介绍pandas的有关DataFrame的高级操作。
1. 数据合并
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame([{'Name': 'Chris', 'Item Purchased': 'Sponge', 'Cost': 22.50}, {'Name': 'Kevyn', 'Item Purchased': 'Kitty Litter', 'Cost': 2.50}, {'Name': 'Filip', 'Item Purchased': 'Spoon', 'Cost': 5.00}], index=['Store 1', 'Store 1', 'Store 2']) df
数据输出:
1.1 加列
df['Date'] = ['December 1', 'January 1', 'mid-May'] df
df['Delivered'] = True df['Feedback'] = ['Positive', None, 'Negative']
重新设置某一列的值:
adf = df.reset_index() adf['Date'] = pd.Series({0: 'December 1', 2: 'mid-May'}) adf
1.2 合并操作
staff_df = pd.DataFrame([{'Name': 'Kelly', 'Role': 'Director of HR'},
{'Name': 'Sally', 'Role': 'Course liasion'},
{'Name': 'James', 'Role': 'Grader'}])
staff_df = staff_df.set_index('Name')
student_df = pd.DataFrame([{'Name': 'James', 'School': 'Business'},
{'Name': 'Mike', 'School': 'Law'},
{'Name': 'Sally', 'School': 'Engineering'}])
student_df = student_df.set_index('Name')
print(staff_df.head())
print()
print(student_df.head())
输出:
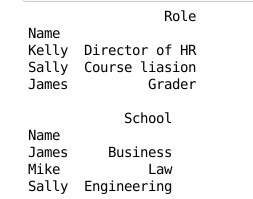
1.3 合并所有的值,能够自动用NaN填充
pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='outer', left_index=True, right_index=True) #合并所有的值
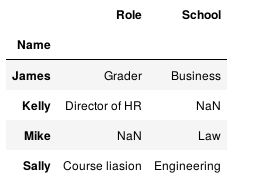
1.4 只连接两者共有部分
pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='inner', left_index=True, right_index=True)
输出:
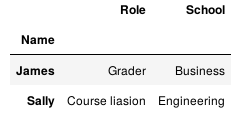
1.5 只考虑左边部分的完整性。
pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='left', left_index=True, right_index=True)
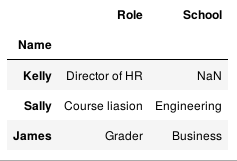
1.6 只考虑右部分的完整性。
pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='right', left_index=True, right_index=True)

1.7 或者按照列进行合并。
staff_df = staff_df.reset_index() student_df = student_df.reset_index() pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='left', left_on='Name', right_on='Name')
1.8 合并两个具有共同列名字的DataFrame,为了区分同名列,一般用_x表示合并操作中左边的DataFrama,_y表示右边的DataFrame。
staff_df = pd.DataFrame([{'Name': 'Kelly', 'Role': 'Director of HR', 'Location': 'State Street'},
{'Name': 'Sally', 'Role': 'Course liasion', 'Location': 'Washington Avenue'},
{'Name': 'James', 'Role': 'Grader', 'Location': 'Washington Avenue'}])
student_df = pd.DataFrame([{'Name': 'James', 'School': 'Business', 'Location': '1024 Billiard Avenue'},
{'Name': 'Mike', 'School': 'Law', 'Location': 'Fraternity House #22'},
{'Name': 'Sally', 'School': 'Engineering', 'Location': '512 Wilson Crescent'}])
pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='left', left_on='Name', right_on='Name')
Example:
staff_df = pd.DataFrame([{'First Name': 'Kelly', 'Last Name': 'Desjardins', 'Role': 'Director of HR'},
{'First Name': 'Sally', 'Last Name': 'Brooks', 'Role': 'Course liasion'},
{'First Name': 'James', 'Last Name': 'Wilde', 'Role': 'Grader'}])
student_df = pd.DataFrame([{'First Name': 'James', 'Last Name': 'Hammond', 'School': 'Business'},
{'First Name': 'Mike', 'Last Name': 'Smith', 'School': 'Law'},
{'First Name': 'Sally', 'Last Name': 'Brooks', 'School': 'Engineering'}])
print(staff_df)
print(student_df)
print(pd.merge(staff_df, student_df, how='inner', left_on=['First Name','Last Name'], right_on=['First Name','Last Name']))
2. Pandas Idioms.
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('census.csv') df.head()
风格1:
( df.where(df['Quantity'] != 0) .dropna() .rename(columns = {'Weight' : 'Weight(oz.)'})) # to modify the DataFrame df in one statement to drop any entries
# where 'Quantity' is 0 and rename the column 'Weight' to 'Weight (oz.)'?.
或者用了drop()方法。效果同上。
print(df.drop(df[df['Quantity'] == 0].index).rename(columns={'Weight': 'Weight (oz.)'})) # to modify the DataFrame df in one statement to drop any entries # where 'Quantity' is 0 and rename the column 'Weight' to 'Weight (oz.)'?.
(df.where(df['SUMLEV']==50) .dropna() .set_index(['STNAME','CTYNAME']) .rename(columns={'ESTIMATESBASE2010': 'Estimates Base 2010'}))
风格2:
df = df[df['SUMLEV']==50] df.set_index(['STNAME','CTYNAME'], inplace=True) df.rename(columns={'ESTIMATESBASE2010': 'Estimates Base 2010'})
2.1 关于apply()方法
import numpy as np def min_max(row): data = row[['POPESTIMATE2010', 'POPESTIMATE2011', 'POPESTIMATE2012', 'POPESTIMATE2013', 'POPESTIMATE2014', 'POPESTIMATE2015']] return pd.Series({'min': np.min(data), 'max': np.max(data)}) df.apply(min_max, axis=1) # axis 将每一行都遍历,得到每一行的最大最小值。
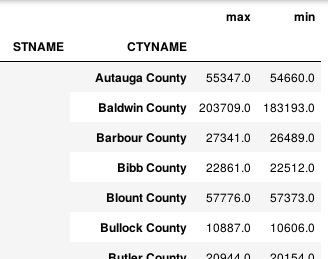
或者返回原来的列加min和max。
import numpy as np def min_max(row): data = row[['POPESTIMATE2010', 'POPESTIMATE2011', 'POPESTIMATE2012', 'POPESTIMATE2013', 'POPESTIMATE2014', 'POPESTIMATE2015']] row['max'] = np.max(data) row['min'] = np.min(data) return row df.apply(min_max, axis=1)
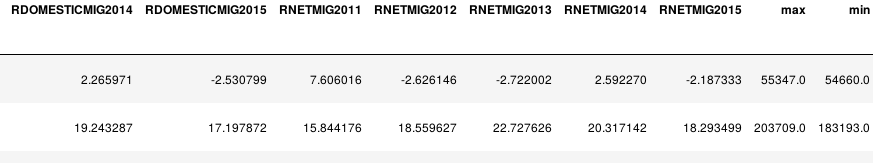
或者使用lambda函数。
rows = ['POPESTIMATE2010', 'POPESTIMATE2011', 'POPESTIMATE2012', 'POPESTIMATE2013', 'POPESTIMATE2014', 'POPESTIMATE2015'] df.apply(lambda x: np.max(x[rows]), axis=1)
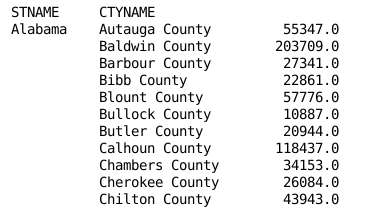
3. Group by 用法
3.1 载入数据
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.read_csv('census.csv') df = df[df['SUMLEV']==50] df.head()
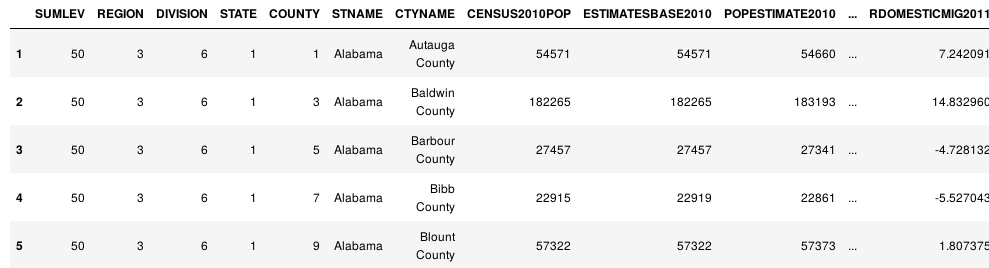
3.2 计算时长
unique() 方法
%%timeit -n 10 for state in df['STNAME'].unique(): avg = np.average(df.where(df['STNAME']==state).dropna()['CENSUS2010POP']) print('Counties in state ' + state + ' have an average population of ' + str(avg)) # 10 loops, best of 3: 1.45 s per loop
或者groupby()方法。
%%timeit -n 10 for group, frame in df.groupby('STNAME'): avg = np.average(frame['CENSUS2010POP']) print('Counties in state ' + group + ' have an average population of ' + str(avg)) #根据state分组计算平均值 #运行时长:10 loops, best of 3: 38.1 ms per loop
或者将索引设置为groupby()需要用的索引,然后根据利用函数进行分割。
df = df.set_index('STNAME') def fun(item): if item[0]<'M': return 0 if item[0]<'Q': return 1 return 2 for group, frame in df.groupby(fun): print('There are ' + str(len(frame)) + ' records in group ' + str(group) + ' for processing.') ''' There are 1177 records in group 0 for processing. There are 1134 records in group 1 for processing. There are 831 records in group 2 for processing. '''
lambda函数和apply()
print(df.groupby('Category').apply(lambda df,a,b: sum(df[a] * df[b]), 'Weight (oz.)', 'Quantity')) # Or alternatively without using a lambda: # def totalweight(df, w, q): # return sum(df[w] * df[q]) # # print(df.groupby('Category').apply(totalweight, 'Weight (oz.)', 'Quantity'))
3.3 关于agg()方法。
df = pd.read_csv('census.csv') df = df[df['SUMLEV']==50] #agg()方法的应用 df.groupby('STNAME').agg({'CENSUS2010POP': np.average})
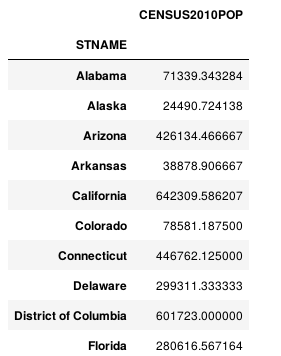
print(type(df.groupby(level=0)['POPESTIMATE2010','POPESTIMATE2011'])) print(type(df.groupby(level=0)['POPESTIMATE2010'])) """ <class 'pandas.core.groupby.DataFrameGroupBy'> <class 'pandas.core.groupby.SeriesGroupBy'> """
groupby 以及 .agg()
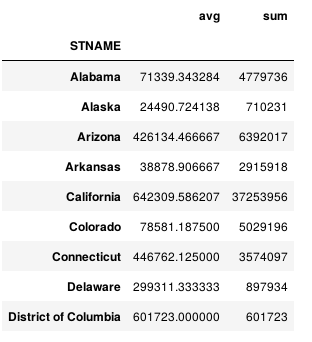
(df.set_index('STNAME').groupby(level=0)['CENSUS2010POP'] .agg({'avg': np.average, 'sum': np.sum}))
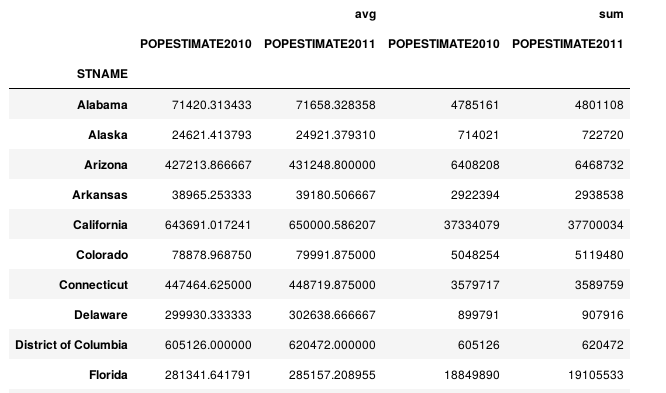
(df.set_index('STNAME').groupby(level=0)['POPESTIMATE2010','POPESTIMATE2011'] .agg({'avg': np.average, 'sum': np.sum}))
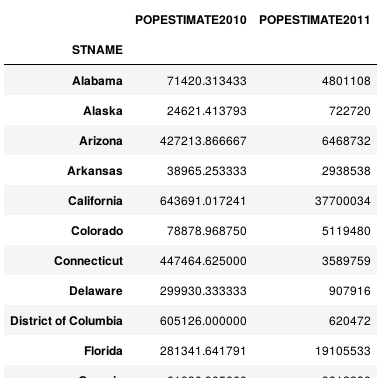
(df.set_index('STNAME').groupby(level=0)['POPESTIMATE2010','POPESTIMATE2011'] .agg({'POPESTIMATE2010': np.average, 'POPESTIMATE2011': np.sum}))
4. Scale
4.1 对数据的排序
s = pd.Series(['Low', 'Low', 'High', 'Medium', 'Low', 'High', 'Low']) s.astype('category', categories=['Low', 'Medium', 'High'], ordered=True) #output: """ 0 Low 1 Low 2 High 3 Medium 4 Low 5 High 6 Low dtype: category Categories (3, object): [Low < Medium < High] """
4.2 数据
df = pd.DataFrame(['A+', 'A', 'A-', 'B+', 'B', 'B-', 'C+', 'C', 'C-', 'D+', 'D'], index=['excellent', 'excellent', 'excellent', 'good', 'good', 'good', 'ok', 'ok', 'ok', 'poor', 'poor']) df.rename(columns={0: 'Grades'}, inplace=True) df

df['Grades'].astype('category').head() #显示 """ excellent A+ excellent A excellent A- good B+ good B Name: Grades, dtype: category Categories (11, object): [A, A+, A-, B, ..., C+, C-, D, D+] """
排序:
grades = df['Grades'].astype('category', categories=['D', 'D+', 'C-', 'C', 'C+', 'B-', 'B', 'B+', 'A-', 'A', 'A+'], ordered=True) grades.head() #output: """ excellent A+ excellent A excellent A- good B+ good B Name: Grades, dtype: category Categories (11, object): [D < D+ < C- < C ... B+ < A- < A < A+] """
比较
grades > 'C' """ excellent True excellent True excellent True good True good True good True ok True ok False ok False poor False poor False Name: Grades, dtype: bool """
4.3 pd.cut()方法分成多个区间。
df = pd.read_csv('census.csv') df = df[df['SUMLEV']==50] df = df.set_index('STNAME').groupby(level=0)['CENSUS2010POP'].agg({'avg': np.average}) pd.cut(df['avg'],3).head() """ STNAME Alabama (11706.0871, 222327.236] Alaska (11706.0871, 222327.236] Arizona (222327.236, 432318.411] Arkansas (11706.0871, 222327.236] California (432318.411, 642309.586] Name: avg, dtype: category Categories (3, object): [(11706.0871, 222327.236] < (222327.236, 432318.411] < (432318.411, 642309.586]] """
5. Pivot Tables.
df = pd.read_csv('cars.csv') df
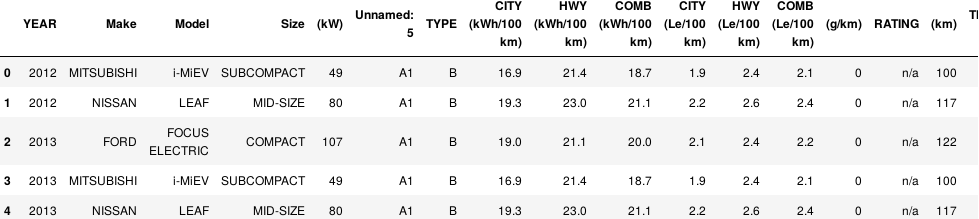
df.pivot_table(values='(kW)', index='YEAR', columns='Make', aggfunc=np.mean)
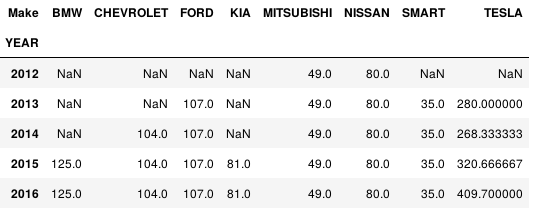
或者用多个aggfunc函数
df.pivot_table(values='(kW)', index='YEAR', columns='Make', aggfunc=[np.mean,np.min], margins=True)
6 .列相除
>> data1 = {'a' : [1., 3., 5., 2.], 'b':[4,8,3,7], 'c' : [5,45,67,34]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data1)
>>> df
#output 输出
"""
a b c
0 1 4 5
1 3 8 45
2 5 3 67
3 2 7 34
"""
b = df['b'] """ >>> b 0 4 1 8 2 3 3 7 """ >>> a = df['a'] """ >>> a 0 1 1 3 2 5 3 2 """ #除法 >>> a = a.div(b) """ >>> a 0 0.250000 1 0.375000 2 1.666667 3 0.285714 Name: a, dtype: float64 """
7. 关于DataFrame的applymap()的使用。
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(3,3)) #output: """ >>> df 0 1 2 0 -0.694165 -0.217500 -0.017622 1 -1.255941 0.442811 -0.490014 2 -1.608948 0.022557 -0.750053 """ dict = {0: 'A', 1 : 'B', 2 : 'C'} #加列, 利用map()函数 df['cat'] = df.index.to_series().map(dict) #输出 """ >>> df 0 1 2 cat 0 -0.69 -0.22 -0.02 A 1 -1.26 0.44 -0.49 B 2 -1.61 0.02 -0.75 C """