mysql数据库优化课程---13、mysql基础操作(mysql如何复制表)
一、总结
一句话总结:
1.复制表结构 :create table student like user;
2.复制表内容:insert into student select * from user;
2、mysql中如何查看索引?
show index:show index from userG
3、mysql普通索引如何创建和删除?
create index:创建:create index i_age on user(age);
drop index:删除:drop index i_age on user;
1)创建
create index i_age on user(age);
2)删除
drop index i_age on user;
4、mysql唯一索引如何创建和删除?
create unique index:创建:create unique index u_username on user(username);
drop index:删除:drop index u_username on user;
1)创建
create unique index u_username on user(username);
2)删除
drop index u_username on user;
5、视图和表的关系?
视图是虚拟表,隶属于表:所以操作视图和操作表的语句是一样的
视图就是虚拟的,相当于等于一条命令
6、mysql中视图如何创建?
create view:create view userclass as select user.username,user.age,class.name from user,class where user.class_id=class.id;
7、视图的特点是什么?
数据变化:当表中数据发生变化时视图数据也会随着发生变化.
视图是虚拟表,隶属于表
所以操作视图和操作表的语句是一样的
视图就是虚拟的,相当于等于一条命令
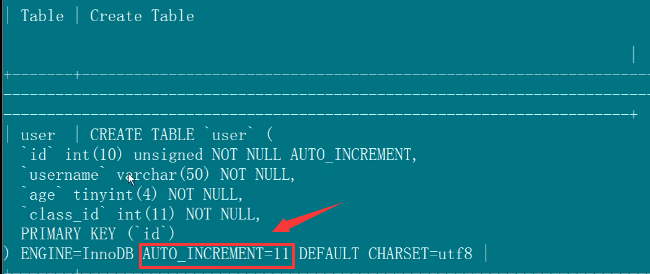
8、mysql中查看表中未来的自增数?
show create table:show create table user;
二、内容在总结中
MySQL数据库优化:
1.Mysql基础操作
2.常用的Sql技巧
3.Sql语句优化
4.Mysql服务器优化
mysql表复制:
1.复制表结构
create table student like user;
2.复制表内容
insert into student select * from user;
mysql索引:
1.查看索引
show index from userG
2.普通索引
1)创建
create index i_age on user(age);
2)删除
drop index i_age on user;
3.唯一索引
1)创建
create unique index u_username on user(username);
2)删除
drop index u_username on user;
mysql视图:
1.创建
create view userclass as select user.username,user.age,class.name from user,class where user.class_id=class.id;
2.删除
drop view userclass;
3.查看
show tables;
4.查看视频数据
select * from userclass;
5.视图的特性
当表中数据发生变化时视图数据也会随着发生变化.
mysql中查看表中未来的自增数:
show create table user;
mysql字符串函数:
1.字符串连接
concat();
例子: select concat('php','linux');
2.转小写
lcase();
例子: select lcase('PHP IS VERY MUCH!');
3.转大写:
ucase();
例子: select id,ucase(username),age from user;
4.长度
length();
例子: select length('linux');
5.取除左边的空格
ltrim();
例子: select length(ltrim(' linux'));
6.取除右边的空格
rtrim();
例子: select length(rtrim('linux '));
7.重复
repeat();
例子: select concat(repeat('-',20),'linux');
8.替换
replace();
例子: select replace('linux and java','linux','php');
9.截取
substring();
例子: select substring('/usr/local/src',6,5);
10.空格
space();
例子: select concat('linux',space(20),'php');
mysql数学函数:
1.bin();
十进制转2进制
例子: select bin(10);
2.ceiling();
取上一个整数
例子: select ceiling(10.5);
3.floor();
取下一个整数
例子: select floor(10.5);
4.max();
取最大数
例子: select max(id) from user;
5.min();
取最小数
例子: select min(id) from user;
6.sqrt();
开平方
例子: select sqrt(100);
7.rand();
求随机数
例子: select * from user order by rand();
mysql日期函数:
1.curdate();
当前日期
例子: select curdate();
2.curtime();
当前时间
例子: select curtime();
3.now();
当前日期和时间
例子: select now();
4.unix_timestamp();
当前时间戳
例子: select unix_timestamp();
5.from_unixtime();
时间戳转日期
例子: select from_unixtime(1492176896);
6.week(date);
一年中的第几周
例子: select week('2017-1-8');
7.year(date);
日期中的年部分
例子: select year('2017-4-14');
8.datediff();
日期差值
例子: select datediff('2017-4-14','2017-4-10');
重排auto_increment方法:
1.delete
1)delete from user;
2)alter table user auto_increment=1;
2.truncate
truncate user;
mysql中命令的帮助:
1.简单
? create
2.更多
? fun%
巧用RAND()提取随机行:
select * from user order by rand limit 3;
正则表达式的使用:
1.以php结尾的数据
select * from user where username regexp 'php$';
2.以php结尾或以linux结尾的数据
select * from user where username regexp 'php$' or username regexp 'linux$';
3.查找包含php或linux或user的数据
select * from user where username regexp 'php|linux|user';
8、mysql中查看表中未来的自增数?
show create table
show create table user;