1 CORTEX-M
1.1 boot程序
以stm32为例,添加在线升级boot程序,rom地址:
LR_IROM1 0x08000000 0x00004000 { ; load region size_region ER_IROM1 0x08000000 0x00004000 { ; load address = execution address *.o (RESET, +First) *(InRoot$$Sections) .ANY (+RO) } RW_IRAM1 0x20000000 0x00020000 { ; RW data .ANY (+RW +ZI) } }
boot引导应用程序:
#define APPLICATION_ADDRESS (uint32_t)0x08004000
JumpAddress = *(__IO uint32_t*) (APPLICATION_ADDRESS + 4);
/* Jump to user application */
Jump_To_Application = (pFunction) JumpAddress;
/* Initialize user application's Stack Pointer */
__set_MSP(*(__IO uint32_t*) APPLICATION_ADDRESS);
Jump_To_Application();
1.2 应用程序
rom地址 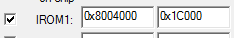
LR_IROM1 0x08004000 0x0001c000 { ; load region size_region ER_IROM1 0x08004000 0x00300000 { ; load address = execution address *.o (RESET, +First) *(InRoot$$Sections) .ANY (+RO) } RW_IRAM1 0x20000000 0x00020000 { ; RW data .ANY (+RW +ZI) } }
启动汇编文件startup***.s中
Stack_Size EQU 0x00000400
;Stack_Size EQU 0x00001000
,,,
Reset_Handler PROC
EXPORT Reset_Handler [WEAK]
IMPORT SystemInit
IMPORT __main
2 对于LINUX的引导和启动过程
2.1 uboot
mian_loop中有
#define CONFIG_BOOTDELAY 3 //设置启动延时时间 //如果延时大于等于零,并且没有在延时过程中接收到按键,则引导内核 if (bootdelay >= 0 && s && !abortboot (bootdelay)) { // # ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED intprev = disable_ctrlc(1);/* disable Control C checking */ # endif //状态设置 # ifndef CFG_HUSH_PARSER { printf("Booting Linux ... "); //启动 linux run_command (s, 0); //运行引导内核的命令,s=getenv("bootcmd") }
加载linux内核时将使用变量“bootcmd”和 “bootargs”,
变量“bootcmd”和 “bootargs”的值可以在在加载linux内核前,
uboot的命令控制台中进行修改
bootcmd=nand read.jffs2 0x30007FC0 kernel; bootm 0x30007FC0
第一条命令 从flash上读出内核 kernel是一个分区标志
第二条命令 启动命令指示了启动地址
bootargs是其它参数信息, run_command (getenv ("bootcmd"), flag)
bootcmd中的bootm,即boot application image from memory
参数形式:"bootm addr",当addr省略的时候bootm加载默认的配置宏
#define CONFIG_SYS_LOAD_ADDR 0x30008000 /* default load address */
2.2 linux内核态
查找标签__mmap_switched所在位置:/linux/arch/arm/kernel/head-common.S
__mmap_switched: /* * The following fragment of code is executed with the MMU on in MMU mode, * and uses absolute addresses; this is not position independent. * * r0 = cp#15 control register * r1 = machine ID * r2 = atags/dtb pointer * r9 = processor ID */ //保存设备信息、设备树及启动参数存储地址 ,, b start_kernel
函数所在位置:/linux/init/Main.c,start_kernel涉及大量初始化工作,只例举重要的初始化工作。
asmlinkage void __init start_kernel(void) { …… //类型判断 smp_setup_processor_id(); //smp相关,返回启动CPU号 …… local_irq_disable(); //关闭当前CPU中断 early_boot_irqs_disabled = true; /* * Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then * enable them */ boot_cpu_init(); page_address_init(); //初始化页地址 pr_notice("%s", linux_banner); //显示内核版本信息 setup_arch(&command_line); mm_init_owner(&init_mm, &init_task); mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm); setup_command_line(command_line); setup_nr_cpu_ids(); setup_per_cpu_areas(); smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */ build_all_zonelists(NULL, NULL); page_alloc_init(); //页内存申请初始化 pr_notice("Kernel command line: %s ", boot_command_line); //打印内核启动命令行参数 parse_early_param(); parse_args("Booting kernel", static_command_line, __start___param, __stop___param - __start___param, -1, -1, &unknown_bootoption); …… /* * Set up the scheduler prior starting any interrupts (such as the * timer interrupt). Full topology setup happens at smp_init() * time - but meanwhile we still have a functioning scheduler. */ sched_init(); //进程调度器初始化 /* * Disable preemption - early bootup scheduling is extremely * fragile until we cpu_idle() for the first time. */ preempt_disable(); //禁止内核抢占 if (WARN(!irqs_disabled(), "Interrupts were enabled *very* early, fixing it ")) local_irq_disable(); //检查关闭CPU中断 /*大量初始化内容 见名知意*/ idr_init_cache(); rcu_init(); tick_nohz_init(); context_tracking_init(); radix_tree_init(); /* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */ early_irq_init(); init_IRQ(); tick_init(); init_timers(); hrtimers_init(); softirq_init(); timekeeping_init(); time_init(); sched_clock_postinit(); perf_event_init(); profile_init(); call_function_init(); WARN(!irqs_disabled(), "Interrupts were enabled early "); early_boot_irqs_disabled = false; local_irq_enable(); //本地中断可以使用了 kmem_cache_init_late(); /* * HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before * we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of * this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong. */ console_init(); //初始化控制台,可以使用printk了 if (panic_later) panic("Too many boot %s vars at `%s'", panic_later, panic_param); lockdep_info(); /* * Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants * to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs * too: */ locking_selftest(); #ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok && page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) { pr_crit("initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - disabling it. ", page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)), min_low_pfn); initrd_start = 0; } #endif page_cgroup_init(); debug_objects_mem_init(); kmemleak_init(); setup_per_cpu_pageset(); numa_policy_init(); if (late_time_init) late_time_init(); sched_clock_init(); calibrate_delay(); pidmap_init(); anon_vma_init(); acpi_early_init(); #ifdef CONFIG_X86 if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES)) efi_enter_virtual_mode(); #endif #ifdef CONFIG_X86_ESPFIX64 /* Should be run before the first non-init thread is created */ init_espfix_bsp(); #endif thread_info_cache_init(); cred_init(); fork_init(totalram_pages); //初始化fork proc_caches_init(); buffer_init(); key_init(); security_init(); dbg_late_init(); vfs_caches_init(totalram_pages); //虚拟文件系统初始化 signals_init(); /* rootfs populating might need page-writeback */ page_writeback_init(); #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS proc_root_init(); #endif cgroup_init(); cpuset_init(); taskstats_init_early(); delayacct_init(); check_bugs(); sfi_init_late(); if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES)) { efi_late_init(); efi_free_boot_services(); } ftrace_init(); /* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */ rest_init(); } 函数最后调用rest_init()函数 /*最重要使命:创建kernel_init进程,并进行后续初始化*/ static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void) { int pid; rcu_scheduler_starting(); /* * We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however * the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if * we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS. */ kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_SIGHAND); //创建kernel_init进程 numa_default_policy(); pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES); rcu_read_lock(); kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns); rcu_read_unlock(); complete(&kthreadd_done); /* * The boot idle thread must execute schedule() * at least once to get things moving: */ init_idle_bootup_task(current); schedule_preempt_disabled(); /* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */ //cpu_idle就是在系统闲置时用来降低电力的使用和减少热的产生的空转函数,函数至此不再返回,其余工作从kernel_init进程处发起 cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE); } kernel_init函数将完成设备驱动程序的初始化,并调用init_post函数启动用户进程 部分书籍介绍的内核启动流程基于经典的2.6版本,kernel_init函数还会调用init_post函数专门负责_init进程的启动,现版本已经被整合到了一起。 static int __ref kernel_init(void *unused) { int ret; kernel_init_freeable(); //该函数中完成smp开启 驱动初始化 共享内存初始化等工作 /* need to finish all async __init code before freeing the memory */ async_synchronize_full(); free_initmem(); //初始化尾声,清除内存无用数据 mark_rodata_ro(); system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING; numa_default_policy(); flush_delayed_fput(); if (ramdisk_execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d) ", ramdisk_execute_command, ret); } /* * We try each of these until one succeeds. * * The Bourne shell can be used instead of init if we are * trying to recover a really broken machine. *寻找init函数,创建一号进程_init (第一个用户空间进程)*/ if (execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d). Attempting defaults... ", execute_command, ret); } if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh")) return 0; panic("No working init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. " "See Linux Documentation/init.txt for guidance."); } static int __ref kernel_init(void *unused) { int ret; kernel_init_freeable(); //该函数中完成smp开启 驱动初始化 共享内存初始化等工作 /* need to finish all async __init code before freeing the memory */ async_synchronize_full(); free_initmem(); //初始化尾声,清除内存无用数据 mark_rodata_ro(); system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING; numa_default_policy(); flush_delayed_fput(); if (ramdisk_execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d) ", ramdisk_execute_command, ret); } /* * We try each of these until one succeeds. * * The Bourne shell can be used instead of init if we are * trying to recover a really broken machine. *寻找init函数,创建一号进程_init (第一个用户空间进程)*/ if (execute_command) { ret = run_init_process(execute_command); if (!ret) return 0; pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d). Attempting defaults... ", execute_command, ret); } if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh")) return 0; panic("No working init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. " "See Linux Documentation/init.txt for guidance."); }
到此,内核初始化已经接近尾声,所有的初始化函数都已经调用,因此free_initmem函数可以舍弃内存的__init_begin至__init_end之间的数据。
当内核被引导并进行初始化后,内核启动了自己的第一个用户空间应用程序_init,这是调用的第一个使用标准C库编译的程序,其进程编号时钟为1.
_init负责出发其他必须的进程,以使系统进入整体可用的状态。
以下为内核启动流程图:
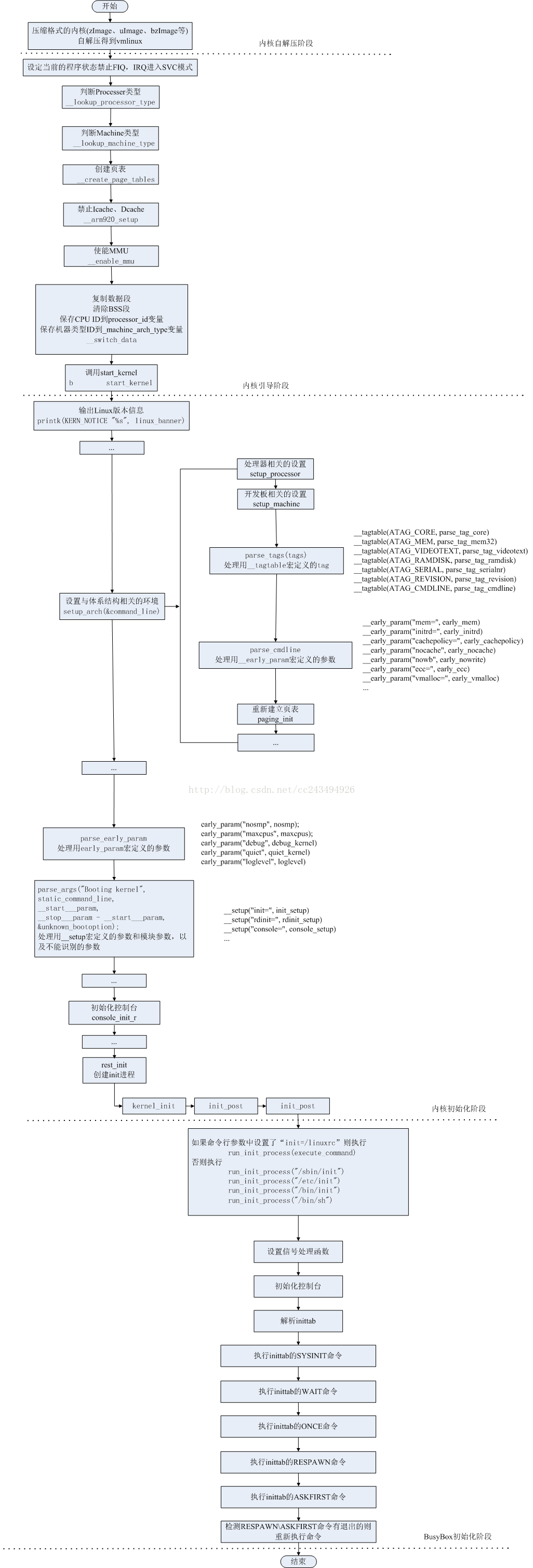
图片来源:https://blog.csdn.net/perfect1t/article/details/81741531
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/perfect1t/article/details/81741531
---
https://blog.csdn.net/perfect1t/article/details/81741531