一、库操作
1.1库的增删改查
(1)系统数据库:

performance_schema:用来收集数据库服务器的性能参数,记录处理查询时发生的各种事件、锁等现象
mysql:授权库,主要存储系统用户的权限信息
test:MySQl数据库系统自动创建的测试数据库
(2)数据库操作
创建:create database db1 charset utf8;
(数据库命名规则:可以是字母、数字、下划线等的组合,不能单独使用数字,不能使用关键字例如create select等)
查看:show databases; 或者 show create database db1;
选择数据库:use db1;
删除:drop database db1;
修改:alter database db1 charset utf8;
二、表操作
2.1存储引擎介绍
(1)类似于处理文本用txt类型,图片用png,音乐用mp3类型,数据库的表也有不同类型。表类型(存储和操作此表的类型)又称存储引擎。MySQL数据库提供了多种存储引 擎。
(2)查看MySQL支持的存储引擎:
show enginesG #查看所有支持的存储引擎
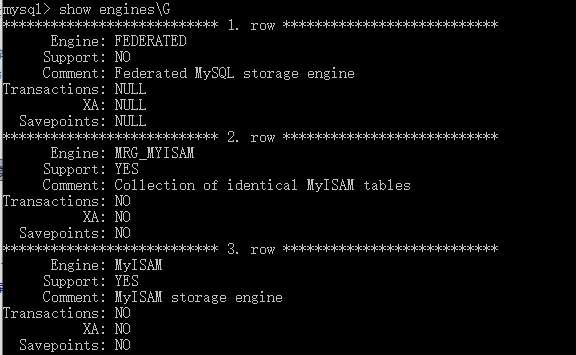
show variables like 'storage_engine%'; #查看正在使用的存储引擎
(3)部分存储引擎的简单介绍:有InnoDB、MyISAM、NDB、Memory、Infobright、NTSE、BLACKHOLE等;其中InnoDB是MySQL默认和最常用的一个存储引擎,具备高可用性、高性能以及高可扩展性。其他详情点击:具体介绍
(4)使用存储引擎
建表时指定
create table innodb_t1(id int,name char)engine=innodb;
show create table innodb_t1;
2.2表的增删改查
(1)表介绍

(2)创建表 create table student(sid int(11),sname char(10),gender enum('男','女'),class_id int(11));
查看库下所有表 show tables;
往表中插入数据 insert into student values(10,'nuo','女',5);
(3)查看表结构 desc student; 或者 show create table studentG; #查看详细表结构,可加G
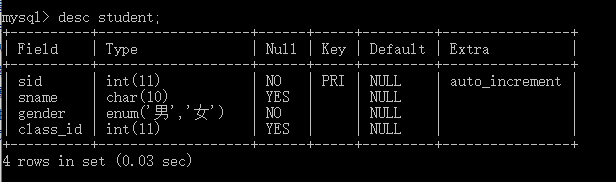
(4)修改表结构
(4.1)修改存储引擎 alter table student engine=NDB;
(4.2)添加字段 alter table student add age int not null;
(4.3)删除字段 alter table student drop age;
(4.4)修改字段类型 alter table student modify age int(9) not null primary key;
(4.5)删除主键 alter table student drop primary key;
(5)复制表
复制表结构+记录 (key不会复制: 主键、外键和索引)
mysql> create table new_service select * from service;
只复制表结构
mysql> select * from service where 1=2; //条件为假,查不到任何记录
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table new1_service select * from service where 1=2;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> create table t4 like employees;
(6)删除表 drop table student;
2.3数据类型
mysql常用数据类型有 数值类型 int , float 等、字符串类型 char varchar 、日期类型 datatime等、枚举类型和集合类型
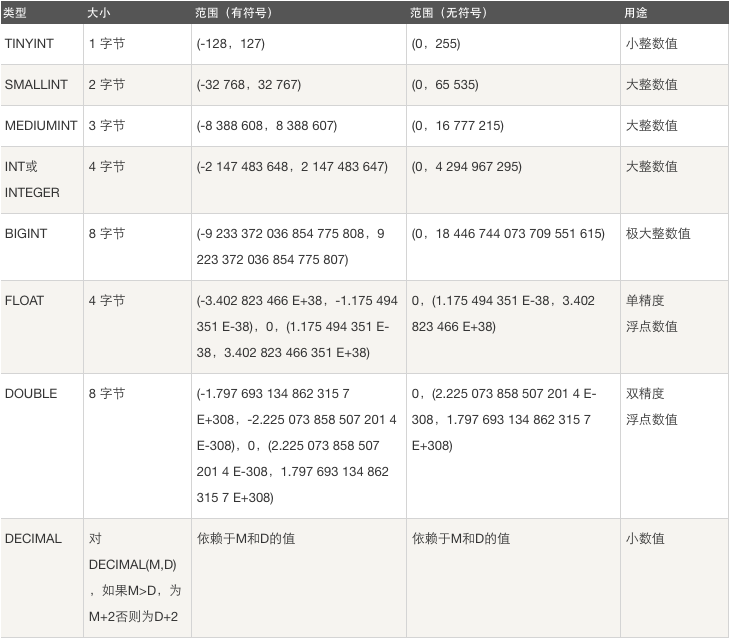
(1)数值类型
(2)日期类型


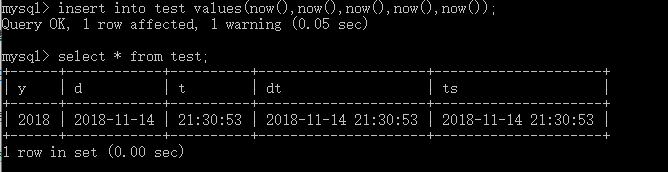
(3)字符串类型 char 和 varchar
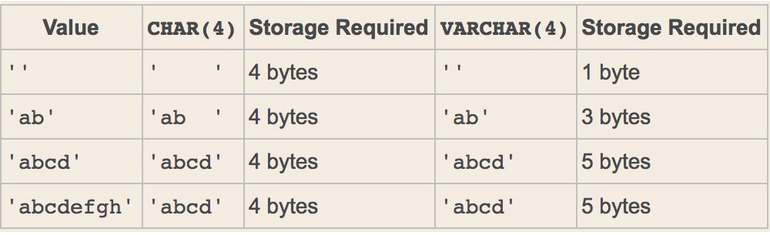
(char定长,varchar不定长,虽然varchar使用起来较为灵活,但是从整个系统的性能角度来说,char数据类型的处理速度更快,有时甚至可以超出varchar处理速度的 50%。因此,在选择时,应该综合考虑,以求达到最佳的平衡。)
(4)枚举类型和集合类型
枚举enum(),集合set();枚举单选,集合可多选;
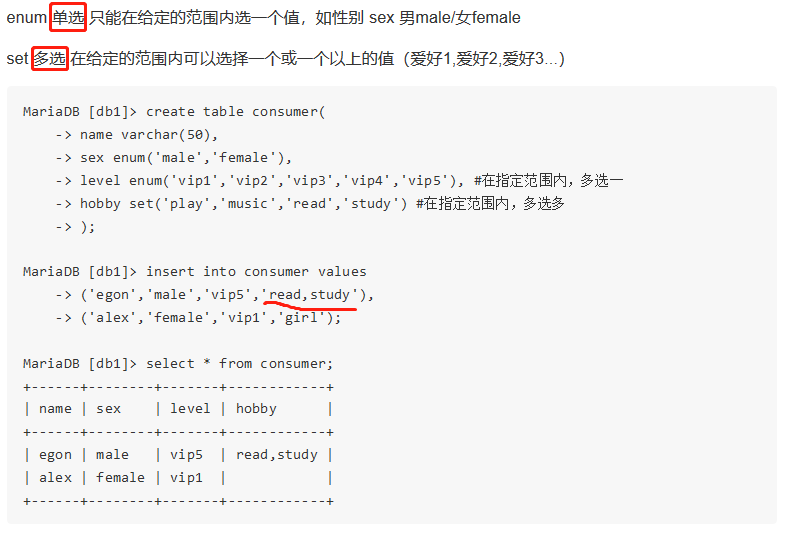
2.4完整性约束
not null (非空)、default (默认)、primary key(主键,唯一)、foreign key(外键)、unique(唯一)、auto_increment(自增,整数类型且为主键)
(1)设置唯一约束unique:

方法一: create table department1( id int, name varchar(20) unique, comment varchar(100) ); 方法二: create table department2( id int, name varchar(20), comment varchar(100), constraint uk_name unique(name) ); create table service( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), host varchar(15) not null, port int not null, unique(host,port) #联合唯一 );
(2)primary key

1 # 单列做主键 2 #方法一:not null+unique 3 create table department1( 4 id int not null unique, #主键 5 name varchar(20) not null unique, 6 comment varchar(100) 7 ); 8 9 #方法二:在某一个字段后用primary key 10 create table department2( 11 id int primary key, #主键 12 name varchar(20), 13 comment varchar(100) 14 ); 15 16 #方法三:在所有字段后单独定义primary key 17 create table department3( 18 id int, 19 name varchar(20), 20 comment varchar(100), 21 constraint pk_name primary key(id); #创建主键并为其命名pk_name

1 create table service( 2 ip varchar(15), 3 port char(5), 4 service_name varchar(10) not null, 5 primary key(ip,port) 6 );
(3)foreign key

#表类型必须是innodb存储引擎,且被关联的字段,即references指定的另外一个表的字段,必须保证唯一 create table department( id int primary key, name varchar(20) not null )engine=innodb; #dpt_id外键,关联父表(department主键id),同步更新,同步删除 create table employee( id int primary key, name varchar(20) not null, dpt_id int, constraint fk_name foreign key(dpt_id) references department(id) on delete cascade on update cascade )engine=innodb; #先往父表department中插入记录 insert into department values (1,'欧德博爱技术有限事业部'), (2,'艾利克斯人力资源部'), (3,'销售部'); #再往子表employee中插入记录 insert into employee values (1,'egon',1), (2,'alex1',2), (3,'alex2',2), (4,'alex3',2), (5,'李坦克',3), (6,'刘飞机',3), (7,'张火箭',3), (8,'林子弹',3), (9,'加特林',3) ;
(4)auto_increment

#不指定id,则自动增长 create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') default 'male' ); #应该用truncate清空表,比起delete一条一条地删除记录,truncate是直接清空表,在删除大表时用它 mysql> truncate student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) #设置步长 sqlserver:自增步长 基于表级别 create table t1( id int。。。 )engine=innodb,auto_increment=2 步长=2 default charset=utf8 mysql自增的步长: show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; #基于会话级别 set session auth_increment_increment=2 #修改会话级别的步长 #基于全局级别的 set global auth_increment_increment=2 #修改全局级别的步长(所有会话都生效) 清空表: delete from t1; #如果有自增id,新增的数据,仍然是以删除前的最后一样作为起始。 truncate table t1;数据量大,删除速度比上一条快,且直接从零开始,
三、数据操作
3.1数据的增删改
假设已经建了一张表student
增加:insert into student values
(值1,值2,值3...),
(值1,值2,值3...),
(值1,值2,值3...);
删除:delete from student
where condition
更新:update student set
字段1=值1,
字段2=值2,
where condition;
3.2单表查询
一、单表查询基本语法
select 字段1,字段2... from 表名
where 条件
group by field
having 筛选
order by field
limit 限制条数
二、关键字在执行中的优先级
重点中的重点:关键字的执行优先级
from
where
group by
having
select
distinct 去重
order by
limit
三、where约束
1、比较运算符:> < >= <= <> !=
2、between 80 and 100 值在10到20之间
3、in(80,90,100) 值是10或20或30
4、like 'egon%'
pattern可以是%或_,
%表示任意多字符
_表示一个字符
5、逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not
四、group by 分组
如果我们用unique的字段作为分组的依据,则每一条记录自成一组,这种分组没有意义 多条记录之间的某个字段值相同,该字段通常用来作为分组的依据
五、聚合函数
#强调:聚合函数聚合的是组的内容,若是没有分组,则默认一组
示例:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=1;
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=3;
六、having
having和where不一样的地方在于:
1、执行优先级从高到低 where > group by > having
2、where 在group by 之前,因此where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不可以使用聚 合函数
3、having发生在分组group by之后,因此可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他 字段,可以使用聚合函数。
七、order by 查询排序
按单列排序:
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC;
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC;
按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序
SELECT * from employee
ORDER BY age, salary DESC;
八、使用正则表达式查询
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP '^ale';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'on$';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'm{2}';
小结:
对字符串匹配的方式
WHERE name = 'egon';
WHERE name LIKE 'yua%';
WHERE name REGEXP 'on$';
3.3多表查询
多表连接查询
符合条件连接查询
子查询
一、多表连接查询
select 字段
from 表一 inner|left|right join 表二
on 表一.字段 = 表二.字段;
(1)交叉连接:不适用任何匹配条件,生成笛卡尔积
假设我们已经生成employee,department两张表
select * from employee,department;
(2) 内连接:只连接匹配的行
select employee.id department.name
from employee inner join department
on employee.id = department.id;
(3)外连接之左连接:优先显示左表全部记录
select employee.id department.name
from employee left join department
on employee.id = department.id;
(4)外连接之右连接:优先显示右表全部记录
right join ,其他参考左连接。
(5)全外连接 :显示左右两个表全部记录
select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id
union
select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
二、符合条件连接查询
#示例:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示
select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,department.name
from employee,department
where employee.dep_id = department.id and age > 25
order by age asc;
三、子查询
# 子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
#2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
#3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
#4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等

1 带IN关键字的子查询 #查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名 select id,name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25); #查看技术部员工姓名 select name from employee where dep_id in (select id from department where name='技术'); #查看不足1人的部门名 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(id) <=1); 2 带比较运算符的子查询 #比较运算符:=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<> #查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄 mysql> select name,age from emp where age > (select avg(age) from emp); +---------+------+ | name | age | +---------+------+ | alex | 48 | | wupeiqi | 38 | +---------+------+ rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄 select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1 inner join (select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2 on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id where t1.age > t2.avg_age; 3 带EXISTS关键字的子查询 EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。 而是返回一个真假值。True或False 当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询 #department表中存在dept_id=203,Ture mysql> select * from employee -> where exists -> (select id from department where id=200); +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | age | dep_id | +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | | 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | | 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | | 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | | 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | | 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ #department表中存在dept_id=205,False mysql> select * from employee -> where exists -> (select id from department where id=204); Empty set (0.00 sec)
