[LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.

The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Thanks Marcos for contributing this image!
思路:
观察下就可以发现被水填满后的形状是先升后降的塔形,因此,先遍历一遍找到塔顶,然后分别从两边开始,往塔顶所在位置遍历,水位只会增高不会减小,且一直和最近遇到的最大高度持平,这样知道了实时水位,就可以边遍历边计算面积。
代码如下:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int trap(vector<int>& height) { 4 int n=height.size(); 5 if(n<2) 6 return 0; 7 int max=-1,maxInd=0; 8 for(int i=0;i<n;++i) 9 { 10 if(height[i]>max) 11 { 12 max=height[i]; 13 maxInd=i; 14 } 15 } 16 int area=0,roof=height[0]; 17 for(int i=0;i<maxInd;++i) 18 { 19 if(roof<height[i]) 20 roof=height[i]; 21 else 22 area+=(roof-height[i]); 23 } 24 for(int i=n-1,roof=height[n-1];i>maxInd;--i) 25 { 26 if(roof<height[i]) 27 roof=height[i]; 28 else 29 area+=(roof-height[i]); 30 } 31 return area; 32 } 33 };
[LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.
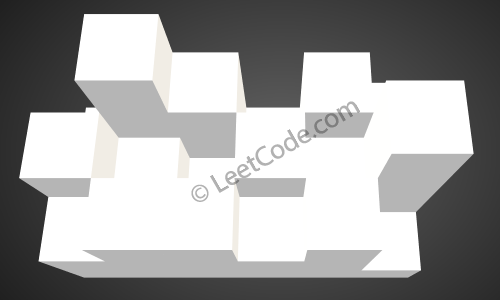
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
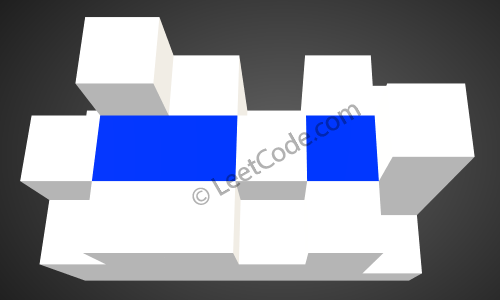
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
思路:
分析:这题算是动态规划吧,读懂题意后,(其实这个题目描述的不清楚啊,图的示例倒是挺好),可以观察,可以从外圈往里圈缩,因为这个过程墙的高度是非递减的,然后,你应该想到用优先队列(priority_queue或者set,又是讨厌的set),先把外圈所有点加入,然后取出高度最小的点,更新四周的点,注意标记这个点是否访问过,这个过程中记录墙增加的高度就是最后的积水量。
代码如下:
1 int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; 2 int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; 3 class Solution { 4 public: 5 6 int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& h) { 7 int n = h.size(); 8 if(n == 0) return 0; 9 int m = h[0].size(); 10 vector<vector<bool> > vis(n, vector<bool>(m, 0)); 11 priority_queue<pair<int, pair<int, int> > > q; 12 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 13 for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { 14 if(i == 0 || j == 0 || i == n - 1 || j == m - 1) { 15 vis[i][j] = 1; 16 q.push({-h[i][j], {i, j}}); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 long long res = 0; 21 while(!q.empty()) { 22 int u = -q.top().first; 23 int ux = q.top().second.first; 24 int uy = q.top().second.second; 25 q.pop(); 26 //cout << ux << " " << uy << " " << u << endl; 27 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 28 int x = ux + dx[i]; 29 int y = uy + dy[i]; 30 if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= n || y >= m || vis[x][y]) 31 continue; 32 if(h[x][y] < u) { 33 res += u - h[x][y]; 34 h[x][y] = u; 35 } 36 vis[x][y] = 1; 37 q.push({-h[x][y],{x, y} }); 38 } 39 } 40 return res; 41 } 42 };