1 commons-lang
1.1 ReflectionToStringBuilder
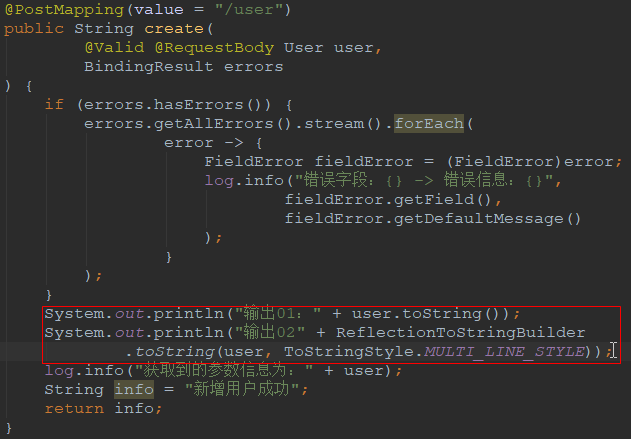
将对象进行字符串拼接

/* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.commons.lang.builder; import java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang.ClassUtils; /** * <p> * Assists in implementing {@link Object#toString()} methods using reflection. * </p> * * <p> * This class uses reflection to determine the fields to append. Because these fields are usually private, the class * uses {@link java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject#setAccessible(java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject[], boolean)} to * change the visibility of the fields. This will fail under a security manager, unless the appropriate permissions are * set up correctly. * </p> * * <p> * A typical invocation for this method would look like: * </p> * * <pre> * public String toString() { * return ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(this); * }</pre> * * * * <p> * You can also use the builder to debug 3rd party objects: * </p> * * <pre> * System.out.println("An object: " + ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(anObject));</pre> * * * * <p> * A subclass can control field output by overriding the methods: * <ul> * <li>{@link #accept(java.lang.reflect.Field)}</li> * <li>{@link #getValue(java.lang.reflect.Field)}</li> * </ul> * </p> * <p> * For example, this method does <i>not</i> include the <code>password</code> field in the returned * <code>String</code>: * </p> * * <pre> * public String toString() { * return (new ReflectionToStringBuilder(this) { * protected boolean accept(Field f) { * return super.accept(f) && !f.getName().equals("password"); * } * }).toString(); * }</pre> * * * * <p> * The exact format of the <code>toString</code> is determined by the {@link ToStringStyle} passed into the * constructor. * </p> * * @author Apache Software Foundation * @author Gary Gregory * @author Pete Gieser * @since 2.0 * @version $Id: ReflectionToStringBuilder.java 905636 2010-02-02 14:03:32Z niallp $ */ public class ReflectionToStringBuilder extends ToStringBuilder { /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value using the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * Transient members will be not be included, as they are likely derived. Static fields will not be included. * Superclass fields will be appended. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to be output * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object is <code>null</code> */ public static String toString(Object object) { return toString(object, null, false, false, null); } /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * Transient members will be not be included, as they are likely derived. Static fields will not be included. * Superclass fields will be appended. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> is used. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to be output * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object or <code>ToStringStyle</code> is <code>null</code> */ public static String toString(Object object, ToStringStyle style) { return toString(object, style, false, false, null); } /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputTransients</code> is <code>true</code>, transient members will be output, otherwise they * are ignored, as they are likely derived fields, and not part of the value of the Object. * </p> * * <p> * Static fields will not be included. Superclass fields will be appended. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> is used. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to be output * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object is <code>null</code> */ public static String toString(Object object, ToStringStyle style, boolean outputTransients) { return toString(object, style, outputTransients, false, null); } /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputTransients</code> is <code>true</code>, transient fields will be output, otherwise they * are ignored, as they are likely derived fields, and not part of the value of the Object. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputStatics</code> is <code>true</code>, static fields will be output, otherwise they are * ignored. * </p> * * <p> * Static fields will not be included. Superclass fields will be appended. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> is used. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to be output * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields * @param outputStatics * whether to include transient fields * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object is <code>null</code> * @since 2.1 */ public static String toString(Object object, ToStringStyle style, boolean outputTransients, boolean outputStatics) { return toString(object, style, outputTransients, outputStatics, null); } /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputTransients</code> is <code>true</code>, transient fields will be output, otherwise they * are ignored, as they are likely derived fields, and not part of the value of the Object. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputStatics</code> is <code>true</code>, static fields will be output, otherwise they are * ignored. * </p> * * <p> * Superclass fields will be appended up to and including the specified superclass. A null superclass is treated as * <code>java.lang.Object</code>. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> is used. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to be output * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields * @param outputStatics * whether to include static fields * @param reflectUpToClass * the superclass to reflect up to (inclusive), may be <code>null</code> * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object is <code>null</code> * @since 2.1 */ public static String toString(Object object, ToStringStyle style, boolean outputTransients, boolean outputStatics, Class reflectUpToClass) { return new ReflectionToStringBuilder(object, style, null, reflectUpToClass, outputTransients, outputStatics) .toString(); } /** * <p> * Builds a <code>toString</code> value through reflection. * </p> * * <p> * It uses <code>AccessibleObject.setAccessible</code> to gain access to private fields. This means that it will * throw a security exception if run under a security manager, if the permissions are not set up correctly. It is * also not as efficient as testing explicitly. * </p> * * <p> * If the <code>outputTransients</code> is <code>true</code>, transient members will be output, otherwise they * are ignored, as they are likely derived fields, and not part of the value of the Object. * </p> * * <p> * Static fields will not be included. Superclass fields will be appended up to and including the specified * superclass. A null superclass is treated as <code>java.lang.Object</code>. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default <code>ToStringStyle</code> is used. * </p> * * @deprecated Use {@link #toString(Object,ToStringStyle,boolean,boolean,Class)} * * @param object * the Object to be output * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields * @param reflectUpToClass * the superclass to reflect up to (inclusive), may be <code>null</code> * @return the String result * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object is <code>null</code> * @since 2.0 */ public static String toString(Object object, ToStringStyle style, boolean outputTransients, Class reflectUpToClass) { return new ReflectionToStringBuilder(object, style, null, reflectUpToClass, outputTransients).toString(); } /** * Builds a String for a toString method excluding the given field name. * * @param object * The object to "toString". * @param excludeFieldName * The field name to exclude * @return The toString value. */ public static String toStringExclude(Object object, final String excludeFieldName) { return toStringExclude(object, new String[]{excludeFieldName}); } /** * Builds a String for a toString method excluding the given field names. * * @param object * The object to "toString". * @param excludeFieldNames * The field names to exclude. Null excludes nothing. * @return The toString value. */ public static String toStringExclude(Object object, Collection /*String*/ excludeFieldNames) { return toStringExclude(object, toNoNullStringArray(excludeFieldNames)); } /** * Converts the given Collection into an array of Strings. The returned array does not contain <code>null</code> * entries. Note that {@link Arrays#sort(Object[])} will throw an {@link NullPointerException} if an array element * is <code>null</code>. * * @param collection * The collection to convert * @return A new array of Strings. */ static String[] toNoNullStringArray(Collection collection) { if (collection == null) { return ArrayUtils.EMPTY_STRING_ARRAY; } return toNoNullStringArray(collection.toArray()); } /** * Returns a new array of Strings without null elements. Internal method used to normalize exclude lists * (arrays and collections). Note that {@link Arrays#sort(Object[])} will throw an {@link NullPointerException} * if an array element is <code>null</code>. * * @param array * The array to check * @return The given array or a new array without null. */ static String[] toNoNullStringArray(Object[] array) { ArrayList list = new ArrayList(array.length); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { Object e = array[i]; if (e != null) { list.add(e.toString()); } } return (String[]) list.toArray(ArrayUtils.EMPTY_STRING_ARRAY); } /** * Builds a String for a toString method excluding the given field names. * * @param object * The object to "toString". * @param excludeFieldNames * The field names to exclude * @return The toString value. */ public static String toStringExclude(Object object, String[] excludeFieldNames) { return new ReflectionToStringBuilder(object).setExcludeFieldNames(excludeFieldNames).toString(); } /** * Whether or not to append static fields. */ private boolean appendStatics = false; /** * Whether or not to append transient fields. */ private boolean appendTransients = false; /** * Which field names to exclude from output. Intended for fields like <code>"password"</code>. */ private String[] excludeFieldNames; /** * The last super class to stop appending fields for. */ private Class upToClass = null; /** * <p> * Constructor. * </p> * * <p> * This constructor outputs using the default style set with <code>setDefaultStyle</code>. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to build a <code>toString</code> for, must not be <code>null</code> * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object passed in is <code>null</code> */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object object) { super(object); } /** * <p> * Constructor. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default style is used. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to build a <code>toString</code> for, must not be <code>null</code> * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object passed in is <code>null</code> */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object object, ToStringStyle style) { super(object, style); } /** * <p> * Constructor. * </p> * * <p> * If the style is <code>null</code>, the default style is used. * </p> * * <p> * If the buffer is <code>null</code>, a new one is created. * </p> * * @param object * the Object to build a <code>toString</code> for * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param buffer * the <code>StringBuffer</code> to populate, may be <code>null</code> * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the Object passed in is <code>null</code> */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object object, ToStringStyle style, StringBuffer buffer) { super(object, style, buffer); } /** * Constructor. * * @deprecated Use {@link #ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object,ToStringStyle,StringBuffer,Class,boolean,boolean)}. * * @param object * the Object to build a <code>toString</code> for * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param buffer * the <code>StringBuffer</code> to populate, may be <code>null</code> * @param reflectUpToClass * the superclass to reflect up to (inclusive), may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object object, ToStringStyle style, StringBuffer buffer, Class reflectUpToClass, boolean outputTransients) { super(object, style, buffer); this.setUpToClass(reflectUpToClass); this.setAppendTransients(outputTransients); } /** * Constructor. * * @param object * the Object to build a <code>toString</code> for * @param style * the style of the <code>toString</code> to create, may be <code>null</code> * @param buffer * the <code>StringBuffer</code> to populate, may be <code>null</code> * @param reflectUpToClass * the superclass to reflect up to (inclusive), may be <code>null</code> * @param outputTransients * whether to include transient fields * @param outputStatics * whether to include static fields * @since 2.1 */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder(Object object, ToStringStyle style, StringBuffer buffer, Class reflectUpToClass, boolean outputTransients, boolean outputStatics) { super(object, style, buffer); this.setUpToClass(reflectUpToClass); this.setAppendTransients(outputTransients); this.setAppendStatics(outputStatics); } /** * Returns whether or not to append the given <code>Field</code>. * <ul> * <li>Transient fields are appended only if {@link #isAppendTransients()} returns <code>true</code>. * <li>Static fields are appended only if {@link #isAppendStatics()} returns <code>true</code>. * <li>Inner class fields are not appened.</li> * </ul> * * @param field * The Field to test. * @return Whether or not to append the given <code>Field</code>. */ protected boolean accept(Field field) { if (field.getName().indexOf(ClassUtils.INNER_CLASS_SEPARATOR_CHAR) != -1) { // Reject field from inner class. return false; } if (Modifier.isTransient(field.getModifiers()) && !this.isAppendTransients()) { // Reject transient fields. return false; } if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers()) && !this.isAppendStatics()) { // Reject static fields. return false; } if (this.getExcludeFieldNames() != null && Arrays.binarySearch(this.getExcludeFieldNames(), field.getName()) >= 0) { // Reject fields from the getExcludeFieldNames list. return false; } return true; } /** * <p> * Appends the fields and values defined by the given object of the given Class. * </p> * * <p> * If a cycle is detected as an object is "toString()'ed", such an object is rendered as if * <code>Object.toString()</code> had been called and not implemented by the object. * </p> * * @param clazz * The class of object parameter */ protected void appendFieldsIn(Class clazz) { if (clazz.isArray()) { this.reflectionAppendArray(this.getObject()); return; } Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); AccessibleObject.setAccessible(fields, true); for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { Field field = fields[i]; String fieldName = field.getName(); if (this.accept(field)) { try { // Warning: Field.get(Object) creates wrappers objects // for primitive types. Object fieldValue = this.getValue(field); this.append(fieldName, fieldValue); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { //this can't happen. Would get a Security exception // instead //throw a runtime exception in case the impossible // happens. throw new InternalError("Unexpected IllegalAccessException: " + ex.getMessage()); } } } } /** * @return Returns the excludeFieldNames. */ public String[] getExcludeFieldNames() { return this.excludeFieldNames; } /** * <p> * Gets the last super class to stop appending fields for. * </p> * * @return The last super class to stop appending fields for. */ public Class getUpToClass() { return this.upToClass; } /** * <p> * Calls <code>java.lang.reflect.Field.get(Object)</code>. * </p> * * @param field * The Field to query. * @return The Object from the given Field. * * @throws IllegalArgumentException * see {@link java.lang.reflect.Field#get(Object)} * @throws IllegalAccessException * see {@link java.lang.reflect.Field#get(Object)} * * @see java.lang.reflect.Field#get(Object) */ protected Object getValue(Field field) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { return field.get(this.getObject()); } /** * <p> * Gets whether or not to append static fields. * </p> * * @return Whether or not to append static fields. * @since 2.1 */ public boolean isAppendStatics() { return this.appendStatics; } /** * <p> * Gets whether or not to append transient fields. * </p> * * @return Whether or not to append transient fields. */ public boolean isAppendTransients() { return this.appendTransients; } /** * <p> * Append to the <code>toString</code> an <code>Object</code> array. * </p> * * @param array * the array to add to the <code>toString</code> * @return this */ public ToStringBuilder reflectionAppendArray(Object array) { this.getStyle().reflectionAppendArrayDetail(this.getStringBuffer(), null, array); return this; } /** * <p> * Sets whether or not to append static fields. * </p> * * @param appendStatics * Whether or not to append static fields. * @since 2.1 */ public void setAppendStatics(boolean appendStatics) { this.appendStatics = appendStatics; } /** * <p> * Sets whether or not to append transient fields. * </p> * * @param appendTransients * Whether or not to append transient fields. */ public void setAppendTransients(boolean appendTransients) { this.appendTransients = appendTransients; } /** * Sets the field names to exclude. * * @param excludeFieldNamesParam * The excludeFieldNames to excluding from toString or <code>null</code>. * @return <code>this</code> */ public ReflectionToStringBuilder setExcludeFieldNames(String[] excludeFieldNamesParam) { if (excludeFieldNamesParam == null) { this.excludeFieldNames = null; } else { this.excludeFieldNames = toNoNullStringArray(excludeFieldNamesParam); Arrays.sort(this.excludeFieldNames); } return this; } /** * <p> * Sets the last super class to stop appending fields for. * </p> * * @param clazz * The last super class to stop appending fields for. */ public void setUpToClass(Class clazz) { if (clazz != null) { Object object = getObject(); if (object != null && clazz.isInstance(object) == false) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified class is not a superclass of the object"); } } this.upToClass = clazz; } /** * <p> * Gets the String built by this builder. * </p> * * @return the built string */ public String toString() { if (this.getObject() == null) { return this.getStyle().getNullText(); } Class clazz = this.getObject().getClass(); this.appendFieldsIn(clazz); while (clazz.getSuperclass() != null && clazz != this.getUpToClass()) { clazz = clazz.getSuperclass(); this.appendFieldsIn(clazz); } return super.toString(); } }
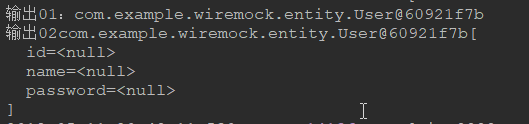
例如:ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(user, ToStringStyle.MULTI_LINE_STYLE)
技巧01:如果一个对象没有重写 toString() 方法,调用该对象的 toString() 方法时就会调用父类Object的toString() 方法,从而输出的信息时常人看不懂的,所以需要使用ReflectionToStringBuilder来进行处理