Valentine's Day
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 0 Accepted Submission(s): 0
Special Judge
Problem Description
Oipotato loves his girlfriend very much. Since Valentine's Day is coming, he decides to buy some presents for her.
There are n presents in the shop, and Oipotato can choose to buy some of them. We know that his girlfriend will possibly feel extremely happy if she receives a present. Therefore, if Oipotato gives k presents to his girlfriend, she has k chances to feel extremely happy. However, Oipotato doesn't want his girlfriend to feel extremely happy too many times for the gifts.
Formally, for each present i, it has a possibility of Pi to make Oipotato's girlfriend feel extremely happy. Please help Oipotato decide what to buy and maximize the possibility that his girlfriend feels extremely happy for exactly one time.
There are n presents in the shop, and Oipotato can choose to buy some of them. We know that his girlfriend will possibly feel extremely happy if she receives a present. Therefore, if Oipotato gives k presents to his girlfriend, she has k chances to feel extremely happy. However, Oipotato doesn't want his girlfriend to feel extremely happy too many times for the gifts.
Formally, for each present i, it has a possibility of Pi to make Oipotato's girlfriend feel extremely happy. Please help Oipotato decide what to buy and maximize the possibility that his girlfriend feels extremely happy for exactly one time.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer T (1≤T≤100), indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤10 000), indicating the number of possible presents.
The second line contains n decimals Pi (0≤Pi≤1) with exactly six digits after the decimal point, indicating the possibility that Oipotato's girlfriend feels extremely happy when receiving present i.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n in all test cases does not exceed 450000.
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤10 000), indicating the number of possible presents.
The second line contains n decimals Pi (0≤Pi≤1) with exactly six digits after the decimal point, indicating the possibility that Oipotato's girlfriend feels extremely happy when receiving present i.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n in all test cases does not exceed 450000.
Output
For each test case output one line, indicating the answer. Your answer will be considered correct if and only if the absolute error of your answer is less than 10−6.
Sample Input
2
3
0.100000 0.200000 0.900000
3
0.100000 0.300000 0.800000
Sample Output
0.900000000000
0.800000000000
题意:
有n种商品,每种商品有pi的概率让女朋友非常开心,现在问买那些商品才能让女朋友恰好非常开心一次的概率最大
思路:
记p为恰好让女朋友非常开心一次的概率,p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m且i!=j)(1-pj),算了一些样例后发现如果pi>0.5,那么无论再买那些商品都会让总概率变小,
如果pi==0.5,则无论再买那些商品都会让总概率=0.5,所以如果存在pi>=0.5,则我们就取一个最大的大于等于0.5概率的商品,否则商品概率都小于0.5时,
队友通过打表发现将商品排序后,从最大的那个开始连续取,总概率会先递增再递减,且只有一个极大值,现在的问题是最坏的情况是要遍历所有商品,复杂度为O(n)
每次都要重新计算总概率,计算总概率的复杂度为O(n*n),所以这样的总复杂度为O(n*n*n),而题目中n最大为1e4,显然n的立方的复杂度是不能接受的,
遍历的O(n)没什么办法优化,但我们可以把计算总概率的O(n*n)的复杂度降为O(n),这样O(n*n)的复杂度是能支持1e4的数据的,所以现在的问题就是怎么优化计算
原始公式为p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m且i!=j)(1-pj),可以将其转换为,p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m)(1-pj)/(1-pi),因为π(j=1->m)(1-pj)与i无关,所以可以把他从累加中提出来,
转换为p=[Σ(i=1->m)pi/(1-pi)]*[π(j=1->m)(1-pj)],于是可以O(n)地计算Σ(i=1->m)pi/(1-pi)和π(j=1->m)(1-pj),最后将两者相乘即为总概率
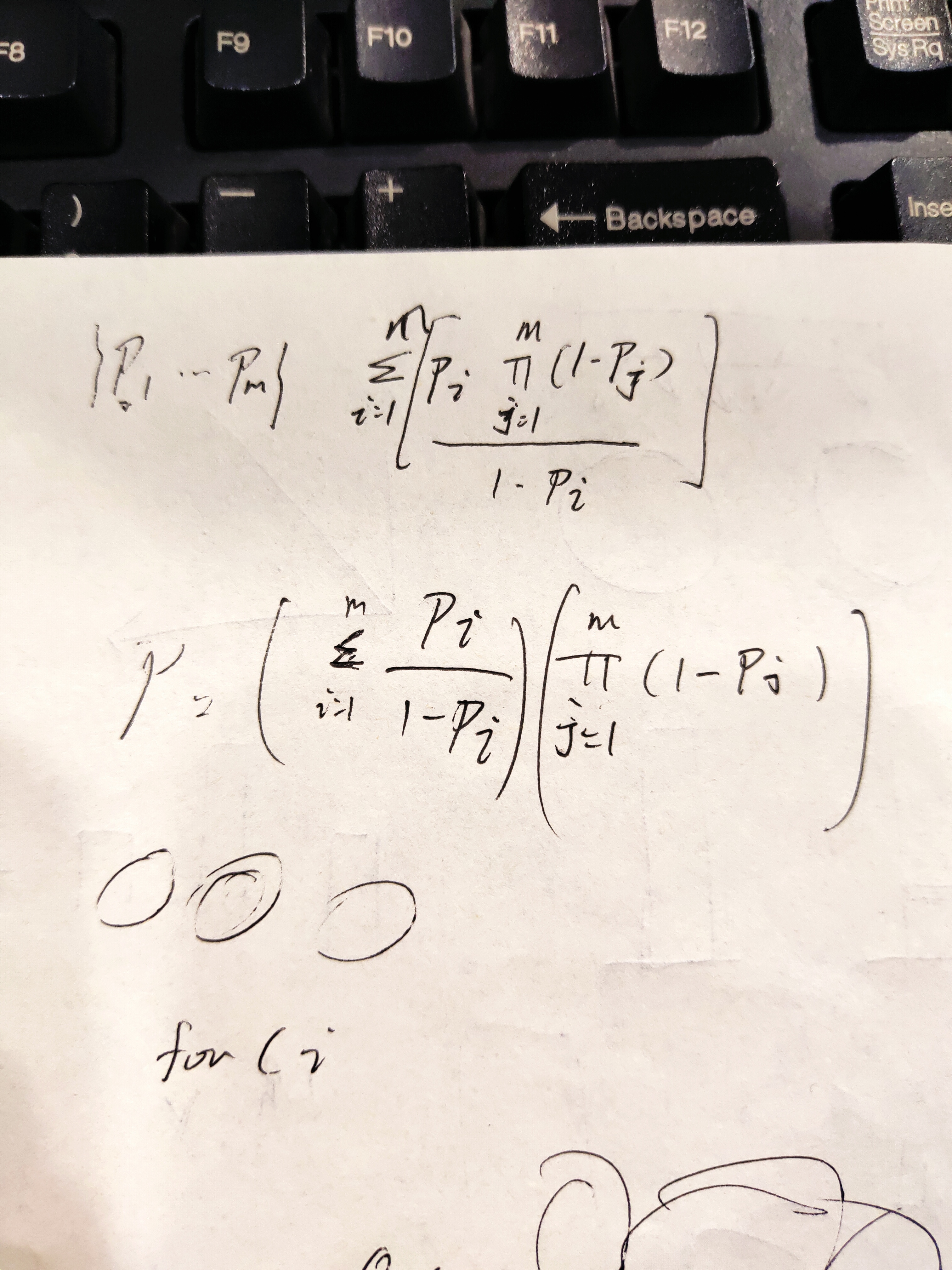
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int amn=1e4+5; 4 struct node{ 5 double p,q; 6 }nm[amn]; 7 double p[amn],q[amn],ans,cnt,maxn,aa,s,t; 8 bool cmp(node a,node b){ 9 if(a.p==b.p)return a.q<b.q; 10 return a.p>b.p; 11 } 12 int main(){ 13 int n,T,tp; 14 ios::sync_with_stdio(0); 15 scanf("%d",&T); 16 while(T--){ 17 scanf("%d",&n); 18 tp=maxn=0; 19 aa=1; 20 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 21 scanf("%lf",&nm[i].p); 22 maxn=max(maxn,nm[i].p); 23 nm[i].q=1-nm[i].p; 24 } 25 if(maxn>=0.5){ 26 ans=maxn; 27 } 28 else{ 29 tp=maxn=0; 30 sort(nm+1,nm+1+n,cmp); 31 ans=nm[1].p; 32 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ 33 s=0,t=1; 34 for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)s+=nm[j].p/nm[j].q; 35 for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)t*=nm[j].q; 36 if(s*t>ans) 37 ans=s*t; 38 else break; 39 } 40 } 41 printf("%.12lf ",ans); 42 } 43 } 44 /** 45 有n种商品,每种商品有pi的概率让女朋友非常开心,现在问买那些商品才能让女朋友恰好非常开心一次的概率最大 46 记p为恰好让女朋友非常开心一次的概率,p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m且i!=j)(1-pj),算了一些样例后发现如果pi>0.5,那么无论再买那些商品都会让总概率变小, 47 如果pi==0.5,则无论再买那些商品都会让总概率=0.5,所以如果存在pi>=0.5,则我们就取一个最大的大于等于0.5概率的商品,否则商品概率都小于0.5时, 48 队友通过打表发现将商品排序后,从最大的那个开始连续取,总概率会先递增再递减,且只有一个极大值,现在的问题是最坏的情况是要遍历所有商品,复杂度为O(n) 49 每次都要重新计算总概率,计算总概率的复杂度为O(n*n),所以这样的总复杂度为O(n*n*n),而题目中n最大为1e4,显然n的立方的复杂度是不能接受的, 50 遍历的O(n)没什么办法优化,但我们可以把计算总概率的O(n*n)的复杂度降为O(n),这样O(n*n)的复杂度是能支持1e4的数据的,所以现在的问题就是怎么优化计算 51 原始公式为p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m且i!=j)(1-pj),可以将其转换为,p=Σ(i=1->m)pi*π(j=1->m)(1-pj)/(1-pi),因为π(j=1->m)(1-pj)与i无关,所以可以把他从累加中提出来, 52 转换为p=[Σ(i=1->m)pi/(1-pi)]*[π(j=1->m)(1-pj)],于是可以O(n)地计算Σ(i=1->m)pi/(1-pi)和π(j=1->m)(1-pj),最后将两者相乘即为总概率 53 **/