Thermal de Broglie wavelengthIn physics, the Thermal de Broglie wavelength is defined for a free ideal gas of massive particles in equilibrium as: where
The thermal de Broglie wavelength is roughly the average de Broglie wavelength of the gas particles in an ideal gas at the specified temperature. We can take the average interparticle spacing in the gas to be approximately (V/N)1/3where V is the volume and N is the number of particles. When the thermal de Broglie wavelength is much smaller than the interparticle distance, the gas can be considered to be a classical or Maxwell-Boltzmann gas. On the other hand, when the thermal de Broglie wavelength is on the order of, or larger than the interparticle distance, quantum effects will dominate and the gas must be treated as a Fermi gas or a Bose gas, depending on the nature of the gas particles. The critical temperature is the transition point between these two regimes, and at this critical temperature, the thermal wavelength will be approximately equal to the interparticle distance. That is, the quantum nature of the gas will be evident for i.e., when the interparticle distance is less than the thermal de Broglie wavelength; in this case the gas will obeyBose-Einstein statistics or Fermi-Dirac statistics, whichever is appropriate. On the other hand, for i.e., when the interparticle distance is much larger than the thermal de Broglie wavelength, the gas will obey Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics.
DerivationFor a derivation of Massless particlesFor a massless particle, the thermal wavelength may be defined as: where c is the speed of light. As with the thermal wavelength for massive particles, this is of the order of the average wavelength of the particles in the gas and defines a critical point at which quantum effects begin to dominate. For example, when the thermal wavelength of the photons in a black body radiator is of the same order as the wavelength of the radiation (or larger), the "classical" Rayleigh-Jeans law becomes inapplicable, and the "quantum"Planck's law must be used. The massless thermal wavelength is derived from the more general definition of the thermal wavelength due to Yan (Yan 2000) described below. General definition of the thermal wavelengthA general definition of the thermal wavelength for an ideal quantum gas in any number of dimensions and for a generalized relationship between energy and momentum (dispersion relationship) has been given by Yan (Yan 2000). It is of practical importance, since there are many experimental situations with different dimensionality and dispersion relationships. If n is the number of dimensions, and the relationship between energy (E) and momentum (p) is given by: where a and s are constants, then the thermal wavelength is defined as: where Γ is the Gamma function. For example, in the usual case of massive particles in a 3-D gas we have n=3 , andE=p2/2m which gives the above results for massive particles. For massless particles in a 3-D gas, we have n=3 , and E=pc which gives the above results for massless particles. References
|
|
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Thermal_de_Broglie_wavelength". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |
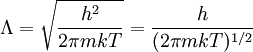
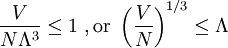
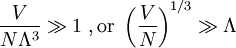
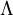 , see configuration integral.
, see configuration integral.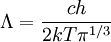
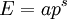
![Lambda=frac{h}{sqrt{pi}}left(frac{a}{kT}
ight)^{1/s} left[frac{Gamma(n/2+1)}{Gamma(n/s+1)}
ight]^{1/n}](http://www.chemeurope.com/en/encyclopedia/images/math/c/a/1/ca1050d0e60e7989dcd9094585235a09.png)