0.目录
1.双向循环链表的实现
2.小结
1.双向循环链表的实现
本节目标:
- 使用 Linux 内核链表实现 StLib 中的双向循环链表
- template <typename T> class DualCircleList;
StLib 中双向循环链表的设计思路:
- 数据结点之间在逻辑上构成双向循环链表,头结点仅用于结点的定位。
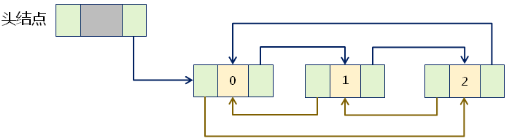
实现思路:
- 通过模板定义 DualCircleList 类,继承自 DualLinkList 类
- 在 DualCircleList 内部使用Linux内核链表进行实现
- 使用 struct list_head 定义 DualCircleList 的头结点
- 特殊处理:循环遍历时忽略头结点
实现要点:
- 通过 list_head 进行目标结点定位( position(i) )
- 通过 list_entry 将 list_head 指针转换为目标结点指针
- 通过 list_for_each 实现 int find(const T& e) 函数
- 遍历函数中的 next() 和 pre() 需要考虑跳过头结点
双向循环链表的实现(DualLinkList.h):
使用到的LinuxList.h头文件放在文字尾部:LinuxList.h
DualLinkList.h
#ifndef DUALCIRCLELIST_H
#define DUALCIRCLELIST_H
#include "LinuxList.h"
#include "DualLinkList.h"
namespace StLib
{
template <typename T>
class DualCircleList : public DualLinkList<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
list_head head;
T value;
};
list_head m_header;
list_head* m_current;
list_head* position(int i) const
{
list_head* ret = const_cast<list_head*>(&m_header);
for(int p=0; p<i; p++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
int mod(int i) const
{
return (this->m_length == 0) ? 0 : (i % this->m_length);
}
public:
DualCircleList()
{
this->m_length = 0;
this->m_step = 1;
m_current = NULL;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&m_header);
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(this->m_length, e);
}
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = true;
Node* node = new Node();
i = i % (this->m_length + 1);
if( node != NULL )
{
node->value = e;
list_add_tail(&node->head, position(i)->next);
this->m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert new element ...");
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret = true;
i = mod(i);
ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < this->m_length));
if( ret )
{
list_head* toDel = position(i)->next;
if( m_current == toDel )
{
m_current = toDel->next;
}
list_del(toDel);
this->m_length--;
delete list_entry(toDel, Node, head);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = true;
i = mod(i);
ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < this->m_length));
if( ret )
{
list_entry(position(i)->next, Node, head)->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
T get(int i) const
{
T ret;
if( get(i, ret) )
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = true;
i = mod(i);
ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < this->m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = list_entry(position(i)->next, Node, head)->value;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
int i = 0;
list_head* slider = NULL;
list_for_each(slider, &m_header)
{
if( list_entry(slider, Node, head)->value == e )
{
ret = i;
break;
}
i++;
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return this->m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while( this->m_length > 0 )
{
remove(0);
}
}
bool move(int i, int step = 1)
{
bool ret = (step > 0);
i = mod(i);
ret = ret && ((0 <= i) && (i < this->m_length));
if( ret )
{
m_current = position(i)->next;
this->m_step = step;
}
return ret;
}
bool end()
{
return (m_current == NULL) || (this->m_length == 0);
}
virtual T current()
{
if( !end() )
{
return list_entry(m_current, Node, head)->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ...");
}
}
bool next()
{
int i = 0;
while( (i < this->m_step) && !end() )
{
if( m_current != &m_header )
{
m_current = m_current->next;
i++;
}
else
{
m_current = m_current->next;
}
}
if( m_current == &m_header )
{
m_current = m_current->next;
}
return (i == this->m_step);
}
bool pre()
{
int i = 0;
while( (i < this->m_step) && !end() )
{
if( m_current != &m_header )
{
m_current = m_current->prev;
i++;
}
else
{
m_current = m_current->prev;
}
}
if( m_current == &m_header )
{
m_current = m_current->prev;
}
return (i == this->m_step);
}
~DualCircleList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // DUALCIRCLELIST_H
main.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "DualCircleList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
DualCircleList<int> d1;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
d1.insert(0, i);
d1.insert(0, 5);
}
cout << "begin" << endl;
d1.move(d1.length()-1);
while( d1.find(5) != -1 )
{
if( d1.current() == 5 )
{
cout << d1.current() << endl;
d1.remove(d1.find(d1.current()));
}
else
{
d1.pre();
}
}
cout << "end" << endl;
// for(int i=0; i<d1.length(); i++)
// {
// cout << d1.get(i) << endl;
// }
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
cout << d1.get(i) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
begin
5
5
5
5
5
end
4
3
2
1
0
4
3
2
1
0
思考题——下面代码中的 pn1 和 pn2 是否相等?为什么?

2.小结
- Linux内核链表是带头结点的双向循环链表
- DualCircleList 使用Linux内核链表进行内部实现
- DualCircleList 在循环遍历时需要跳过头结点
- 将 list_head 指针转换为目标结点指针时,使用 list_entry 宏
LinuxList.h:
需要将LinuxList.h中的new改成node。
#ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H
#define _LINUX_LIST_H
// #include <linux/types.h>
// #include <linux/stddef.h>
// #include <linux/poison.h>
// #include <linux/prefetch.h>
#ifndef offsetof
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#endif
#ifndef container_of
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ((type *)((char *)ptr - offsetof(type,member)))
#endif
#define prefetch(x) ((void)x)
#define LIST_POISON1 (NULL)
#define LIST_POISON2 (NULL)
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
struct hlist_head {
struct hlist_node *first;
};
struct hlist_node {
struct hlist_node *next, **pprev;
};
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name)
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static void __list_add(struct list_head *node,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = node;
node->next = next;
node->prev = prev;
prev->next = node;
}
#else
extern void __list_add(struct list_head *node,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next);
#endif
/**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static void list_add(struct list_head *node, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(node, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static void list_add_tail(struct list_head *node, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(node, head->prev, head);
}
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
static void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
static void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
#else
extern void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry);
extern void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
#endif
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *node)
{
node->next = old->next;
node->next->prev = node;
node->prev = old->prev;
node->prev->next = node;
}
static void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *node)
{
list_replace(old, node);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
/**
* list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
*/
static void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
/**
* list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
/**
* list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head
* @list: the entry to test
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
/**
* list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/**
* list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified
* @head: the list to test
*
* Description:
* tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be
* in the process of modifying either member (next or prev)
*
* NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization
* can only be safe if the only activity that can happen
* to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used
* if another CPU could re-list_add() it.
*/
static int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *next = head->next;
return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}
/**
* list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first;
if (!list_empty(head)) {
first = head->next;
list_move_tail(first, head);
}
}
/**
* list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry.
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
static void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry;
entry->next = list;
head->next = new_first;
new_first->prev = head;
}
/**
* list_cut_position - cut a list into two
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
* and if so we won't cut the list
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and
* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should
* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list
* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about
* losing its data.
*
*/
static void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
if (list_empty(head))
return;
if (list_is_singular(head) &&
(head->next != entry && head != entry))
return;
if (entry == head)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
else
__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
}
static void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
/**
* list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member)
container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member)
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
/**
* list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head);
pos = pos->next)
/**
* __list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*
* This variant differs from list_for_each() in that it's the
* simplest possible list iteration code, no prefetching is done.
* Use this for code that knows the list to be very short (empty
* or 1 entry) most of the time.
*/
#define __list_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->prev; prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head);
pos = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head);
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev;
prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head);
pos = n, n = pos->prev)
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member);
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member);
prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue()
* @pos: the type * to use as a start point
* @head: the head of the list
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue().
*/
#define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member)
((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member);
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member);
prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member)
for (; prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member),
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,
* safe against removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member),
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against
* removal of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member)
for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal
* of list entry.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member),
n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member))
/**
* list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @pos: the loop cursor used in the list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @n: temporary storage used in list_for_each_entry_safe
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be
* modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An
* exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list,
* and list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before
* completing the current iteration of the loop body.
*/
#define list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member)
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)
/*
* Double linked lists with a single pointer list head.
* Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is
* too wasteful.
* You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1).
*/
#define HLIST_HEAD_INIT { .first = NULL }
#define HLIST_HEAD(name) struct hlist_head name = { .first = NULL }
#define INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL)
static void INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct hlist_node *h)
{
h->next = NULL;
h->pprev = NULL;
}
static int hlist_unhashed(const struct hlist_node *h)
{
return !h->pprev;
}
static int hlist_empty(const struct hlist_head *h)
{
return !h->first;
}
static void __hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
struct hlist_node *next = n->next;
struct hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev;
*pprev = next;
if (next)
next->pprev = pprev;
}
static void hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
__hlist_del(n);
n->next = LIST_POISON1;
n->pprev = LIST_POISON2;
}
static void hlist_del_init(struct hlist_node *n)
{
if (!hlist_unhashed(n)) {
__hlist_del(n);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(n);
}
}
static void hlist_add_head(struct hlist_node *n, struct hlist_head *h)
{
struct hlist_node *first = h->first;
n->next = first;
if (first)
first->pprev = &n->next;
h->first = n;
n->pprev = &h->first;
}
/* next must be != NULL */
static void hlist_add_before(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
n->pprev = next->pprev;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
*(n->pprev) = n;
}
static void hlist_add_after(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
next->next = n->next;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
if(next->next)
next->next->pprev = &next->next;
}
/* after that we'll appear to be on some hlist and hlist_del will work */
static void hlist_add_fake(struct hlist_node *n)
{
n->pprev = &n->next;
}
/*
* Move a list from one list head to another. Fixup the pprev
* reference of the first entry if it exists.
*/
static void hlist_move_list(struct hlist_head *old,
struct hlist_head *node)
{
node->first = old->first;
if (node->first)
node->first->pprev = &node->first;
old->first = NULL;
}
#define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member)
#define hlist_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1; });
pos = pos->next)
#define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; });
pos = n)
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry(tpos, pos, head, member)
for (pos = (head)->first;
pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) &&
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;});
pos = pos->next)
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry_continue - iterate over a hlist continuing after current point
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_continue(tpos, pos, member)
for (pos = (pos)->next;
pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) &&
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;});
pos = pos->next)
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry_from - iterate over a hlist continuing from current point
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_from(tpos, pos, member)
for (; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) &&
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;});
pos = pos->next)
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct hlist_node to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_safe(tpos, pos, n, head, member)
for (pos = (head)->first;
pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }) &&
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;});
pos = n)
#endif