import java.util.Hashtable; class DLinkedList { String key; //键 int value; //值 DLinkedList pre; //双向链表前驱 DLinkedList next; //双向链表后继 } public class LRUCache { private Hashtable<String,DLinkedList> cache = new Hashtable<String,DLinkedList>(); private int count; private int capacity; private DLinkedList head, tail; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.count = 0; this.capacity = capacity; head = new DLinkedList(); head.pre = null; tail = new DLinkedList(); tail.next = null; head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } public int get(String key) { DLinkedList node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) return -1; this.moveToHead(node); return node.value; } public void set(String key,int value) { DLinkedList node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) { DLinkedList newNode = new DLinkedList(); newNode.key = key; newNode.value = value; this.cache.put(key, newNode); this.addNode(newNode); ++count; if(count>capacity) { DLinkedList tail = this.popTail(); this.cache.remove(tail.key); --count; } } else { node.value = value; this.moveToHead(node); } } private void addNode(DLinkedList node) { node.pre = head; node.next = head.next; head.next.pre = node; head.next = node; } private void removeNode(DLinkedList node) { DLinkedList pre = node.pre; DLinkedList next = node.next; pre.next = next; next.pre = pre; } private void moveToHead(DLinkedList node) { this.removeNode(node); this.addNode(node); } private DLinkedList popTail() { DLinkedList res = tail.pre; this.removeNode(res); return res; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); DLinkedList node = head; while(node != null){ sb.append(String.format("%s:%s ", node.key,node.value)); node = node.next; } return sb.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { LRUCache lru = new LRUCache(3); lru.set("1", 7); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.set("2", 0); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.set("3", 1); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.set("4", 2); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.get("2"); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.set("5", 3); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.get("2"); System.out.println(lru.toString()); lru.set("6", 4); System.out.println(lru.toString()); /* 0ull:0 1:7 null:0 null:0 2:0 1:7 null:0 null:0 3:1 2:0 1:7 null:0 null:0 4:2 3:1 2:0 null:0 null:0 2:0 4:2 3:1 null:0 null:0 5:3 2:0 4:2 null:0 null:0 2:0 5:3 4:2 null:0 null:0 6:4 2:0 5:3 null:0 */ } }
那么如何设计一个LRU缓存,使得放入和移除都是 O(1) 的,我们需要把访问次序维护起来,但是不能通过内存中的真实排序来反应,有一种方案就是使用双向链表。
整体的设计思路是,可以使用 HashMap 存储 key,这样可以做到 save 和 get key的时间都是 O(1),而 HashMap 的 Value 指向双向链表实现的 LRU 的 Node 节点,如图所示。
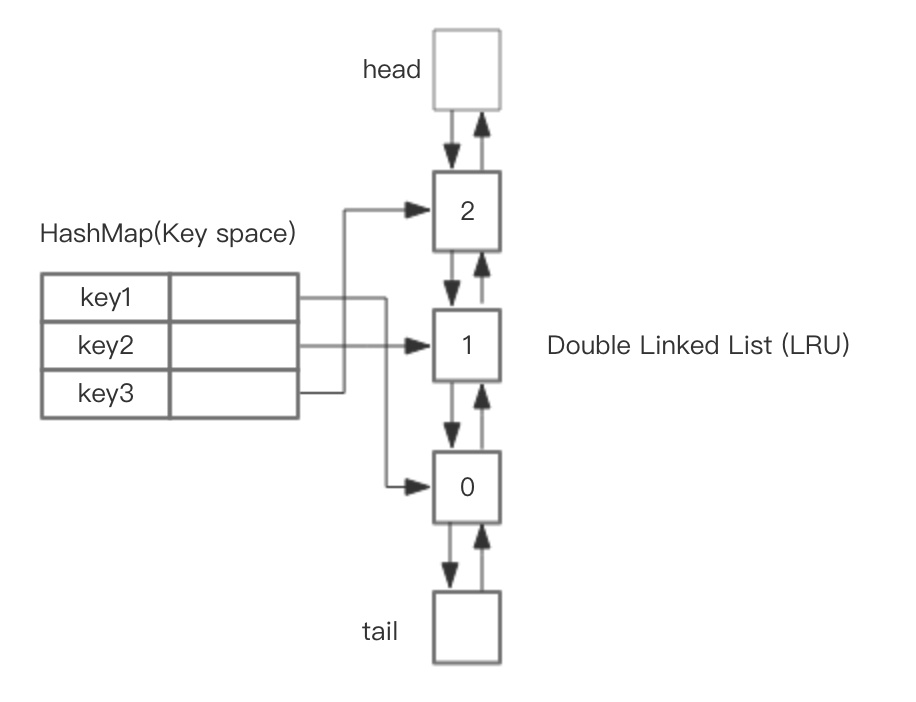
LRU 存储是基于双向链表实现的,下面的图演示了它的原理。其中 head 代表双向链表的表头,tail 代表尾部。首先预先设置 LRU 的容量,如果存储满了,可以通过 O(1) 的时间淘汰掉双向链表的尾部,每次新增和访问数据,都可以通过 O(1)的效率把新的节点增加到对头,或者把已经存在的节点移动到队头。
下面展示了,预设大小是 3 的,LRU存储的在存储和访问过程中的变化。为了简化图复杂度,图中没有展示 HashMap部分的变化,仅仅演示了上图 LRU 双向链表的变化。我们对这个LRU缓存的操作序列如下:
save("key1", 7)
save("key2", 0)
save("key3", 1)
save("key4", 2)
get("key2")
save("key5", 3)
get("key2")
save("key6", 4)
相应的 LRU 双向链表部分变化如下:
 s = save, g = get
s = save, g = get
总结一下核心操作的步骤:
- save(key, value),首先在 HashMap 找到 Key 对应的节点,如果节点存在,更新节点的值,并把这个节点移动队头。如果不存在,需要构造新的节点,并且尝试把节点塞到队头,如果LRU空间不足,则通过 tail 淘汰掉队尾的节点,同时在 HashMap 中移除 Key。
- get(key),通过 HashMap 找到 LRU 链表节点,因为根据LRU 原理,这个节点是最新访问的,所以要把节点插入到队头,然后返回缓存的值。
【https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34133067】