此前了解的栈与队列和堆
python中的大小堆 heapq - PiaYie - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
队列 - PiaYie - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
树的遍历 - PiaYie - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出,堆是满足特定结构
此外队列还有双端队列
栈和队列是STL(C++标准库)里面的两个数据结构,C++标准库有很多版本,要知道自己使用标准是啥,和堆栈的底层实现
(1条消息) 数据结构:堆栈的区别_SongXJ的博客-CSDN博客_堆栈区别
关于栈
Stack in C++ STL - GeeksforGeeks
栈是C++标准库中的一种数据结构,栈是一种后进先出(LIFO,last in first out)类型的容器适配器,即在一端(顶部)添加一个新元素,然后从(顶部)删除一个元素。Stack使用封装的vector或deque(默认情况下)或list(顺序容器类)对象作为其底层容器,提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。
堆栈的语法:为了创建堆栈,我们必须在代码中包含<stack>头文件。
The functions associated with stack are:
empty() – Returns whether the stack is empty – Time Complexity : O(1)
size() – Returns the size of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
top() – Returns a reference to the top most element of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
push(g) – Adds the element ‘g’ at the top of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
pop() – Deletes the top most element of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
栈四个问题
C++中stack 是容器么?
是一种数据结构,STL中栈往往不被归类为容器,而被归类为container adapter(容器适配器)
我们使用的stack是属于那个版本的STL?
SGI-STL
我们使用的STL中stack是如何实现的?
SGI STL栈的底层实现是用双端队列deque实现的。
P.s 栈是以底层容器完成其所有的工作,对外提供统一的接口,底层容器是可插拔的(也就是说我们可以控制使用哪种容器来实现栈的功能),默认是deque
- 我们也可以指定vector为栈的底层实现,初始化语句如下:
std::stack<int, std::vector<int> > third; // 使用vector为底层容器的栈
- 队列也可以指定list 为其底层实现,初始化queue的语句如下:
std::queue<int, std::list<int>> third; // 定义以list为底层容器的队列
stack 提供迭代器来遍历stack空间么?
不提供,只有特定的方法 top push pop empty等等
关于队列
Queue in C++ Standard Template Library (STL) - GeeksforGeeks
队列是一种采用先进先出(FIFO, first in first out)方式操作的容器适配器。元素被插入到后面(末端),并从前面删除。队列使用封装的deque或list(顺序容器类)对象作为其底层容器,提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。
队列四个问题
C++中queue是容器么?
是容器适配器
我们使用的queue是属于那个版本的STL?
SGI-STL
我们使用的STL中queue是如何实现的?
默认是双端队列deque
queue 提供迭代器来遍历queue空间么?
不提供,只有一些方法,Methods of Queue are:
| Method | Definition |
|---|---|
| queue::empty() | Returns whether the queue is empty. |
| queue::size() | Returns the size of the queue. |
| queue::swap() | Exchange the contents of two queues but the queues must be of the same type, although sizes may differ. |
| queue::emplace() | Insert a new element into the queue container, the new element is added to the end of the queue. |
| queue::front() | Returns a reference to the first element of the queue. |
| queue::back() | Returns a reference to the last element of the queue. |
| queue::push(g) | Adds the element ‘g’ at the end of the queue. |
| queue::pop() | Deletes the first element of the queue. |
用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() -- 返回队列是否为空
思路:c++中栈的操作有 pop() push() top() empty() size(),要实现先进先出的队列的基本方法pop() empty() push() peek()?返回队列开头的元素,那么方法之一是使用两个栈,一个作为输入栈,一个作为输出栈

要注意将元素从输入栈到输出栈加入的时机。需要等到输出栈为空的那一刻,并且要讲输入栈的所有元素pop到输出栈。
当两个栈都为空时,该队列为空。
peek可以复用pop函数。
class MyQueue { public: stack<int> stackIn; stack<int> stackOut; MyQueue() { } void push(int x) { stackIn.push(x); } int pop() { //只有当输出栈空时,才将输出栈的所有元素导入输出栈 if(stackOut.empty()){ while(!stackIn.empty()){ stackOut.push(stackIn.top()); stackIn.pop(); } } //pop要return最早进栈的元素 int res = stackOut.top(); stackOut.pop(); return res; } int peek() { int res = this->pop(); stackOut.push(res); return res; } bool empty() { return stackIn.empty() && stackOut.empty(); } };
用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
队列有接口pop()不返回元素只管pop push() empty() front(), 或许还有双端队列deque,来实现栈操作 pop() push() top() empty()
思路:
- 用双端队列deque只用一端的接口
- 只用单向队列的话怎么做呢(可以用两个队列来模拟栈,不像上一题一个做输入一个做输出,这里模拟的两个队列一个仅仅用来做备份)
- 只用一个单向队列怎么做?(一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时在去弹出队首元素)
使用deque解法:
class MyStack { public: deque<int> dequeList; MyStack() { } void push(int x) { dequeList.push_front(x); } int pop() { int res = dequeList.front(); dequeList.pop_front(); return res; } int top() { return dequeList.front(); } bool empty() { return dequeList.empty(); } };
使用一个queue实现stack:
class MyStack2 { public: queue<int> queueList; MyStack2() { } void push(int x) { queueList.push(x); } int pop() { int lenSize = queueList.size() -1; while(lenSize--){ queueList.push(queueList.front()); queueList.pop(); } int res = queueList.front(); queueList.pop(); return res; } int top() { //返回队尾 return queueList.back(); } bool empty() { return queueList.empty(); } };
有效的括号
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
示例 4:
输入:s = "([)]"
输出:false
示例 5:
输入:s = "{[]}"
输出:true
思路:首先分析一下不匹配的情况,理清思路
carl哥说只要覆盖三种不匹配模式就可以:
- 字符串里左方向的括号多余了
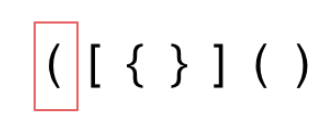
- 括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上
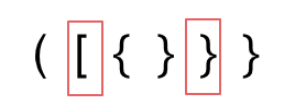
- 字符串里右方向的括号多余了
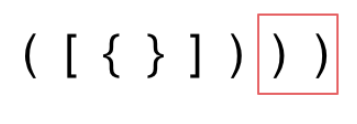
题解:
- 如果遇到了左括弧,肯定要匹配一个其右括弧,而且后遇到的要先匹配,即后进先出,用栈!
- 碰到了右括弧,就要往栈顶找匹配,如果匹配到了就把栈顶删了,继续往下;如果没有匹配到就要返回false
- 如果找到一个右括弧,但是之前没有对应的左括弧,即栈为空或者和栈顶右括弧不匹配(相等),返回false
- 最后匹配完了,栈一定为空,才能返回true!
//正确匹配括号,且只有括号的字符串‘[](){}’ class matchSolution { public: bool isValid(string s) { stack<int> st; for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')'); else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}'); else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']'); // 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false // 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有我们要匹配的字符。所以return false else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false; else st.pop(); // st.top() 与 s[i]相等,栈弹出元素 } // 第一种情况:此时我们已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false,否则就return true return st.empty(); } };
删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。
在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。
在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。
示例:
- 输入:"abbaca"
- 输出:"ca"
思路:使用栈,入栈的元素和栈顶元素做对比,如果相同,忽略该元素,删除栈顶元素。最后返回栈中元素的反转
class Solution { public: string removeDuplicates(string s) { stack<char> st; for(char ch: s){ if(st.empty() || ch != st.top()){ st.push(ch); }else{ st.pop(); } } //返回栈中元素的反转 string res = ""; while(!st.empty()){ res += st.top(); st.pop(); } reverse(res.begin(),res.end()); return res; } };
上面代码在leetcode上的评分并不高。改进,直接把字符串当作栈,省去反转字符串的开销:
class Solution { public: string removeDuplicates(string s) { string st = ""; for(char ch: s){ if(st.empty() || ch != st.back()){ st.push_back(ch); }else{ st.pop_back(); } } return st; } };
P.S.原来 string还有 empty()方法啊 还有back()方法啊 还有 pushpop_back()方法啊是
逆波兰表达式求值
150. 逆波兰表达式求值 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
- 有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
- 注意 两个整数之间的除法只保留整数部分。
- 可以保证给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
输入:tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"]
输出:9
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
示例 2:
输入:tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"]
输出:6
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
示例 3:
输入:tokens = ["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"]
输出:22
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22
也就是说,A • B 是按左算子A 右算子B 运算符• 展开的
那么就和二叉树的后序遍历有点意思了。这其实叫做后缀表达式,即运算符写在后面
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
-
去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成 1 2 + 3 4 + * 也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。所以后缀表达式对计算机来说是非常友好的
-
适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中(解题思路,dei就是这么简单)。
class Solution { public: int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { stack<int> elementStack; for(int i=0;i<tokens.size();i++){ if(tokens[i]=="+"||tokens[i]=="-"||tokens[i]=="*"||tokens[i]=="/"){ int element1 = elementStack.top(); elementStack.pop(); int element2 = elementStack.top(); elementStack.pop(); if(tokens[i]=="+") elementStack.push(element2 + element1); //顺序应该是反过来,因为是栈的原因 if(tokens[i]=="-") elementStack.push(element2 - element1); if(tokens[i]=="*") elementStack.push(element2 * element1); if(tokens[i]=="/") elementStack.push(element2 / element1); }else{ //因为是string,所以要转化为数 elementStack.push(stoi(tokens[i])); } } return elementStack.top(); } };
滑动窗口最大值
239. 滑动窗口最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
- 返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
- 在线性时间复杂度内解决此题。
思路:维护一个单调队列(长度不一定是k,只要包含窗中最大值就可以了),可以用deque来做,这样的话最大的出去的很方便找到第二大的元素。
- 单调队列的头放着最大的元素(几个元素),尾巴位置用来加入新的元素
- 如果窗口要移除的元素刚好单调队列中的最大值,即头位置的元素,就把头pop出去
- 窗口往前移会新增一个元素,为了保证单调,切在尾巴back位置加入,要把小于这个新元素的尾部给pop出去,再在尾巴加新元素
- 输出的话,当窗口移到第k个元素才输出最大值。
class Solution { public: vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { //滑动窗口 + 维护一个单调的队列 deque<int> monoQueue; //c++中也有deque 常用这个才对 vector<int> res; int n = nums.size(); for(int i = -k+1;i<n-k+1;i++){ int j = i+k-1; // 如果出窗口的刚好是上一轮的最大值 if(i>0 && nums[i-1] == monoQueue.front()){ monoQueue.pop_front(); } //保证单调的队列 while(!monoQueue.empty() && monoQueue.back() <nums[j]){ monoQueue.pop_back(); } monoQueue.push_back(nums[j]); if(i>=0){ res.push_back(monoQueue.front()); } } return res; } };
前 K 个高频元素
347. 前 K 个高频元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
- 可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。
- 你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 $O(n \log n)$ , n 是数组的大小。
- 题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前 k 个高频元素的集合是唯一的
用字典不就完事了吗?统计完还要排序的,排序用快排?
首先想到的就是map
map可以实现统计功能,但是对频数进行排序还是挺麻烦的,有没有可能我统计完,排序也出来了?有 ------容器适配器:优先级队列
可以理解为披着队列外衣的堆,常说的大小堆就是优先级队列
如果懒得自己实现的话,就直接用priority_queue(优先级队列)就可以了,底层实现都是一样的,从小到大排就是小顶堆,从大到小排就是大顶堆。
python中的大小堆 heapq - PiaYie - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
大顶堆:每次弹出最大的元素
小顶堆:每次弹出最小的元素
思路:使用小顶堆存频数。当堆中数据多与k组时,每次把频数最小的数据弹出,最后返回的k个数据就是前 K 个高频元// 时间复杂度:O(nlogk)
// 空间复杂度:O(n) class Solution { public: // 小顶堆 class mycomparison { public: bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& lhs, const pair<int, int>& rhs) { return lhs.second > rhs.second; } }; vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) { // 要统计元素出现频率 unordered_map<int, int> map; // map<nums[i],对应出现的次数> for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { map[nums[i]]++; } // 对频率排序 // 定义一个小顶堆,大小为k priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, mycomparison> pri_que;//不可以用greater<int> 因为比较的是一个,我们要根据pair<int,int>的第二个值比较
// 用固定大小为k的小顶堆,扫面所有频率的数值 for (unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++) { pri_que.push(*it); if (pri_que.size() > k) { // 如果堆的大小大于了K,则队列弹出,保证堆的大小一直为k pri_que.pop(); } } // 找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒序来输出到数组 vector<int> result(k); for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) { result[i] = pri_que.top().first; pri_que.pop(); } return result; } };