前言:
如果定义一个类,有其默认的构造函数,则使用new动态实例化一个对象数组,不是件难事,如下代码:
1 #include <memory>
2 #include <iostream>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class Animal
7 {
8 public:
9 #if 1 //用于后面演示,无默认构造函数
10 Animal() : num(0)
11 {
12 cout << "Animal constructor default" << endl;
13 }
14 #endif
15 Animal(int _num) : num(_num)
16 {
17 cout << "Animal constructor param" << endl;
18 }
19
20 ~Animal()
21 {
22 cout << "Animal destructor" << endl;
23 }
24
25 void show()
26 {
27 cout << this->num << endl;
28 }
29
30 private:
31 int num;
32 };
33
34 int main()
35 {
36 Animal *ani = new Animal[5];
37
38 delete[]ani;
39
40 system("pause");
41 return 0;
42 }
运行结果:
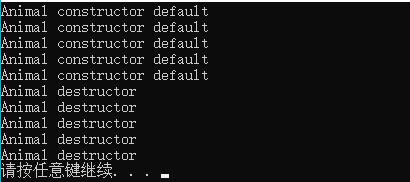
但是,如果没有默认构造函数,会出现怎么样呢?
看下图报错提示:

那要如何实例化一个没有默认构造函数的对象数组呢?
下面我将介绍两种方法:
1. 使用C++11新特性allocator类
2. 使用placement new 即operator new(第三个重载版本)void* operator new(size_t size, void *p)函数
一、allocator类
对于allocator类,请看 我的另一篇blog http://www.cnblogs.com/SimonKly/p/7819122.html
请看一下代码关于使用如何实现无默认构造函数,动态实例化对象数组的allocator方法

1 //#include "CAnimal.h" 2 #include <memory> 3 #include <iostream> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Animal 8 { 9 public: 10 #if 1 //即使为0,没有默认构造也是可以, 11 Animal() : num(0) 12 { 13 cout << "Animal constructor default" << endl; 14 } 15 #endif 16 Animal(int _num) : num(_num) 17 { 18 cout << "Animal constructor param" << endl; 19 } 20 21 ~Animal() 22 { 23 cout << "Animal destructor" << endl; 24 } 25 26 void show() 27 { 28 cout << this->num << endl; 29 } 30 31 private: 32 int num; 33 }; 34 35 /* 36 由于allocator将内存空间的分配和对象的构建分离 37 故使用allocator分为以下几步: 38 1.allocator与类绑定,因为allocator是一个泛型类 39 2.allocate()申请指定大小空间 40 3.construct()构建对象,其参数为可变参数,所以可以选择匹配的构造函数 41 4.使用,与其它指针使用无异 42 5.destroy()析构对象,此时空间还是可以使用 43 6.deallocate()回收空间 44 */ 45 46 int main() 47 { 48 allocator<Animal> alloc; //1. 49 Animal *a = alloc.allocate(5); //2. 50 51 //3. 52 alloc.construct(a, 1); 53 alloc.construct(a + 1); 54 alloc.construct(a + 2, 3); 55 alloc.construct(a + 3); 56 alloc.construct(a + 4, 5); 57 58 //4. 59 a->show(); 60 (a + 1)->show(); 61 (a + 2)->show(); 62 (a + 3)->show(); 63 (a + 4)->show(); 64 65 //5. 66 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 67 { 68 alloc.destroy(a + i); 69 } 70 //对象销毁之后还可以继续构建,因为构建和内存的分配是分离的 71 //6. 72 alloc.deallocate(a, 5); 73 74 cin.get(); 75 return 0; 76 }
运行结果
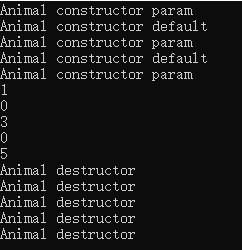
通过运行结果可以看出,无论是否有默认构造,allocator会选择出最匹配的构造函数(重载)
二、placement new
函数原型:
void* operator new(size_t size, void* p) throw();
函数执行忽略size,只返回p指针,不分配内存。
placement new具体的用法和相关技术点,请参看我的另一篇博文的第三节
http://www.cnblogs.com/SimonKly/p/7826651.html
具体实现:C++中若类中没有默认构造函数,如何使用对象数组??
请看下面的代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class animal 6 { 7 public: 8 #if 1 //用于后面演示,无默认构造函数 9 animal() : num(0) 10 { 11 cout << "animal constructor default" << endl; 12 } 13 #endif 14 animal(int _num) : num(_num) 15 { 16 cout << "animal constructor param" << endl; 17 } 18 19 ~animal() 20 { 21 cout << "animal destructor" << endl; 22 } 23 24 void show() 25 { 26 cout << this->num << endl; 27 } 28 29 void * operator new(size_t size, void *p) 30 { 31 return p; 32 } 33 34 private: 35 int num; 36 }; 37 38 39 int main(int args, char ** argv) 40 { 41 // 一个动态animal数组 42 void *p = operator new(5 * sizeof(animal)); // 申请缓冲器 43 animal *a = static_cast<animal *>(p); // 转换类型 44 45 // 2.对象构建 46 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 47 { 48 new(a + i) animal(i);// 调用重载构造 49 } 50 new(a + 4) animal; // 也可以调用默认构造 51 52 // 3.使用 53 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 54 { 55 (a + i)->show(); 56 } 57 58 // 4.销毁对象 59 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 60 { 61 (a + i)->~animal(); 62 } 63 64 // 5.回收空间 65 delete[]p; 66 67 cin.get(); 68 return 0; 69 }
运行结果:
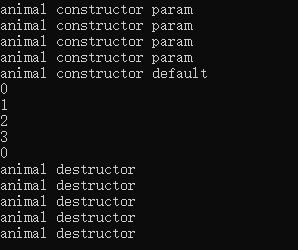
通过运行结果可以看出,无论是否有默认构造,placement new会向已经申请的空间重新构建对象。
