000-- define a Dulinklist
A empty DuLinklist:

typedef struct DualNode{ ElemType data; struct DualNode *prior; struct DualNode *next; }DualNode, *DuLinkList;

- Add a new Node
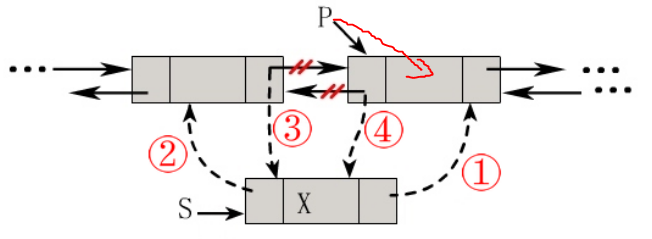
s->next = p; s->prior = p->prior; p->prior->next = s; p->prior = s;
- Delete a Node
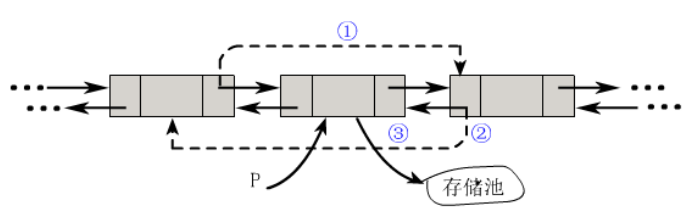
p->prior->next = p->next; p->next->prior = p->prior; free(p);
print A-Z with the defined sequence by user
e.g. user input 3
then should be DEFG....ZABC
user input -3
then should be XYZABCEFG.....W
#define OK 1; #define ERROR 0; typedef char ElemType; typedef int Status; typedef struct DualNode; { ElemType data; struct DualNode *prior; struct DualNode *next; }DualNode, *DuLinkList; Status InitList(DuLinkList *L) { DualNode *p,*q; int i; *L = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DualNode)); if(!(*L)) return ERROR; (*L)->next = (*L)->prior = NULL; p = (*L); for(i=0;i<26;i++) { q = (DualNode *)malloc(sizeof(DualNode)); if(!q) return ERROR; q->data = 'A'+i; q->prior = p; q->next = p->next; p->next = q; p=q; } p->next = (*L)->next; //the last Node points to the first Node (*L)->next->prior = p; //set the first Node with data 'A' as head Node return OK; } void caser(DuLinkList *L, int i) { if(i>0) { do{ (*L) = (*L)->next; } while(--i); } if(i>0) { i = i-1; (*L)=(*L)->next; do{ (*L) = (*L)->prior; }while (++i); } } int main() { DuLinkList L; int i n; InitList(&L); printf("Please input a integer: "); scanf("%d", &n); printf(" "); caser(&L,n); for(i=0;i<26;i++) { L = L->next; printf("%c", L->data); } printf(" "); return 0; }