概念:
序列化 (Serialization)将对象的状态信息转换为可以存储或传输的形式的过程。在序列化期间,对象将其当前状态写入到临时或持久性存储区。以后,可以通过从存储区中读取或反序列化对象的状态,重新创建该对象。
实现例子:
写一个MyClass类,提供了可被序列化的属性,不用其余操作,如下:
using UnityEngine; using UnityEditor; [InitializeOnLoad] public class MyClass : ScriptableObject { public void SetBoolenTest(bool value) { boolenTest = value; DirtyEditor(); } public void SetIntTest(int value) { intTest = value; DirtyEditor(); } public void SetStrTest(string value) { strTest = value; DirtyEditor(); } public void SetStrIndex(int index) { strIndex = index; SetStrTest(strList[index]); DirtyEditor(); } private void DirtyEditor() { EditorUtility.SetDirty(Instance); } public bool BoolenTest { get { return Instance.boolenTest; } } public int IntTest { get { return Instance.intTest; } } public string StrTest { get { return Instance.strTest; } } public int StrIndex { get { return strIndex; } } [SerializeField] private bool boolenTest = true; [SerializeField] private int intTest = 1; [SerializeField] private string strTest = "hello world"; [SerializeField] private int strIndex = 0; public string[] strList = new string[] { "str_1", "str_2", "str_3" }; private static MyClass _instance; public static MyClass Instance { get { if (_instance == null) { _instance = Resources.Load("MyClass") as MyClass; } if (_instance == null) { _instance = CreateInstance<MyClass>(); AssetDatabase.CreateAsset(_instance, "Assets/Resources/MyClass.asset"); } return _instance; } } }
写一个测试类,不用其余操作,如下:
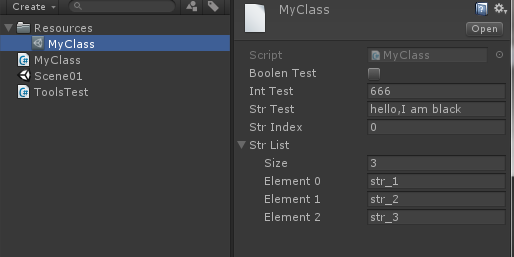
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEditor; using UnityEngine; public class ToolsTest : MonoBehaviour { // Use this for initialization void Start () { } // Update is called once per frame void Update () { } [MenuItem("EditorTools/Test")] public static void Test() { var myClass = MyClass.Instance; myClass.SetIntTest(666); myClass.SetBoolenTest(false); myClass.SetStrTest("hello,I am black"); } }
Unity菜单栏会出现 EditorTools —Test 按钮,此时新建一个Resources文件夹,然后点击按钮(没有Resources文件夹点击按钮没反应),就会在Resources文件夹下产生一个存储的文件,(没有反应的话重新打开此场景)如下: