优化原则
1.在select语句中避免使用*
2.使用Truncate清空表
2.1语法
Truncate [table|cluster] shema.[table_name][cluster_name][drop|reuse storage]
- table_name:要清空的表
- cluster_name:要清空的簇名
- drop|reuse storage:表示保留被删除的空间以供该表的新数据使用,默认为drop storage,收回被删除的空间系统。
3.使用ROWID高效删除重复记录
rowid是可以唯一标记记录的物理位置
delete from TMP001 a where rowid not in ( select max(rowid) from TMP001 b where a.id=b.id and a.name=b.name and a.gender=b.gender and a.age=b.age and a.address=b.address )
4.高效统计表的记录行数
select table_name, t.num_rows, t.last_analyzed from tabs t WHERE table_name=’TABLE_NAME’;
可能统计的不是很准确,在统计前先在command下面执行EXEC dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('【空间名称】','【tablename】',cascade=>true);刷新表中的num_rows
5.尽量多使用commit
commit所释放的资源:
- 回滚段上用于恢复数据的信息,撤销表空间也只作短暂的保留
- 被程序语句获得的锁
- redo log buffer中的空间
- Oracle为管理上述资源的花费
6.使用EXISTS替代IN
在子查询中,[NOT]IN子句将执行一个内部的排序与合并,无论哪种情况,[NOT]IN都是最低效的,因为他要对子查询中的表执行一个全表遍历。
7.修改Oracle中SGA的大小
alter system set sga_max_size=1000M scope=spfile;
此处修改SGA的大小为1000M
8.使用合理的索引
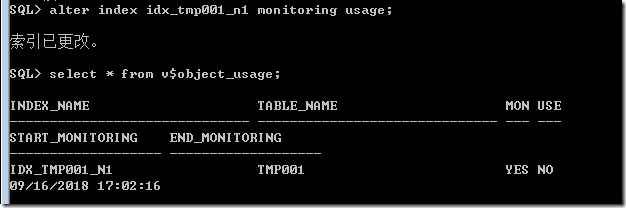
8.1监视索引是否被引用
首先建立索引
create index idx_tmp001_n1 on tmp001(id);
监视
以上结果说明,该索引建立还未使用过,那么我们按照ID查询一次在看看结果,先执行查询语句
select * from tmp001 where id=1
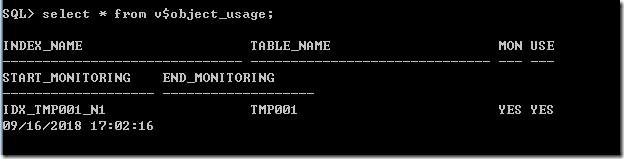
再次监视
此时的结果已经变为YES
9.避免全表扫描
以下情况为全表扫描:
- 所查询的表没有索引
- 需要返回所有的行
- 带like并使用%这样的语句就是全表扫描
- 对索引列使用了函数
- 带有is null、is not null或!=等子句也会导致全表扫描