Spring缓存作用准备:
1、准备数据(准备一个有数据的库和表/导入数据库文件,准备好表和表里面的数据)
2、创建javaBean封装数据
3、整合MyBatis操作数据库( 这里用MyBatis)
1,配置数据源信息
2、使用注解版的MyBatis;
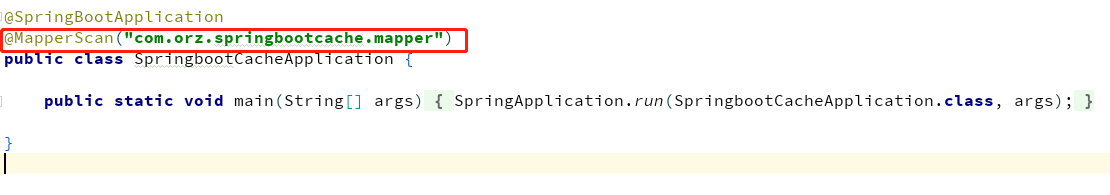
1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的Mapper接口所在的包
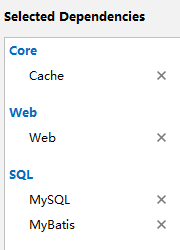
创建一个springboot项目 -》选择依赖(Core->Cache、Web->Web、SQL->MySQL,MyBatis) -》
1,配置数据源信息

spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_cache?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root # 不写的时候从url识别 # spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 开启驼峰命名匹配规则,将数据库中表的字段含有下划线分割符的匹配到javaBean的驼峰风格属性
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
logging.level.com.orz.springbootcache.mapper= debug
2、使用注解版的MyBatis;
1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的Mapper接口所在的包
package com.orz.springbootcache.mapper; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Department; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; @Mapper public interface DepartmentMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM department WHERE id = #{id}") Department getDeptById(Integer id); }
package com.orz.springbootcache.mapper; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Employee; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*; @Mapper public interface EmployeeMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}") public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); @Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}") public void updateEmp(Employee employee); @Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}") public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); @Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})") public void insertEmployee(Employee employee); @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}") Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName); }
EmployeeService
package com.orz.springbootcache.service; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Employee; import com.orz.springbootcache.mapper.EmployeeMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.web.context.annotation.ApplicationScope; /** * @Author ^_^ * @Create 2019/3/10 */ @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ System.out.println("查询"+id + "号员工"); Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return emp; } }
EmployeeController
package com.orz.springbootcache.controller; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Employee; import com.orz.springbootcache.service.EmployeeService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @Author ^_^ * @Create 2019/3/10 */ @RestController public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeService employeeService; @GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ Employee emp = employeeService.getEmp(id); return emp; } }
Spring缓存步骤:
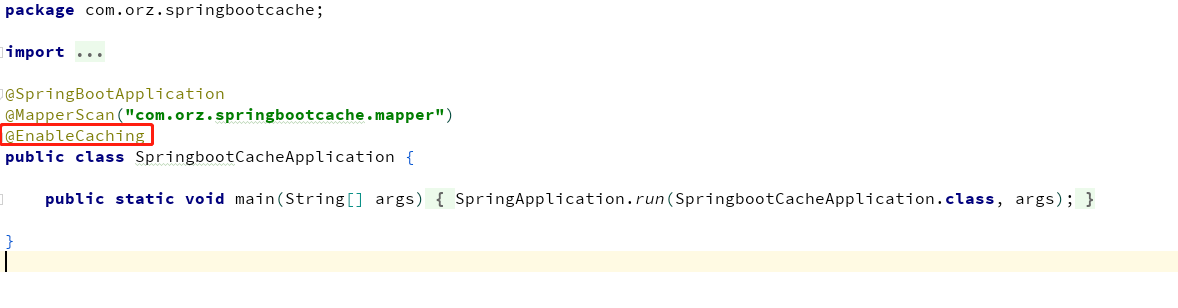
1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
2、标注缓存注解即可
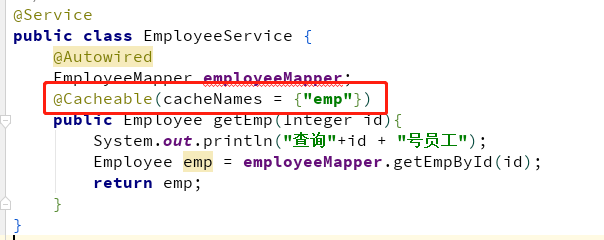
@Cachable
@CachePut
@CacheEvict
@Cachable将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法;
CacheManager管理多个 Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在 Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
几个属性::
cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
getEmp[2]
keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
condition = "#id>0"
condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存
unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
unless = "#result == null"
unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;
sync:是否使用异步模式
程序入口开启使用缓存@EnableCaching和持久层方法上加入可缓存注解@Cacheable
缓存工作原理和@Cachable工作流程
我们引入了缓存模块,那么缓存的自动配置就会生效
原理:
1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
2、缓存的配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration;
4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager
5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中;
运行流程:
@Cacheable:
1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取;
CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
核心:
1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
@Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"}) public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ System.out.println("查询"+id + "号员工"); Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return emp; } }
自定义KeyGenerator
package com.orz.springbootcache.config; import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @Author ^_^ * @Create 2019/3/11 */ @Configuration public class MyCacheConfig { @Bean("myKeyGenerator") public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... objects) { return method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(objects) + "]"; } }; } }
调用自定义KeyGenerator
@Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"},keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator", condition = "#id>0", unless="#a0==2") public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ System.out.println("查询"+id + "号员工"); Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return emp; } }
@CachePut
@CachePut: 既调用方法,又更新缓存数据:同步更新缓存
修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存
运行时机:
1,先调用目标方法
2,将目标方法的结果缓存起来
需要注意缓存的数据
@CachePut 没有指定key时,默认用传参做key,查询result做value
需要要指定和@Cacheable用相同的key,更新的key和查询的key达到一致
service:
package com.orz.springbootcache.service; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Employee; import com.orz.springbootcache.mapper.EmployeeMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @Author ^_^ * @Create 2019/3/10 */ @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"}) public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ System.out.println("查询"+id + "号员工"); Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return emp; } /** * @CachePut: 既调用方法,又更新缓存数据:同步更新缓存 * 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存 * 运行时机: * 1,先调用目标方法 * 2,将目标方法的结果缓存起来 * * * 需要注意缓存的数据 * @CachePut 没有指定key时,默认用传参做key,查询result做value * 需要要指定和@Cacheable用相同的key,更新的key和查询的key达到一致 * */ @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id") public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){ System.out.println("updateEmp:" + employee); employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); return employee; } }
controller
package com.orz.springbootcache.controller; import com.orz.springbootcache.bean.Employee; import com.orz.springbootcache.service.EmployeeService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @Author ^_^ * @Create 2019/3/10 */ @RestController public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeService employeeService; @GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ Employee emp = employeeService.getEmp(id); return emp; } @GetMapping("/emp") public Employee update(Employee employee){ Employee emp = employeeService.updateEmp(employee); return emp; } }
@