| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 杨振鹏 |
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结
1.1 栈
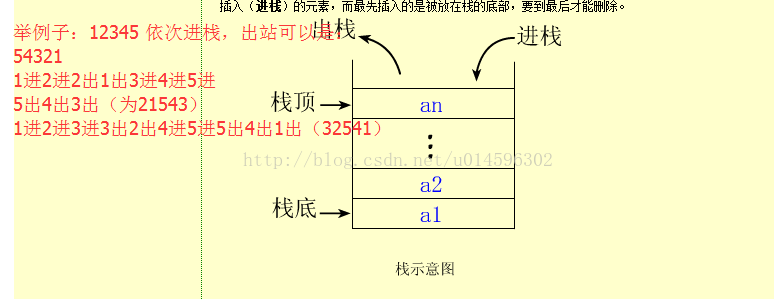
- 1.1.1顺序栈
结构体:
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top; //栈顶指针
}Stack,*SqStack;
初始化:
void CreatStack(SqStack s) {
s = new Stack;
s->top = -1;
}
进栈:
bool Push(SqStack s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == MaxSize-1) {
cout << "full";
return false;
}
s->data[++s->top] = e;
return true;
}
出栈:
bool Pop(SqStack s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == -1) {
cout << "empty";
return false;
}
e=s->data[s->top--];
return true;
}
- 1.1.2链栈
结构体:
typedef struct StackNode
{
ElemType data;
struct StackNode *next;
}Node,*Stack;
初始化:
bool InitStack(Stack &s)
{
s = NULL;
return true;
}
进栈:
void Push(Stack& s, ElemType e)
{
Stack p;
p = new Node;
p->data = e;
p->next = s->next;
s->next = p;
}
出栈:
bool Pop(Stack& s, ElemType& e)
{
Stack p;
if (StackEmpty(s))
return false;
p = s->next;
e = p->data;
s->next = p->next;
delete p;
return true;
}
1.2 栈的应用
1.中缀表达式转后缀表达式
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a;
stack<char>s;
int c=0,printk=0;
cin>>a;
map<char,int>p;
p['*']=p['/']=1;
p['(']=p[')']=2;
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++)
{
if((i<1||a[i-1]=='(')&&(a[i]=='+'||a[i]=='-')||a[i]=='.'||a[i]>='0'&&a[i]<='9')
{
if(printk)
{
cout<<" ";
}
printk++;
if(a[i]!='+')cout<<a[i];
while(a[i+1]=='.'||a[i+1]>='0'&&a[i+1]<='9')
{
i++;
cout<<a[i];
}
}
else
{
if(a[i]==')')
{
while(s.size()>0&&s.top()!='(')
{
cout<<" "<<s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.pop();
}
else if(s.size()==0||p[a[i]]>p[s.top()])
{
s.push(a[i]);
}
else
{
while(s.size()>0&&s.top()!='(')
{
cout<<" "<<s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.push(a[i]);
}
}
}
while(s.size())
{
cout<<" "<<s.top();
s.pop();
}
}
2.符号配对
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct linknode
{
ElemType data;//数据域
struct linknode* next;//指针域
}LiNode,*LinkStack;
int main()
{
string str;//存储字符串
stack<char> s;//初始化栈
int flag = 1;//判断是否配对
int i;
cin >> str;
for (i = 0;str[i] != '�';i++)//遍历字符串
{
if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{')//如果字符为左括号
s.push(str[i]);//进栈
else if (str[i] == ')' || str[i] == ']' || str[i] == '}')//如果字符为右括号
{
if (s.empty() == true)//空栈
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
else
{
if ((str[i]==')'&& s.top()=='(')||(str[i]==']'&&s.top()=='[')||(str[i]=='}'&&s.top()=='{'))//配对成功
{
s.pop();//出栈
}
else
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (s.empty() == true && flag == 1)//匹配
{
cout << "yes";
}
else//不匹配
{
if (s.empty() == true)//栈空
cout << "no";
else cout << s.top() << endl << "no";
}
//销毁栈
while (s.empty() != true)
{
s.pop();
}
}
1.3 队列

- 1.3.1顺序队列
结构体:
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
ElemType front, rear;
}Queue,*SqQueue;
初始化:
void CreatQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{
Q == new Queue;
Q->front = Q->rear = -1;
}
进队:
bool EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType e)
{
if (Q->rear + 1 == MaxSize)return false;
Q->data[++Q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
出队:
bool DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType& e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)return false;
e = Q->data[Q->front--];
return true;
- 1.3.2环形队列
结构体:
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front,rear;
} Queue;
typedef Queue *SqQueue;
初始化:
void InitQueue(SqQueue &q)
{ q=new Queue;
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
进队:
bool enQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType e)
{ if ((q->rear+1)%MaxSize==q->front) //队满上溢出
return false;
q->rear=(q->rear+1)%MaxSize;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
出队:
bool deQueue(SqQueue &q,ElemType &e)
{ if (q->front==q->rear) //队空下溢出
return false;
q->front=(q->front+1)%MaxSize;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
- 1.3.3链队列
结构体:
//定义节点结构
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}QueueNode;
//定义头节点
typedef struct {
QueueNode* front;
QueueNode* rear;
}LinkQueue;
初始化:
void InitQueue(LinkQueue* Q)
{
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
}
进队:
void EnLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType v)
{
QueueNode* p;
p = new QueueNode;//为新的节点分配空间
p->data = v;
p->next = NULL;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))
Q->front = Q->rear = p;
else
{
Q->rear->next = p; //将新的节点连接到队列
Q->rear = p; //指向队列尾
}
}
出队:
bool DeLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType &e)
{
QueueNode* s;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))return false; //判断队列是否为空
s = Q->front;
e = s->data;
if (Q->front == Q->rear) //判断队列是否只有一个节点
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
else
Q->front = s->next;
delete s;
return true;
}
- 1.3.4队列应用
舞伴问题
#include<iostream>
#define MAXQSIZE 100//队列可能达到的最大长度
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define OVERFLOW -2
using namespace std;
typedef struct {
char name[20]; //姓名
char sex; //性别,'F'表示女性,'M'表示男性
} Person;
//- - - - - 队列的顺序存储结构- - - - -
typedef struct {
Person data[MAXQSIZE];
int front; //头指针
int rear; //尾指针
} Queue;
typedef Queue *SqQueue;
SqQueue Mdancers, Fdancers; //分别存放男士和女士入队者队列
int InitQueue(SqQueue &Q);
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue &q);
int QueueLen(SqQueue Q);//队列长度
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person e);//加入队列
int QueueEmpty(SqQueue &Q);//队列是否为空
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person &e);//出队列
void DancePartner(Person dancer[], int num); //配对舞伴
int main(){
int i;
int n;
Person dancer[MAXQSIZE];
cin>>n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) cin>> dancer[i].name >> dancer[i].sex;
InitQueue(Mdancers); //男士队列初始化
InitQueue(Fdancers); //女士队列初始化
cout << "The dancing partners are:" << endl;
DancePartner(dancer, n);
if (!QueueEmpty(Fdancers)) {
cout << "F:"<<QueueLen(Fdancers) ;
} else if (!QueueEmpty(Mdancers)) {
cout << "M:"<<QueueLen(Mdancers) ;
}
DestroyQueue(Fdancers);
DestroyQueue(Mdancers);
return 0;
}
int InitQueue(SqQueue &Q) {//构造一个空队列Q
Q = new Queue; //为队列分配一个最大容量为MAXSIZE的数组空间
if (!Q->data)
exit( OVERFLOW); //存储分配失败
Q->front = Q->rear = 0; //头指针和尾指针置为零,队列为空
return OK;
}
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue &q)
{
delete q;
}
int QueueLen(SqQueue Q)//队列长度
{
return Q->rear-Q->front;
}
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person e)//加入队列
{
Q->data[++Q->rear]=e;
return 0;
}
int QueueEmpty(SqQueue &Q)//队列是否为空
{
if(Q->front==Q->rear)return 1;
return 0;
}
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person &e)//出队列
{
e=Q->data[++Q->front];
return 0;
}
void DancePartner(Person dancer[], int num) //配对舞伴
{
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(dancer[i].sex=='M'){
EnQueue(Mdancers,dancer[i]);
}else{
EnQueue(Fdancers,dancer[i]);
}
}
while(QueueEmpty(Mdancers)!=1&&QueueEmpty(Fdancers)!=1){
Person x,y;
DeQueue(Mdancers, x);
DeQueue(Fdancers, y);
cout<<y.name<<" "<<x.name<<endl;
}
}
2.PTA实验作业
2.1 符号配对
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
思路:建立一个链栈,遍历字符串,如果遇到左括号则入栈,遇到右括号就判断是否与栈顶的符号对应,是则栈顶元素出栈,继续遍历,遍历完成后,若栈空则yes,否则为no
伪代码:
定义字符数组str存储输入的字符串,栈s为存储左括号'(', '[', '{'的栈,flag表示此时的状态,flag = 1表示匹配,flag = 0表示不匹配;
for (i = 0;str[i] != '�';i++)//遍历字符串
if str[i]为左括号'(', '[', '{'
进栈;
else if str[i]为右括号')', ']', '}'
if 此时为空栈
不匹配,flag = 0;break;
else if str[i]与栈顶元素s.top()为相匹配的左右括号
匹配,栈顶元素出栈;
else
不匹配,flag = 0;break;
end for;
if 栈为空和flag == 1 匹配;
else 不匹配;
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
入栈出栈的操作
判断栈是否为空
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
思路:建立AB两个队列,A放单数号,B放双数号,然后执行出队,在两队都不为空的前提下,每次执行两次A出队,一次B出队,若其中一队为空后,直接将另外一队全部出队
伪代码:
定义两个队列A,B,分别输入数据,对2取余不为0的存入A队列,对2取余为0的存入B队列;
while A和B都不为空
{
输出一个A队列元素;
A元素出队;
输出一个A队列元素;
A元素出队;
输出一个B队列元素;
B元素出队;
}
while A不为空
输出A元素;A元素出队;
while B不为空
输出B元素,B元素出队;
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
进队出队的操作
判断对空
3.阅读代码
3.1 题目及解题代码

class CQueue {
LinkedList<Integer> stack1;
LinkedList<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new LinkedList<>();
stack2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.add(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
if (stack1.isEmpty()) return -1;
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.add(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.pop();
} else return stack2.pop();
}
}
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
输入: ["CQueue","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"] 这里是要执行的方法,从左到右执行
[[],[3],[],[]]对应上面的方法,是上面方法的参数。CQueue和deleteHead方法不需要指定数字,只有添加才需要指定数字
1.创建队列,返回值为null
2.将3压入栈,返回值为null
3.将栈底的元素删除,也就是消息队列中先进来的元素,所以是deleteHead,返回该元素的数值,所以为3
4.继续删除栈底的元素,但是没有元素了,所以返回-1
所以就有了下面的输出 输出:[null,null,3,-1]
示例 2: 输入: ["CQueue","deleteHead","appendTail","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"]
[[],[],[5],[2],[],[]]
1.创建队列,返回值为null
2.删除栈底的元素,但是没有元素,所以返回-1
3.把5压入栈,返回null
4.把2压入栈,返回null
5.删除栈底的一个元素,也就是消息队列中先进来的元素,所以是deleteHead,就是最先进来的5,返回值为5,
6.删除栈底的一个元素,就是后进来的2,返回值为2