0.目录
1.归并排序
2.快速排序
3.排序的工程应用示例
4.小结
1.归并排序
归并排序的基本思想:

归并的套路:
- 将 3 个有序序列归并为一个新的有序序列,称为 3 路归并
- 将 N 个有序序列归并为一个新的有序序列,称为 N 路归并
- 将多个有序序列归并为一个新的有序序列,称为多路归并
2 路归并示例:

归并排序的代码实现:
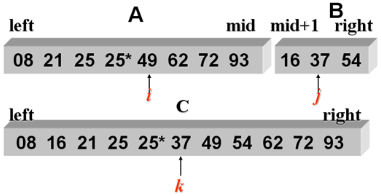
实现归并排序(在Sort.h中):
private:
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int mid, int end, bool min2max = true) // 真正的归并操作
{
int i = begin;
int j = mid + 1;
int k = begin;
while( (i <= mid) && (j <= end) )
{
if( min2max ? (src[i] < src[j]) : (src[i] > src[j]) )
{
helper[k++] = src[i++];
}
else
{
helper[k++] = src[j++];
}
}
while( i <= mid ) helper[k++] = src[i++];
while( j <= end ) helper[k++] = src[j++];
for(i=begin; i<=end; i++)
{
src[i] = helper[i];
}
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int end, bool min2max = true) // 归并的递归调用
{
if( begin < end )
{
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, mid+1, end, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, end, min2max); // 合并两个已经排好序的序列
}
}
public:
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true) // 2路归并排序
{
T* helper = new T[len];
if( helper != NULL )
{
Merge(array, helper, 0, len-1, min2max);
}
delete[] helper;
}
main.cpp测试:
#include <iostream>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
int array[] = {9, 7, 3, 1, 6, 2, 8, 5, 4};
Sort::Merge(array, 9);
for(int i=0; i<9; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
cout << "~~~" << endl;
Sort::Merge(array, 9, false);
for(int i=0; i<9; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
~~~
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
2.快速排序
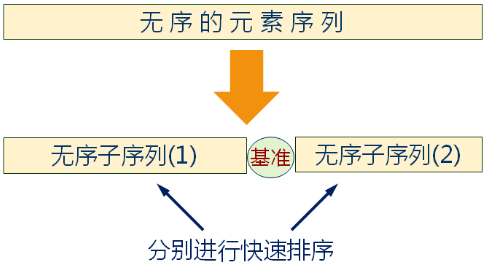
快速排序的基本思想:
- 任取序列中的某个数据元素作为基准将整个序列划分为左右两个子序列
- 左侧子序列中所有元素都小于或等于基准元素
- 右侧子序列中所有元素都大于基准元素
- 基准元素排在这两个子序列中间
- 分别对这两个子序列重复进行划分,直到所有的数据元素都排在相应位置上为止
快速排序示例:
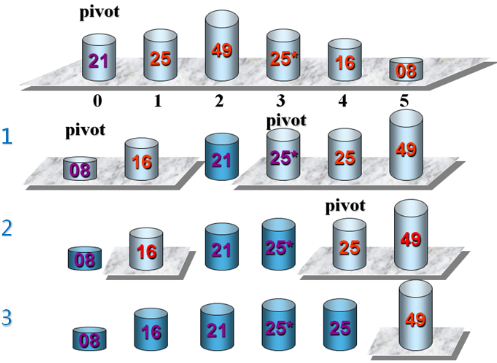
实现快速排序(在Sort.h中):
private:
template <typename T>
static int Partition(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max) // 返回划分后基准的下标
{
T pv = array[begin];
while( begin < end )
{
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[end] > pv) : (array[end] < pv)) )
{
end--;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[begin] <= pv) : (array[begin] >= pv)) )
{
begin++;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
}
array[begin] = pv;
return begin;
}
template <typename T>
static void Quick(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max) // 快排的递归调用
{
if( begin < end )
{
int pivot = Partition(array, begin, end, min2max);
Quick(array, begin, pivot-1, min2max);
Quick(array, pivot+1, end, min2max);
}
}
public:
template <typename T>
static void Quick(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
Quick(array, 0, len-1, min2max);
}
main.cpp测试:
#include <iostream>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
int array[] = {9, 7, 3, 1, 6, 2, 8, 5, 4};
Sort::Quick(array, 9);
for(int i=0; i<9; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
cout << "~~~" << endl;
Sort::Quick(array, 9, false);
for(int i=0; i<9; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
~~~
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
3.排序的工程应用示例
排序类 ( Sort ) 与数组类 ( Array ) 的关系:
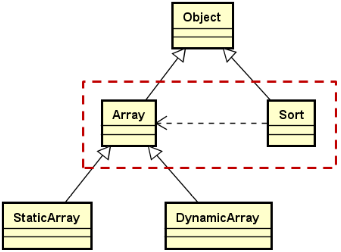
新增的成员函数:
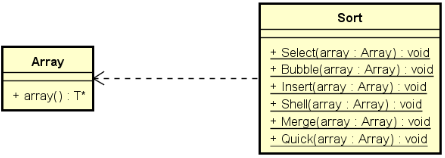
在Array.h中的新增成员函数:
public:
T* array() const
{
return m_array;
}
在Sort.h中的新增成员函数:
#include "Array.h"
public:
template <typename T>
static void Select(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Select(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Insert(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Insert(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Bubble(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Bubble(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Shell(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Shell(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Merge(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Quick(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Quick(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
main.cpp测试:
#include <iostream>
#include "StaticArray.h"
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
StaticArray<double, 5> sa;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
sa[i] = i;
}
Sort::Quick(sa, false);
for(int i=0; i<sa.length(); i++)
{
cout << sa[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
4
3
2
1
0
问题:
- 当待排数据元素为体积庞大的对象时,如何提高排序的效率?
问题示例:
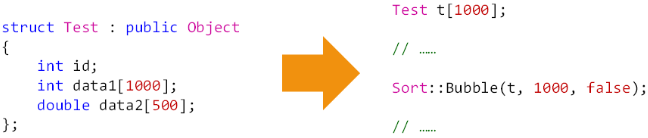
问题分析:
- 排序过程中不可避免的需要进行交换操作
- 交换操作的本质为数据元素间的相互复制
- 当数据元素体积较大时,交换操作耗时巨大
解决方案:代理模式
- 为待排数据元素设置代理对象
- 对代理对象所组成的序列进行排序
- 需要访问有序数据元素时,通过访问代理序列完成
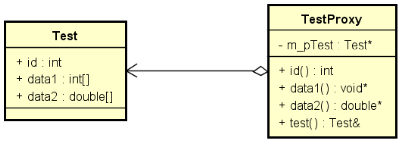
真的能够提高排序效率吗?
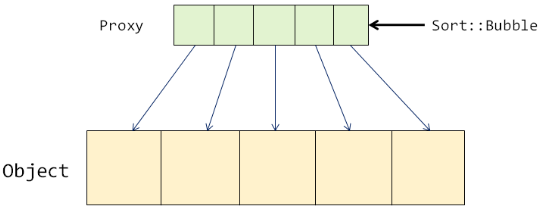
使用代理模式:
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
struct Test : public Object
{
int id;
int data1[1000];
double data2[500];
bool operator < (const Test& obj)
{
return id < obj.id;
}
bool operator >= (const Test& obj)
{
return id >= obj.id;
}
bool operator > (const Test& obj)
{
return id > obj.id;
}
bool operator <= (const Test& obj)
{
return id <= obj.id;
}
};
class TestProxy : public Object
{
protected:
Test* m_pTest;
public:
int id()
{
return m_pTest->id;
}
int* data1()
{
return m_pTest->data1;
}
double* data2()
{
return m_pTest->data2;
}
Test& test() const
{
return *m_pTest;
}
bool operator < (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() < obj.test();
}
bool operator >= (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() >= obj.test();
}
bool operator > (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() > obj.test();
}
bool operator <= (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() <= obj.test();
}
Test& operator = (Test& test)
{
m_pTest = &test;
return test;
}
};
Test t[1000];
TestProxy pt[1000];
int main()
{
clock_t begin = 0;
clock_t end = 0;
for(int i=0; i<1000; i++)
{
t[i].id = i;
pt[i] = t[i]; // 进行代理
}
begin = clock();
Sort::Bubble(t, 1000, false);
end = clock();
cout << "不使用代理Time: " << (end - begin) << endl;
begin = clock();
Sort::Bubble(pt, 1000);
end = clock();
cout << "使用代理Time: " << (end - begin) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
不使用代理Time: 3849
使用代理Time: 21
4.小结
- 归并排序需要额外的辅助空间才能完成,空间复杂度为 O(n)
- 归并排序的时间复杂度为 O(n*logn),是一种稳定的排序法
- 快速排序通过递归的方式对排序问题进行划分
- 快速排序的时间复杂度为 O(n*logn),是一种不稳定的排序法
- StLib中的排序类和数组类之间存在关联关系
- 排序类能够对数组类对象进行排序
- 当排序体积庞大的对象时,使用代理模式间接完成
- 代理模式的使用有效避开大对象交换时的耗时操作
- 代理模式解决方案是空间换时间思想的体现
最终实现的Sort.h:
#ifndef SORT_H
#define SORT_H
#include "Object.h"
#include "Array.h"
namespace StLib
{
class Sort : public Object
{
private:
Sort();
Sort(const Sort&);
Sort& operator = (const Sort&);
template <typename T>
static void Swap(T& a, T&b)
{
T c(a);
a = b;
b = c;
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int mid, int end, bool min2max) // 真正的归并操作
{
int i = begin;
int j = mid + 1;
int k = begin;
while( (i <= mid) && (j <= end) )
{
if( min2max ? (src[i] < src[j]) : (src[i] > src[j]) )
{
helper[k++] = src[i++];
}
else
{
helper[k++] = src[j++];
}
}
while( i <= mid ) helper[k++] = src[i++];
while( j <= end ) helper[k++] = src[j++];
for(i=begin; i<=end; i++)
{
src[i] = helper[i];
}
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int end, bool min2max) // 归并的递归调用
{
if( begin < end )
{
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, mid+1, end, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, end, min2max); // 合并两个已经排好序的序列
}
}
template <typename T>
static int Partition(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max) // 返回划分后基准的下标
{
T pv = array[begin];
while( begin < end )
{
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[end] > pv) : (array[end] < pv)) )
{
end--;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[begin] <= pv) : (array[begin] >= pv)) )
{
begin++;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
}
array[begin] = pv;
return begin;
}
template <typename T>
static void Quick(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max) // 快排的递归调用
{
if( begin < end )
{
int pivot = Partition(array, begin, end, min2max);
Quick(array, begin, pivot-1, min2max);
Quick(array, pivot+1, end, min2max);
}
}
public:
template <typename T>
static void Select(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
int min = i;
for(int j=i+1; j<len; j++)
{
if( min2max ? (array[min] > array[j]) : (array[min] < array[j]) )
{
min = j;
}
}
if( min != i )
{
Swap(array[i], array[min]);
}
}
}
template <typename T>
static void Insert(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true) // 一边比较一边移动
{
for(int i=1; i<len; i++)
{
int k = i;
T e = array[i];
for(int j=i-1; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j]>e) : (array[j]<e)); j--)
{
array[j+1] = array[j];
k = j;
}
if( k != i )
{
array[k] = e;
}
}
}
template <typename T>
static void Bubble(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
bool exchange = true;
for(int i=0; (i<len) && exchange; i++)
{
exchange = false;
for(int j=len-1; j>i; j--)
{
if( min2max ? (array[j] < array[j-1]) : (array[j] > array[j-1]) )
{
Swap(array[j], array[j-1]);
exchange = true;
}
}
}
}
template <typename T>
static void Shell(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
int d = len;
do
{
d = d / 3 + 1; // d--
// 采用插入排序
for(int i=d; i<len; i+=d)
{
int k = i;
T e = array[i];
for(int j=i-d; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j]>e) : (array[j]<e)); j-=d)
{
array[j+d] = array[j];
k = j;
}
if( k != i )
{
array[k] = e;
}
}
} while( d > 1 );
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true) // 2路归并排序
{
T* helper = new T[len];
if( helper != NULL )
{
Merge(array, helper, 0, len-1, min2max);
}
delete[] helper;
}
template <typename T>
static void Quick(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
Quick(array, 0, len-1, min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Select(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Select(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Insert(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Insert(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Bubble(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Bubble(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Shell(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Shell(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Merge(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Merge(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template <typename T>
static void Quick(Array<T>& array, bool min2max = true)
{
Quick(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
};
}
#endif // SORT_H