kobject,kset,ktype三个很重要的概念贯穿Linux内核驱动架构,特转载一篇博文:
(转载自http://blog.csdn.net/gdt_a20/article/details/6424597)
一、sysfs文件系统下的每个目录对应于一个kobj,kset是kobj的封装,内嵌了一个kobj,其代表kset自身,ktype代表属性操作集,但由于通用性,因此把ktype单独剥离出来,kobj,kset,ktype成为了各个驱动模型最底层的关联元素,并由此形成了sys下的各种拓扑结构。
二、关于kobject
首先看一下kobject的原型
struct kobject {
const char *name; //名字
struct list_head entry; //连接到kset建立层次结构
struct kobject *parent; //指向父节点,面向对象的层次架构
struct kset *kset;
struct kobj_type *ktype; //属性文件
struct sysfs_dirent *sd;
struct kref kref; //引用计数
unsigned int state_initialized:1; //初始化状态...
unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;
};
分析一下kobject的初始化过程
初始化函数为
---int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype, //参数为kobject和属性结构体
struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
int retval;
kobject_init(kobj, ktype);
va_start(args, fmt);
retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
return retval;
}
---void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype)
{
char *err_str;
if (!kobj) { //kobj为NULL错误退出
err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!";
goto error;
}
if (!ktype) { //ktype为NULL错误退出
err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!/n";
goto error;
}
if (kobj->state_initialized) { //如果初始化状态为1报错
/* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized "
"object, something is seriously wrong./n", kobj);
dump_stack();
}
kobject_init_internal(kobj); //初始化kobj
kobj->ktype = ktype; //关联obj和ktype
return;
error:
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s/n", kobj, err_str);
dump_stack();
}
-------static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (!kobj)
return;
kref_init(&kobj->kref); //计数变成1
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry); //都指向自己,prev和next
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0;
kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_initialized = 1;
}
-------static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent,
const char *fmt, va_list vargs)
{
int retval;
retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs); //设置名字,名字中不能有“/”
if (retval) {
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!/n");
return retval;
}
kobj->parent = parent; //设置parent,其父节点
return kobject_add_internal(kobj);
}
----static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
int error = 0;
struct kobject *parent;
if (!kobj)
return -ENOENT;
if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) { //名字不能为空
WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty "
"name!/n", kobj);
return -EINVAL;
}
parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent); //如果parent为真,则增加kobj->kref计数,也就是父节点的引用计数
/* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */
if (kobj->kset) {
if (!parent)
parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj); //如果kobj-parent父节点为NULL那么就用kobj->kset->kobj
// 作其父节点,并增加其引用计数
kobj_kset_join(kobj); //把kobj的entry成员添加到kobj->kset>list的尾部,现在的层次就是
kobj->parent = parent; //kobj->kset->list指向kobj->parent
} // ->parent 指向kset->kobj
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'/n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__,
parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "<NULL>",
kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "<NULL>");
error = create_dir(kobj); //利用kobj创建目录和属性文件,其中会判断,如果parent为NULL那么就在sysfs_root下创建
if (error) {
kobj_kset_leave(kobj);
kobject_put(parent);
kobj->parent = NULL;
/* be noisy on error issues */
if (error == -EEXIST)
printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with "
"-EEXIST, don't try to register things with "
"the same name in the same directory./n",
__func__, kobject_name(kobj));
else
printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)/n",
__func__, kobject_name(kobj), error);
dump_stack();
} else
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1;
return error;
}
---static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj)
{
int error = 0;
if (kobject_name(kobj)) {
error = sysfs_create_dir(kobj); //创建目录
if (!error) {
error = populate_dir(kobj); //创建属性文件
if (error)
sysfs_remove_dir(kobj);
}
}
return error;
}
三、关于 kset
首先看一下kset的原型
struct kset {
struct list_head list; //连接着他下面的kobj成员,与kobj-entry关联
spinlock_t list_lock;
struct kobject kobj; //代表kset自己
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
};
再来看一下kset的初始化操作,kset表现为更高级一点的kobj,其初始化操作仍然是围绕其内部的kobj展开的。
struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name,
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
struct kobject *parent_kobj)
{
struct kset *kset;
int error;
kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj); //创建kset,关联操作函数和其父节点
if (!kset)
return NULL;
error = kset_register(kset);
if (error) {
kfree(kset);
return NULL;
}
return kset;
}
---static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name,
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
struct kobject *parent_kobj)
{
struct kset *kset;
int retval;
kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL); //申请结构体内存
if (!kset)
return NULL;
retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, name); //设置名字
if (retval) {
kfree(kset);
return NULL;
}
kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops; //关联操作函数
kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj; //关联父节点
/*
* The kobject of this kset will have a type of kset_ktype and belong to
* no kset itself. That way we can properly free it when it is
* finished being used.
*/
kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype; //关联属性文件
kset->kobj.kset = NULL;
return kset;
}
----int kset_register(struct kset *k)
{
int err;
if (!k)
return -EINVAL;
kset_init(k);
err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj); //调用kobj操作函数
if (err)
return err;
kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
return 0;
}
----void kset_init(struct kset *k)
{
kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj); //调用kobj操作函数
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);
spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);
}
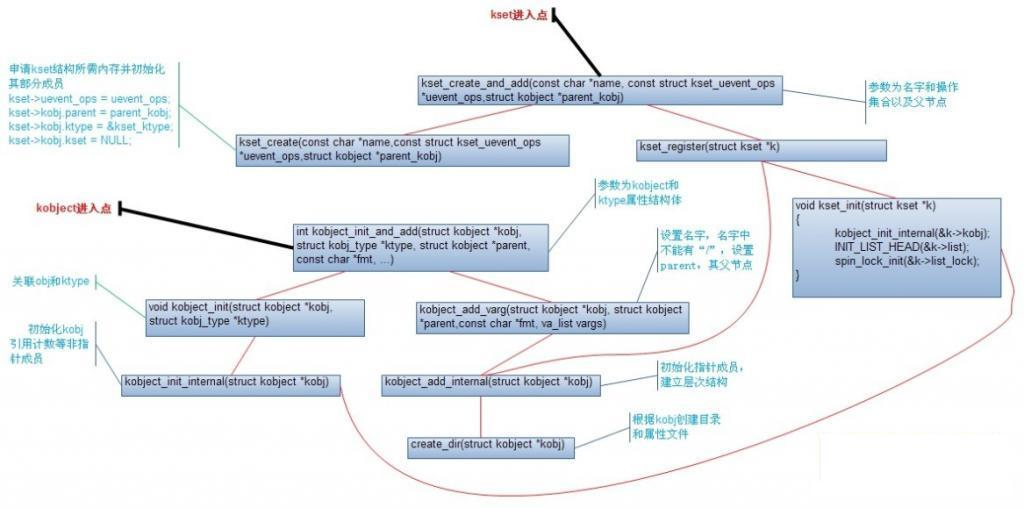
四、上面给出了kobj,kset的初始化过程,以及相互产生关联的关键点,下面给出整体的一个流程图: