主要是根据一些例子,熟悉使用list和tuple
1. 判断 list 内有无重复元素
还记的列表的count方法吗?
除了count,还有集合的思想也有帮助。(集合的运行时间明显比使用列表count方法短)
import time def is_duplicated(lst): # 检验容器list对象lst是否有重复的元素 for x in lst: if lst.count(x) > 1: return True return False def is_duplicated_using_set(lst): # 使用集合的思想检验容器list对象lst是否有重复的元素 return len(lst) != len(set(lst)) def main(): a = [1, -2, 3, 4, 1, 2] startTime1 = time.time() print(is_duplicated(a)) totalTime1 = round(time.time() - startTime1, 20) startTime2 = time.time() print(is_duplicated_using_set(a)) totalTime2 = round(time.time() - startTime2, 20) print("totalTime1:%s " % totalTime1) print("totalTime2:%s " % totalTime2) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
输出:
True
True
totalTime1:0.03096175193786621
totalTime2:0.0009534358978271484
2. 列表反转
那必须用切片来做啊 一行代码,起飞:
[::-1]生成逆向索引(负号表示逆向),步长为 1 的切片。
3. 找出列表中的所有重复元素
count方法,返回一个列表就好,而不要返回简单的True 和 False
def find_duplicate(lst): ret = [] for x in lst: #if lst.count(x) > 1: if lst.count(x) > 1 and x not in ret: ret.append(x) return ret
4. 斐波那契数列
由于fibonacci数列是从最基本的两个元生成而来,自然然想到
先建一个list,再往列表后添加一个元素,他是他的前两个元素的和就完事了
还有一种想法,学到了,使用生成器。 优点,代码简洁而且节省内存!
def gene_fibonacii(n): # 生成长度为n的Fibonacci数列 普通实现 if n <= 1: return [1] fbnq = [1, 1] while len(fbnq) < n: fbnq.append(fbnq[len(fbnq) - 1] + fbnq[len(fbnq) - 2]) return fbnq def gene_fibonacii_by_yield(n): # 使用生成器 来生成fibonacci数列 # 返回一个object,需要用list来手动生成列表 a, b = 1, 1 for _ in range(n): yield a a, b = b, a + b
调用:
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765]
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
5. 出镜最多
list中,要求出现次数最多的元素:
给大家介绍一下新朋友: max函数 python内置函数所以无需import
max() 方法的语法:
max(arg1: _T, arg2: _T, /, *_args: _T, key: Callable[[_T], Any]=...) -> _T
def get_maxi_freq_items_of_list(lst): # 返回出现次数的那些元素 可以是多个 # 使用python内置的max方法 if not lst: return None max_freq_elem = max(lst, key=lambda v: lst.count(v)) max_freq = lst.count(max_freq_elem) # 出现最多次数 ret = [] for i in lst: if i not in ret and lst.count(i) == max_freq: ret.append(i) return ret
lambda 的参数 v 是 lists 中的一个元素
6. 取几个列表中更长列表
def get_maxlen_list_from_lists(*lists): # 得到多个元素lists中长度最大的哪一个 # 带有一个 * 的参数为可变的位置参数,意味着能传入任意多个位置参数。 return max(*lists, key=lambda v: len(v))
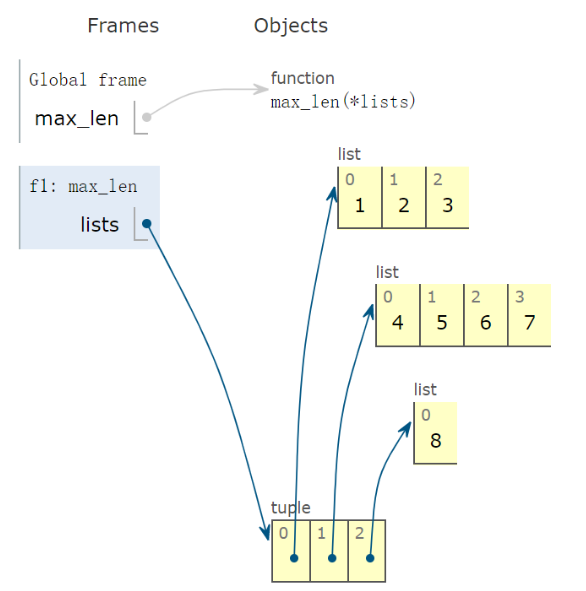
7. 求表头表尾
表头lst[0]表尾lst[-1],当lst为空时,返回None
def get_head_from_lst(lst): # 求表头 return lst[0] if len(lst) > 0 else None def get_tail_from_lst(lst): # 求表尾 return lst[-1] if len(lst) > 0 else None
8. 打印乘法表
我们打印肯定是一行一行向下打印,:
1.每行做一个循环,每行输出完后打印一个换行
2.两个循环是直接方便的,内层循环用来打印每行的输出。
def mul_table2(): # 打印乘法表 for i in range(1, 10): for j in range(1, i + 1): print(str(j) + str("*") + str(i) + "=" + str(i*j), end=" ") print() # 打印一个换行
1*1=1
1*2=2 2*2=4
1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9
1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16
1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
9. 元素对(a, b)
zip(iter1, iter2):实现 iter1 和 iter2 的对应索引处的元素拼接。
def pair_of_lst_element(lst): # 生成元素对 # zip(list1, list2) 其中两个列表的长度一致,一边各取一个成对,依次往下,如果长度不一致,当有一个list的元素遍历完后就结束 return list(zip(lst[1:-1],lst[1:]))
10. 样本抽样
从样本空间中,随机抽取若干个样本
- 使用列表生成式,生成大列表(样本空间)
- random 内置模块的sample函数来抽样:
def get_sample_from_random_numlst(mini, maxi, omg, sam): # 从样本空间中,随机抽取若干个样本, # mini, maxi, omg, sam 分别是整数样本空间的下限、上限、样本空间个数、样本个数 from random import randint,sample lst = [randint(mini,maxi) for _ in range(omg)] if sam < omg: lst_sample = sample(lst, sam) print(lst_sample) else: print("请重新配置样本空间大小和样本数!")
11. 重洗数据集
内置 random 中的 shuffle 函数,能重洗数据(打乱)。
shuffle 是对输入列表就地(in place)洗牌,节省存储空间:
shuffle(list) # list直接就被重洗了
12. 生成满足均匀分布的坐标点
random 模块,uniform(a,b) 生成 [a,b) 内的一个随机数。
借助列表生成式,生成 100 个均匀分布的坐标点。
然后再打印出来。使用 PyEcharts 绘图。
def plot_mean_dot_in_biaxis(lower_bound, upper_bound, numb): # 生成满足均匀分布的坐标点 # lower_bound, upper_bound, numb 分别是下届,上界, 坐标点的个数 # x 存储index,y存储值 from random import uniform from pyecharts.charts import Scatter import pyecharts.options as opts x, y = [i for i in range(numb)], [ round(uniform(lower_bound, upper_bound),2) for _ in range(numb)] print(y) # 用 PyEcharts 绘图 c = ( Scatter() .add_xaxis(x) .add_yaxis('y', y) ) print(c.render()) #在当前工作区生成了一个 html文件
[1.41, 4.49, 1.16, 8.53, 7.33, 7.5, 6.54, 2.77, 3.37, 9.41, 6.12, 5.92, 1.95, 0.32, 9.08, 3.68, 7.98, 9.9, 9.97, 9.15, 9.53, 0.95, 4.89, 8.43, 4.89, 4.29, 0.4, 6.4, 5.76, 8.66, 9.84, 0.29, 2.36, 8.57, 3.17, 8.73, 6.03, 8.32,
1.79, 1.19, 3.85, 6.23, 7.71, 3.39, 7.65, 9.79, 1.11, 7.54, 9.8, 4.8, 5.68, 0.83, 6.88, 0.91, 2.0, 2.98, 5.61, 1.99, 4.4, 0.47, 2.95, 9.17, 3.75, 1.33, 1.74, 1.2, 4.18, 7.05, 7.08, 5.01, 9.28, 6.36, 9.9, 0.93, 7.05, 8.49, 1.94, 8.74, 4.47, 5.82, 6.42, 7.93, 1.48, 5.52, 4.57, 7.92, 8.31, 8.09, 3.99, 8.52, 7.81, 3.3, 9.03, 4.98, 7.7, 3.75, 1.73, 8.37, 4.8, 0.15]
