except:
raise AuthenticationFailed()
return (user, token)
"""
# 自定义认证类
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
class TokenAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
prefix = 'Token'
def authenticate(self, request):
# 拿到前台的token
auth = request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION')
# 没有返回None,有进行校验
if not auth:
return None
auth_list = auth.split()
if not (len(auth_list) == 2 and auth_list[0].lower() == self.prefix.lower()):
raise AuthenticationFailed('非法用户')
token = auth_list[1]
# 校验算法
user = _get_obj(token)
# 校验失败抛异常,成功返回(user, token)
return (user, token)
校验算法
# 校验算法(认证类)与签发算法配套
"""
拆封token:一段 二段 三段
用户名:b64decode(一段)
用户主键:b64decode(二段)
碰撞解密:md5(用户名+用户主键+服务器秘钥) == 三段
"""
import base64, json, hashlib
from django.conf import settings
from api.models import User
def _get_obj(token):
token_list = token.split('.')
if len(token_list) != 3:
raise AuthenticationFailed('token异常')
username = json.loads(base64.b64decode(token_list[0])).get('username')
pk = json.loads(base64.b64decode(token_list[1])).get('pk')
md5_dic = {
'username': username,
'pk': pk,
'key': settings.SECRET_KEY
}
if token_list[2] != hashlib.md5(json.dumps(md5_dic).encode()).hexdigest():
raise AuthenticationFailed('token内容异常')
user_obj = User.objects.get(pk=pk, username=username)
return user_obj
自定义权限类
# 自定义权限类
"""
权限模块工作原理
1)继承BasePermission类,重写has_permission方法
2)权限规则(has_permission方法实现体):
返回True,代表有权限
返回False,代表无权限
"""
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
class SuperUserPermission(BasePermission):
def has_permission(self, request, view):
# print(request.user)
# print(request.auth)
return request.user and request.user.is_superuser#确定那些用户有访问权限
限制登陆才能访问
查看所有用户信息,前提:必须是登录的超级管理员
# 登录接口:如果是超级管理员登录,返回一个可以交易出超级管理员的token字符串
# 只要有用户登录,就可以返回一个与登录用户相关的token字符串 => 返回给前台 => 签发token => user_obj -> token_str
from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
class LoginAPIView(APIView):
# 登录接口一定要做:局部禁用 认证 与 权限 校验
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = serializers.LoginModelSerializer(data=request.data)
# 重点:校验成功后,就可以返回信息,一定不能调用save方法,因为该post方法只完成数据库查操作
# 所以校验会得到user对象,并且在校验过程中,会完成token签发(user_obj -> token_str)
serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
return APIResponse(data={
'username': serializer.user.username,
'token': serializer.token
})
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate
class LoginModelSerializer(ModelSerializer):
# username和password字段默认会走系统校验,而系统的post请求校验,一定当做增方式校验,所以用户名会出现 重复 的异常
# 所以自定义两个字段接收前台的账号密码
usr = serializers.CharField(write_only=True)
pwd = serializers.CharField(write_only=True)
class Meta:
model = models.User
fields = ('usr', 'pwd')
def validate(self, attrs):
usr = attrs.get('usr')
pwd = attrs.get('pwd')
try:
user_obj = authenticate(username=usr, password=pwd)
except:
raise ValidationError({'user': '提供的用户信息有误'})
# 拓展名称空间
self.user = user_obj
# 签发token
self.token = _get_token(user_obj)
return attrs
自定义签发token
# 自定义签发token
# 分析:拿user得到token,后期还需要通过token得到user
# token:用户名(base64加密).用户主键(base64加密).用户名+用户主键+服务器秘钥(md5加密)
# eg: YWJj.Ao12bd.2c953ca5144a6c0a187a264ef08e1af1
# 签发算法:b64encode(用户名).b64encode(用户主键).md5(用户名+用户主键+服务器秘钥)
# 校验算法(认证类)与签发算法配套
"""
拆封token:一段 二段 三段
用户名:b64decode(一段)
用户主键:b64decode(二段)
碰撞解密:md5(用户名+用户主键+服务器秘钥) == 三段
"""
def _get_token(obj):
import base64, json, hashlib
from django.conf import settings
t1 = base64.b64encode(json.dumps({'username': obj.username}).encode()).decode()
t2 = base64.b64encode(json.dumps({'pk': obj.id}).encode()).decode()
t3_json = json.dumps({
'username': obj.username,
'pk': obj.id,
'key': settings.SECRET_KEY
})
t3 = hashlib.md5(t3_json.encode()).hexdigest()
return '%s.%s.%s' % (t1, t2, t3)
频率认证
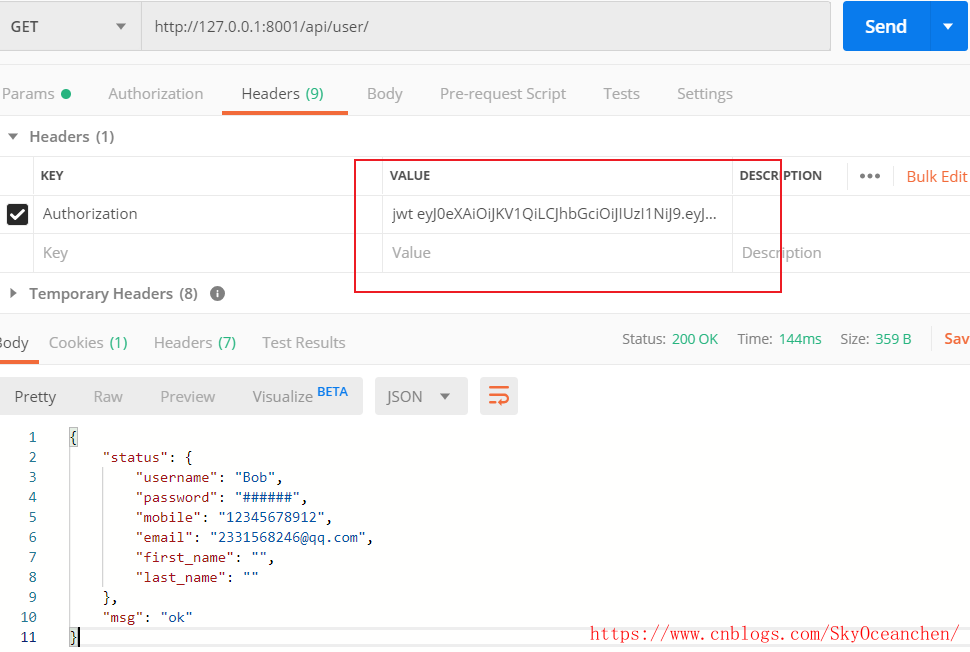
返回个人中心:全部信息
局部配置
# 频率模块局部配置throttle_classes = [ThreeTimeUserThrottle]
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from utils.throttles import ThreeTimeUserThrottle
class UserCenterAPIView(APIView):
# 认证全局配置吗,权限局部配置
# authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
# 频率模块局部配置
throttle_classes = [ThreeTimeUserThrottle]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
user = request.user
serializer = serializers.UserModelSerializer(user)
return APIResponse(data=serializer.data)
# @Author : OceanSkychen # @File : serializers.py
# 只参与序列化
class UserModelSerializer(ModelSerializer):
# 改了原数据库字段的序列化方式
password = SerializerMethodField()
def get_password(self, obj):
return '########' #设置密码返回为###########
class Meta:
model = models.User
fields = ('username', 'password', 'mobile', 'email', 'first_name', 'last_name')
自定义频率类
1)定义类继承SimpleRateThrottle,重写get_cache_key方法,设置scope类属性
2)scope就是一个认证字符串,在配置文件中配置scope字符串对应的频率设置
3)get_cache_key的返回值是字符串,该字符串是缓存访问次数的缓存key
# @Author : OceanSkychen # @File : throttles.py
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle
# 1)定义类继承SimpleRateThrottle,重写get_cache_key方法,设置scope类属性
# 2)scope就是一个认证字符串,在配置文件中配置scope字符串对应的频率设置
# 3)get_cache_key的返回值是字符串,该字符串是缓存访问次数的缓存key
class ThreeTimeUserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'three'
# 当前用户缓存的key
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return 'throttle:user_%s' % (request.user.id)
全局配置:settings.py
# drf的配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 异常模块
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'utils.exception.exception_handler',
# 认证模块
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
# jwt认证类
'rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication',
],
# 权限模块
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
# 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
# 自定义权限类
],
# 频率设置
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'three': '3/min',
},
}
前后台分离模式下信息交互规则
"""
1)任何人都能直接访问的接口
请求不是是get、还是post等,不需要做任何校验
2)必须登录后才能访问的接口
任何请求方式都可能做该方式的限制,请求必须在请求头中携带认证信息 - authorization
3)前台的认证信息获取只能通过登录接口
前台提供账号密码等信息,去后台换认证信息token
4)前台如何完成登录注销
前台登录成功一般在cookie中保存认证信息token,分离注销就是前台主动清除保存的token信息
"""
