1 servlet简介
servlet是一种用于开发动态web资源的技术
参考博客:servlet基础知识 httpservlet详解
2 在springboot应用中添加servlet
springboot的主servlet是DispacherServlet,它默认的url-pattern是“/”,如果我们还需要其他的servlet就需要开发人员自己进行定义和注册
2.1 springboot支持代码和注解来注册servlet
2.1.1 代码注册
通过ServletRegistrationBean获得控制
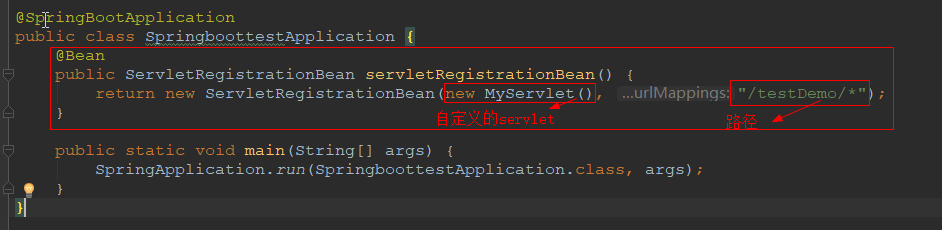

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest; import cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo.MyServlet; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringboottestApplication { @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean() { return new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(), "/testDemo/*"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringboottestApplication.class, args); } }
2.1.2 注解注册
在启动类上标注@ServletComponentScan,在自定义的servlet类上标注@WebServlet即可
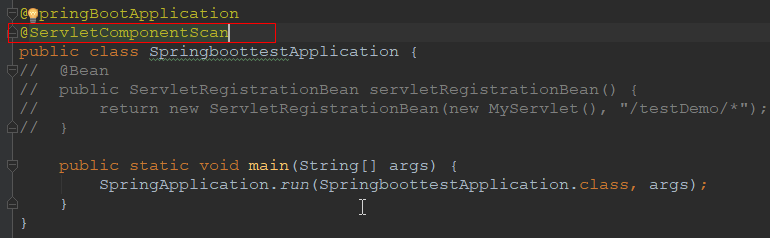

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest; import cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo.MyServlet; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class SpringboottestApplication { // @Bean // public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean() { // return new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(), "/testDemo/*"); // } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringboottestApplication.class, args); } }

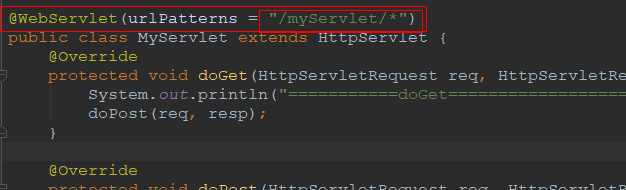
package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/myServlet") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("===========doGet===================="); doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>doPost()<<<<<<<<<<<"); resp.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter(); out.println("hello warrior"); } @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { super.service(req, resp); } @Override public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { super.service(req, res); } }
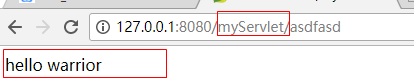
2.1.3 效果展示
任何url是以/myServlet开始的请求都会返回一样的结果
2.2 自定义servlet
继承HttpServlet,再根据需求重写相关方法即可

技巧01:如果是用代码进行注册就不需要在自定义的servlet类上标注@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/myServlet")

/* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package javax.servlet.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * This annotation is used to declare the configuration of an * {@link javax.servlet.Servlet}. <br> * * If the name attribute is not defined, the fully qualified name of the class * is used.<br> * <br> * * At least one URL pattern MUST be declared in either the {@code value} or * {@code urlPattern} attribute of the annotation, but not both.<br> * <br> * * The {@code value} attribute is recommended for use when the URL pattern is * the only attribute being set, otherwise the {@code urlPattern} attribute * should be used.<br> * <br> * * The class on which this annotation is declared MUST extend * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet}. <br> * <br> * * E.g. <code>@WebServlet("/path")}<br> * public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet ... {</code><br> * * E.g. * <code>@WebServlet(name="TestServlet", urlPatterns={"/path", "/alt"}) <br> * public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet ... {</code><br> * * @since Servlet 3.0 (Section 8.1.1) * */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface WebServlet { /** * @return name of the Servlet */ String name() default ""; /** * A convenience method, to allow extremely simple annotation of a class. * * @return array of URL patterns * @see #urlPatterns() */ String[] value() default {}; /** * @return array of URL patterns to which this Filter applies */ String[] urlPatterns() default {}; /** * @return load on startup ordering hint */ int loadOnStartup() default -1; /** * @return array of initialization params for this Servlet */ WebInitParam[] initParams() default {}; /** * @return asynchronous operation supported by this Servlet */ boolean asyncSupported() default false; /** * @return small icon for this Servlet, if present */ String smallIcon() default ""; /** * @return large icon for this Servlet, if present */ String largeIcon() default ""; /** * @return description of this Servlet, if present */ String description() default ""; /** * @return display name of this Servlet, if present */ String displayName() default ""; }

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/myServlet") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("===========doGet===================="); doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>doPost()<<<<<<<<<<<"); resp.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter(); out.println("hello warrior"); } @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { super.service(req, resp); } @Override public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { super.service(req, res); } }
2.3 参考博文
3 过滤器
过滤器和servlet一样,支持代码注册和注解注册;
过滤器可以拿到原始请求和响应的相关信息但是拿不到控制方法的相关信息
3.1 实现方式01
3.1.1 编写自定义过滤器
技巧01:必须实现 Filter 接口
技巧02:init() 方法用于初始化,项目启动的时候就会被调用,而且只会被调用一次
技巧03:destroy() 方法用于销毁,项目关闭的时候会被调用,而且只会被调用一次
技巧04:doFilter() 方法用户处理过滤逻辑,只要满足过滤条件就会被执行;在doFilter方法中必须执行FilterChain对象的doFilter方法,否则前端过来的请求就不会进入到控制层
技巧05:@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*") 注解的作用是指定过滤的请求路径,是一个String类型的数组
技巧06:可以利用 @Order(Integer类型) 来设置该过滤器的顺序号(PS: 实在类级别设置,本博文未进行设置;参考博文 -> 点击前往)


package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.commons.filters; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*") @Slf4j public class TestFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { log.info("自定义顾虑器初始化"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { log.info("自定义过滤操作"); chain.doFilter(request, response); } @Override public void destroy() { log.info("自定义过滤器销毁操作"); } }
3.1.2 在springboot应用启动类上标注@ServletComponentScan

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest; import cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo.MyServlet; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class SpringboottestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringboottestApplication.class, args); } }
3.2 实现方式02
创建一个过滤器类,该类必须实现Filter接口;直接在该过滤器类中添加@Component注解后该过滤器就会生效,无需再做其他任何操作
技巧01:这种方式默认会对所有的请求进行拦截
技巧02:通常只有一个过滤器时使用这种方式,而且这种方式只适用于自定义的过滤器

/** * */ package cn.xiangxu.web.filter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author a * */ @Component public class TimeFilter implements Filter { @Override public void destroy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter destroy"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter start"); Long start = new Date().getTime(); filterChain.doFilter(request, response); System.out.println("filter Timefilter use time : " + (new Date().getTime() - start)); System.out.println("filter TimeFilter finish"); } @Override public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter init"); } }
3.3 实现方式03
实现方式01和实现方式02都只适用于自定义的过滤器,而不适用与第三方的过滤器;如果需要实现第三方的过滤器就必须在web.xml中进行Bean配置
技巧01:SpringBoot项目没有web.xml文件,所以必须进行java配置
技巧02:推荐使用这种方式实现过滤器
3.3.1 导入第三方的过滤器相关jar包
技巧01:本案例用一个自定义的过滤器类来模拟第三方过滤器;该自定义过滤器仅仅实现了Filter接口,在类级别上没有任何注解

/** * */ package cn.xiangxu.web.filter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author a * */ //@Component public class TimeFilter implements Filter { @Override public void destroy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter destroy"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter start"); Long start = new Date().getTime(); filterChain.doFilter(request, response); System.out.println("filter Timefilter use time : " + (new Date().getTime() - start)); System.out.println("filter TimeFilter finish"); } @Override public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("filter TimeFilter init"); } }
3.3.2 java配置类
技巧01:创建一个java类,类级别上添加 @Configuration 来注明该类是一个java配置类;这个类的作用就相当于web.xml
技巧02:定义一个方法,该方法的返回类型是 FilterRegistrationBean ;并在自定义方法上添加 @Bean 注解;这个方法的作用就相当于在web.xml中配置Bean
技巧03:可以在配置类中设置过滤器名称、过滤器顺序号以及过滤排除规则
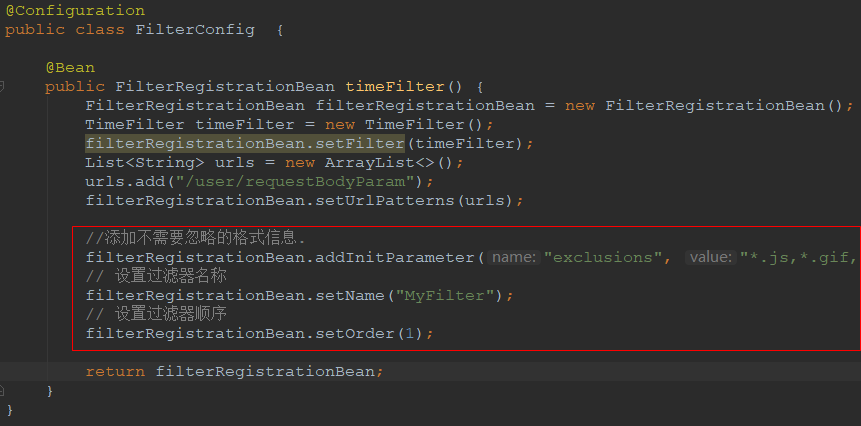

package cn.xiangxu.demo03.comm.config; import cn.xiangxu.demo03.comm.filters.TimeFilter; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import javax.servlet.FilterRegistration; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王杨帅 * @create 2018-06-06 14:31 * @desc 过滤器配置类 **/ @Configuration public class FilterConfig { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean timeFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); TimeFilter timeFilter = new TimeFilter(); filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(timeFilter); List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); urls.add("/user/requestBodyParam"); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(urls); //添加不需要忽略的格式信息. filterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("exclusions", "*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid2/*"); // 设置过滤器名称 filterRegistrationBean.setName("MyFilter"); // 设置过滤器顺序 filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(1); return filterRegistrationBean; } }

package cn.xiangxu.web.config; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import cn.xiangxu.web.filter.TimeFilter; @Configuration public class WebConfig { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean timeFilter() { // 01 实例化过滤器注册对象 FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); // 02 实例化自定义过滤器 TimeFilter timeFilter = new TimeFilter(); // 03 利用过滤器注册对象对自定义过滤器进行注册 filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(timeFilter); // 04 设置自定义过滤器的过滤路径 List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); urls.add("/*"); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(urls); return filterRegistrationBean; } }
4 监听器
监听器同样支持代码和注解两种注册方式
4.1 自定义监听器


package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.commons.listeners; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener; @WebListener @Slf4j public class TestServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { log.info("测试上下文监听初始化"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { log.info("测试上下文监听销毁"); } }
4.2 在springboot应用启动类上标注@ServletComponentScan

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest; import cn.xiangxu.springboottest.TestDemo.MyServlet; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class SpringboottestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringboottestApplication.class, args); } }
5 拦截器
5.1 HandlerInterceptor
spring为我们提供了HandlerInterceptor接口来实现拦截器功能
HandlerInterceptor在调用controller之前和调用controller之后以及视图渲染完成之后都可以得到控制;我们不可以通过拦截器来修改request内容,但是我们可以通过抛出异常或者返回false来结束请求
技巧01:拦截器可以获取到原始的请求和响应信息,也可以拿到controlelr层的类名信息和方法名信息;但是拿不到方法的参数信息;因为DispatcherServlet在进行请求分发时先执行拦截器,然后在将请求数据封装到controller层中控制方法的参数上去的。

* Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. package org.springframework.web.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContext; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils; import org.springframework.http.server.ServletServerHttpRequest; import org.springframework.ui.context.ThemeSource; import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletWebRequest; import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager; import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncUtils; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartHttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver; import org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException; import org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils; /** * Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers * or HTTP-based remote service exporters. Dispatches to registered handlers for processing * a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities. * * <p>This servlet is very flexible: It can be used with just about any workflow, with the * installation of the appropriate adapter classes. It offers the following functionality * that distinguishes it from other request-driven web MVC frameworks: * * <ul> * <li>It is based around a JavaBeans configuration mechanism. * * <li>It can use any {@link HandlerMapping} implementation - pre-built or provided as part * of an application - to control the routing of requests to handler objects. Default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping} and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping}. * HandlerMapping objects can be defined as beans in the servlet's application context, * implementing the HandlerMapping interface, overriding the default HandlerMapping if * present. HandlerMappings can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>It can use any {@link HandlerAdapter}; this allows for using any handler interface. * Default adapters are {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter}, * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter}, for Spring's * {@link org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler} and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller} interfaces, respectively. A default * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter} * will be registered as well. HandlerAdapter objects can be added as beans in the * application context, overriding the default HandlerAdapters. Like HandlerMappings, * HandlerAdapters can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>The dispatcher's exception resolution strategy can be specified via a * {@link HandlerExceptionResolver}, for example mapping certain exceptions to error pages. * Default are * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver}, * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver}, and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver}. * These HandlerExceptionResolvers can be overridden through the application context. * HandlerExceptionResolver can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>Its view resolution strategy can be specified via a {@link ViewResolver} * implementation, resolving symbolic view names into View objects. Default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver}. * ViewResolver objects can be added as beans in the application context, overriding the * default ViewResolver. ViewResolvers can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>If a {@link View} or view name is not supplied by the user, then the configured * {@link RequestToViewNameTranslator} will translate the current request into a view name. * The corresponding bean name is "viewNameTranslator"; the default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator}. * * <li>The dispatcher's strategy for resolving multipart requests is determined by a * {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver} implementation. * Implementations for Apache Commons FileUpload and Servlet 3 are included; the typical * choice is {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver}. * The MultipartResolver bean name is "multipartResolver"; default is none. * * <li>Its locale resolution strategy is determined by a {@link LocaleResolver}. * Out-of-the-box implementations work via HTTP accept header, cookie, or session. * The LocaleResolver bean name is "localeResolver"; default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver}. * * <li>Its theme resolution strategy is determined by a {@link ThemeResolver}. * Implementations for a fixed theme and for cookie and session storage are included. * The ThemeResolver bean name is "themeResolver"; default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver}. * </ul> * * <p><b>NOTE: The {@code @RequestMapping} annotation will only be processed if a * corresponding {@code HandlerMapping} (for type-level annotations) and/or * {@code HandlerAdapter} (for method-level annotations) is present in the dispatcher.</b> * This is the case by default. However, if you are defining custom {@code HandlerMappings} * or {@code HandlerAdapters}, then you need to make sure that a corresponding custom * {@code DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping} and/or {@code AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter} * is defined as well - provided that you intend to use {@code @RequestMapping}. * * <p><b>A web application can define any number of DispatcherServlets.</b> * Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context * with mappings, handlers, etc. Only the root application context as loaded by * {@link org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener}, if any, will be shared. * * <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code DispatcherServlet} may now be injected with a web * application context, rather than creating its own internally. This is useful in Servlet * 3.0+ environments, which support programmatic registration of servlet instances. * See the {@link #DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)} javadoc for details. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Rob Harrop * @author Chris Beams * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @see org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller * @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { /** Well-known name for the MultipartResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "multipartResolver"; /** Well-known name for the LocaleResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "localeResolver"; /** Well-known name for the ThemeResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "themeResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerMapping object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerMappings" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerMappings */ public static final String HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME = "handlerMapping"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerAdapter object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerAdapters" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerAdapters */ public static final String HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerAdapter"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerExceptionResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers */ public static final String HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerExceptionResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the RequestToViewNameTranslator object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME = "viewNameTranslator"; /** * Well-known name for the ViewResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllViewResolvers" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllViewResolvers */ public static final String VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "viewResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the FlashMapManager object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "flashMapManager"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current web application context. * Otherwise only the global web app context is obtainable by tags etc. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#findWebApplicationContext */ public static final String WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current LocaleResolver, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getLocaleResolver */ public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".LOCALE_RESOLVER"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current ThemeResolver, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getThemeResolver */ public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_RESOLVER"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current ThemeSource, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getThemeSource */ public static final String THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_SOURCE"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds a read-only {@code Map<String,?>} * with "input" flash attributes saved by a previous request, if any. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getInputFlashMap(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".INPUT_FLASH_MAP"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds the "output" {@link FlashMap} with * attributes to save for a subsequent request. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getOutputFlashMap(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds the {@link FlashMapManager}. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getFlashMapManager(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".FLASH_MAP_MANAGER"; /** * Name of request attribute that exposes an Exception resolved with an * {@link HandlerExceptionResolver} but where no view was rendered * (e.g. setting the status code). */ public static final String EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".EXCEPTION"; /** Log category to use when no mapped handler is found for a request. */ public static final String PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY = "org.springframework.web.servlet.PageNotFound"; /** * Name of the class path resource (relative to the DispatcherServlet class) * that defines DispatcherServlet's default strategy names. */ private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties"; /** * Common prefix that DispatcherServlet's default strategy attributes start with. */ private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX = "org.springframework.web.servlet"; /** Additional logger to use when no mapped handler is found for a request. */ protected static final Log pageNotFoundLogger = LogFactory.getLog(PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY); private static final Properties defaultStrategies; static { // Load default strategy implementations from properties file. // This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized // by application developers. try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage()); } } /** Detect all HandlerMappings or just expect "handlerMapping" bean? */ private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true; /** Detect all HandlerAdapters or just expect "handlerAdapter" bean? */ private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true; /** Detect all HandlerExceptionResolvers or just expect "handlerExceptionResolver" bean? */ private boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = true; /** Detect all ViewResolvers or just expect "viewResolver" bean? */ private boolean detectAllViewResolvers = true; /** Throw a NoHandlerFoundException if no Handler was found to process this request? **/ private boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = false; /** Perform cleanup of request attributes after include request? */ private boolean cleanupAfterInclude = true; /** MultipartResolver used by this servlet */ private MultipartResolver multipartResolver; /** LocaleResolver used by this servlet */ private LocaleResolver localeResolver; /** ThemeResolver used by this servlet */ private ThemeResolver themeResolver; /** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet */ private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings; /** List of HandlerAdapters used by this servlet */ private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters; /** List of HandlerExceptionResolvers used by this servlet */ private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers; /** RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet */ private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator; /** FlashMapManager used by this servlet */ private FlashMapManager flashMapManager; /** List of ViewResolvers used by this servlet */ private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers; /** * Create a new {@code DispatcherServlet} that will create its own internal web * application context based on defaults and values provided through servlet * init-params. Typically used in Servlet 2.5 or earlier environments, where the only * option for servlet registration is through {@code web.xml} which requires the use * of a no-arg constructor. * <p>Calling {@link #setContextConfigLocation} (init-param 'contextConfigLocation') * will dictate which XML files will be loaded by the * {@linkplain #DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS default XmlWebApplicationContext} * <p>Calling {@link #setContextClass} (init-param 'contextClass') overrides the * default {@code XmlWebApplicationContext} and allows for specifying an alternative class, * such as {@code AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext}. * <p>Calling {@link #setContextInitializerClasses} (init-param 'contextInitializerClasses') * indicates which {@code ApplicationContextInitializer} classes should be used to * further configure the internal application context prior to refresh(). * @see #DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) */ public DispatcherServlet() { super(); setDispatchOptionsRequest(true); } /** * Create a new {@code DispatcherServlet} with the given web application context. This * constructor is useful in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based registration * of servlets is possible through the {@link ServletContext#addServlet} API. * <p>Using this constructor indicates that the following properties / init-params * will be ignored: * <ul> * <li>{@link #setContextClass(Class)} / 'contextClass'</li> * <li>{@link #setContextConfigLocation(String)} / 'contextConfigLocation'</li> * <li>{@link #setContextAttribute(String)} / 'contextAttribute'</li> * <li>{@link #setNamespace(String)} / 'namespace'</li> * </ul> * <p>The given web application context may or may not yet be {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refreshed}. If it has <strong>not</strong> * already been refreshed (the recommended approach), then the following will occur: * <ul> * <li>If the given context does not already have a {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#setParent parent}, the root application context * will be set as the parent.</li> * <li>If the given context has not already been assigned an {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#setId id}, one will be assigned to it</li> * <li>{@code ServletContext} and {@code ServletConfig} objects will be delegated to * the application context</li> * <li>{@link #postProcessWebApplicationContext} will be called</li> * <li>Any {@code ApplicationContextInitializer}s specified through the * "contextInitializerClasses" init-param or through the {@link * #setContextInitializers} property will be applied.</li> * <li>{@link ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh refresh()} will be called if the * context implements {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext}</li> * </ul> * If the context has already been refreshed, none of the above will occur, under the * assumption that the user has performed these actions (or not) per their specific * needs. * <p>See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples. * @param webApplicationContext the context to use * @see #initWebApplicationContext * @see #configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer */ public DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) { super(webApplicationContext); setDispatchOptionsRequest(true); } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerMapping beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerMapping" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerMapping, despite multiple HandlerMapping beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerMappings(boolean detectAllHandlerMappings) { this.detectAllHandlerMappings = detectAllHandlerMappings; } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerAdapter beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerAdapter" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerAdapter, despite multiple HandlerAdapter beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerAdapters(boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters) { this.detectAllHandlerAdapters = detectAllHandlerAdapters; } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerExceptionResolver beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerExceptionResolver" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerExceptionResolver, despite multiple HandlerExceptionResolver beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers(boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) { this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers; } /** * Set whether to detect all ViewResolver beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "viewResolver" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * ViewResolver, despite multiple ViewResolver beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllViewResolvers(boolean detectAllViewResolvers) { this.detectAllViewResolvers = detectAllViewResolvers; } /** * Set whether to throw a NoHandlerFoundException when no Handler was found for this request. * This exception can then be caught with a HandlerExceptionResolver or an * {@code @ExceptionHandler} controller method. * <p>Note that if {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler} * is used, then requests will always be forwarded to the default servlet and a * NoHandlerFoundException would never be thrown in that case. * <p>Default is "false", meaning the DispatcherServlet sends a NOT_FOUND error through the * Servlet response. * @since 4.0 */ public void setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound; } /** * Set whether to perform cleanup of request attributes after an include request, that is, * whether to reset the original state of all request attributes after the DispatcherServlet * has processed within an include request. Otherwise, just the DispatcherServlet's own * request attributes will be reset, but not model attributes for JSPs or special attributes * set by views (for example, JSTL's). * <p>Default is "true", which is strongly recommended. Views should not rely on request attributes * having been set by (dynamic) includes. This allows JSP views rendered by an included controller * to use any model attributes, even with the same names as in the main JSP, without causing side * effects. Only turn this off for special needs, for example to deliberately allow main JSPs to * access attributes from JSP views rendered by an included controller. */ public void setCleanupAfterInclude(boolean cleanupAfterInclude) { this.cleanupAfterInclude = cleanupAfterInclude; } /** * This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}. */ @Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } /** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); } /** * Initialize the MultipartResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * no multipart handling is provided. */ private void initMultipartResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.multipartResolver = context.getBean(MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, MultipartResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using MultipartResolver [" + this.multipartResolver + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Default is no multipart resolver. this.multipartResolver = null; if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate MultipartResolver with name '" + MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': no multipart request handling provided"); } } } /** * Initialize the LocaleResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver. */ private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using LocaleResolver [" + this.localeResolver + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate LocaleResolver with name '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.localeResolver + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the ThemeResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to a FixedThemeResolver. */ private void initThemeResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.themeResolver = context.getBean(THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ThemeResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using ThemeResolver [" + this.themeResolver + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.themeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, ThemeResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate ThemeResolver with name '" + THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.themeResolver + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerAdapters used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerAdapter beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter. */ private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerAdapters = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) { // Find all HandlerAdapters in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<HandlerAdapter>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerAdapters in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters); } } else { try { HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class); this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerAdapter later. } } // Ensure we have at least some HandlerAdapters, by registering // default HandlerAdapters if no other adapters are found. if (this.handlerAdapters == null) { this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerAdapters found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerExceptionResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to no exception resolver. */ private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) { // Find all HandlerExceptionResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerExceptionResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils .beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<HandlerExceptionResolver>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerExceptionResolvers in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerExceptionResolvers); } } else { try { HandlerExceptionResolver her = context.getBean(HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerExceptionResolver.class); this.handlerExceptionResolvers = Collections.singletonList(her); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, no HandlerExceptionResolver is fine too. } } // Ensure we have at least some HandlerExceptionResolvers, by registering // default HandlerExceptionResolvers if no other resolvers are found. if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers == null) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerExceptionResolvers found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } } /** * Initialize the RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet instance. * <p>If no implementation is configured then we default to DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator. */ private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.viewNameTranslator = context.getBean(REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using RequestToViewNameTranslator [" + this.viewNameTranslator + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.viewNameTranslator = getDefaultStrategy(context, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate RequestToViewNameTranslator with name '" + REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.viewNameTranslator + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the ViewResolvers used by this class. * <p>If no ViewResolver beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this * namespace, we default to InternalResourceViewResolver. */ private void initViewResolvers(ApplicationContext context) { this.viewResolvers = null; if (this.detectAllViewResolvers) { // Find all ViewResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, ViewResolver.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<ViewResolver>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep ViewResolvers in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.viewResolvers); } } else { try { ViewResolver vr = context.getBean(VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ViewResolver.class); this.viewResolvers = Collections.singletonList(vr); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default ViewResolver later. } } // Ensure we have at least one ViewResolver, by registering // a default ViewResolver if no other resolvers are found. if (this.viewResolvers == null) { this.viewResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, ViewResolver.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No ViewResolvers found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } } /** * Initialize the {@link FlashMapManager} used by this servlet instance. * <p>If no implementation is configured then we default to * {@code org.springframework.web.servlet.support.DefaultFlashMapManager}. */ private void initFlashMapManager(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.flashMapManager = context.getBean(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME, FlashMapManager.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using FlashMapManager [" + this.flashMapManager + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.flashMapManager = getDefaultStrategy(context, FlashMapManager.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate FlashMapManager with name '" + FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.flashMapManager + "]"); } } } /** * Return this servlet's ThemeSource, if any; else return {@code null}. * <p>Default is to return the WebApplicationContext as ThemeSource, * provided that it implements the ThemeSource interface. * @return the ThemeSource, if any * @see #getWebApplicationContext() */ public final ThemeSource getThemeSource() { if (getWebApplicationContext() instanceof ThemeSource) { return (ThemeSource) getWebApplicationContext(); } else { return null; } } /** * Obtain this servlet's MultipartResolver, if any. * @return the MultipartResolver used by this servlet, or {@code null} if none * (indicating that no multipart support is available) */ public final MultipartResolver getMultipartResolver() { return this.multipartResolver; } /** * Return the default strategy object for the given strategy interface. * <p>The default implementation delegates to {@link #getDefaultStrategies}, * expecting a single object in the list. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param strategyInterface the strategy interface * @return the corresponding strategy object * @see #getDefaultStrategies */ protected <T> T getDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { List<T> strategies = getDefaultStrategies(context, strategyInterface); if (strategies.size() != 1) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "DispatcherServlet needs exactly 1 strategy for interface [" + strategyInterface.getName() + "]"); } return strategies.get(0); } /** * Create a List of default strategy objects for the given strategy interface. * <p>The default implementation uses the "DispatcherServlet.properties" file (in the same * package as the DispatcherServlet class) to determine the class names. It instantiates * the strategy objects through the context's BeanFactory. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param strategyInterface the strategy interface * @return the List of corresponding strategy objects */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { String key = strategyInterface.getName(); String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); if (value != null) { String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length); for (String className : classNames) { try { Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); strategies.add((T) strategy); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class", err); } } return strategies; } else { return new LinkedList<T>(); } } /** * Create a default strategy. * <p>The default implementation uses * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean}. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param clazz the strategy implementation class to instantiate * @return the fully configured strategy instance * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext#getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean */ protected Object createDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<?> clazz) { return context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().createBean(clazz); } /** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } } /** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } } /** * Do we need view name translation? */ private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception { if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) { mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request)); } } /** * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView. */ private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } } /** * Build a LocaleContext for the given request, exposing the request's primary locale as current locale. * <p>The default implementation uses the dispatcher's LocaleResolver to obtain the current locale, * which might change during a request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the corresponding LocaleContext */ @Override protected LocaleContext buildLocaleContext(final HttpServletRequest request) { if (this.localeResolver instanceof LocaleContextResolver) { return ((LocaleContextResolver) this.localeResolver).resolveLocaleContext(request); } else { return new LocaleContext() { @Override public Locale getLocale() { return localeResolver.resolveLocale(request); } }; } } /** * Convert the request into a multipart request, and make multipart resolver available. * <p>If no multipart resolver is set, simply use the existing request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the processed request (multipart wrapper if necessary) * @see MultipartResolver#resolveMultipart */ protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException { if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) { if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) { logger.debug("Request is already a MultipartHttpServletRequest - if not in a forward, " + "this typically results from an additional MultipartFilter in web.xml"); } else if (hasMultipartException(request) ) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for current request before - " + "skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering"); } else { try { return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request); } catch (MultipartException ex) { if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex); // Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below } else { throw ex; } } } } // If not returned before: return original request. return request; } /** * Check "javax.servlet.error.exception" attribute for a multipart exception. */ private boolean hasMultipartException(HttpServletRequest request) { Throwable error = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE); while (error != null) { if (error instanceof MultipartException) { return true; } error = error.getCause(); } return false; } /** * Clean up any resources used by the given multipart request (if any). * @param request current HTTP request * @see MultipartResolver#cleanupMultipart */ protected void cleanupMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) { MultipartHttpServletRequest multipartRequest = WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class); if (multipartRequest != null) { this.multipartResolver.cleanupMultipart(multipartRequest); } } /** * Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request. * <p>Tries all handler mappings in order. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found */ protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; } /** * No handler found -> set appropriate HTTP response status. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception if preparing the response failed */ protected void noHandlerFound(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (pageNotFoundLogger.isWarnEnabled()) { pageNotFoundLogger.warn("No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } if (this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { throw new NoHandlerFoundException(request.getMethod(), getRequestUri(request), new ServletServerHttpRequest(request).getHeaders()); } else { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); } } /** * Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object. * @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for * @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error. */ protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); } if (ha.supports(handler)) { return ha; } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); } /** * Determine an error ModelAndView via the registered HandlerExceptionResolvers. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the time of the exception * (for example, if multipart resolution failed) * @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution * @return a corresponding ModelAndView to forward to * @throws Exception if no error ModelAndView found */ protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers... ModelAndView exMv = null; for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) { exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (exMv != null) { break; } } if (exMv != null) { if (exMv.isEmpty()) { request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex); return null; } // We might still need view name translation for a plain error model... if (!exMv.hasView()) { exMv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request)); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Handler execution resulted in exception - forwarding to resolved error view: " + exMv, ex); } WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName()); return exMv; } throw ex; } /** * Render the given ModelAndView. * <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name. * @param mv the ModelAndView to render * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @param response current HTTP servlet response * @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved * @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view */ protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request); response.setLocale(locale); View view; if (mv.isReference()) { // We need to resolve the view name. view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + "' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } else { // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView(); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } // Delegate to the View object for rendering. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } try { if (mv.getStatus() != null) { response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); } view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } } /** * Translate the supplied request into a default view name. * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the view name (or {@code null} if no default found) * @throws Exception if view name translation failed */ protected String getDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { return this.viewNameTranslator.getViewName(request); } /** * Resolve the given view name into a View object (to be rendered). * <p>The default implementations asks all ViewResolvers of this dispatcher. * Can be overridden for custom resolution strategies, potentially based on * specific model attributes or request parameters. * @param viewName the name of the view to resolve * @param model the model to be passed to the view * @param locale the current locale * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the View object, or {@code null} if none found * @throws Exception if the view cannot be resolved * (typically in case of problems creating an actual View object) * @see ViewResolver#resolveViewName */ protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); if (view != null) { return view; } } return null; } private void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, Exception ex) throws Exception { if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, ex); } throw ex; } /** * Restore the request attributes after an include. * @param request current HTTP request * @param attributesSnapshot the snapshot of the request attributes before the include */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void restoreAttributesAfterInclude(HttpServletRequest request, Map<?,?> attributesSnapshot) { // Need to copy into separate Collection here, to avoid side effects // on the Enumeration when removing attributes. Set<String> attrsToCheck = new HashSet<String>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attrsToCheck.add(attrName); } } // Add attributes that may have been removed attrsToCheck.addAll((Set<String>) attributesSnapshot.keySet()); // Iterate over the attributes to check, restoring the original value // or removing the attribute, respectively, if appropriate. for (String attrName : attrsToCheck) { Object attrValue = attributesSnapshot.get(attrName); if (attrValue == null){ request.removeAttribute(attrName); } else if (attrValue != request.getAttribute(attrName)) { request.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue); } } } private static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) { String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE); if (uri == null) { uri = request.getRequestURI(); } return uri; } }
5.2 创建自定义拦截器
自定义拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口,然后根据自己的需求去重写相应的方法
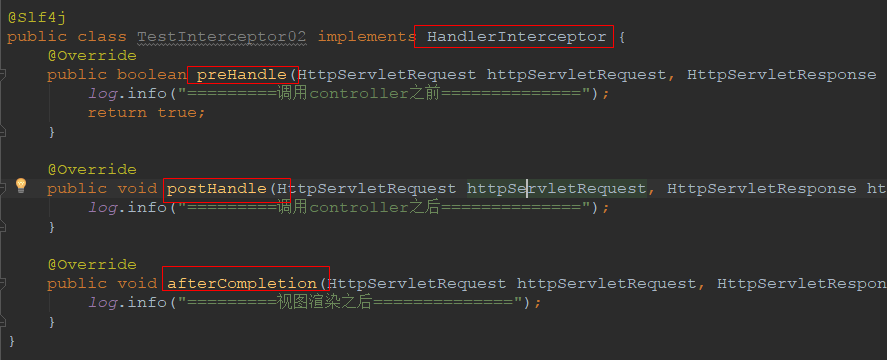

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.commons.intereceptors; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @Slf4j public class TestInterceptor02 implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o) throws Exception { log.info("=========调用controller之前=============="); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { log.info("=========调用controller之后=============="); } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception { log.info("=========视图渲染之后=============="); } }
5.2.1 preHandle
调用controller之前执行,如果该方法返回false或者抛出异常就会结束请求
技巧01:preHandle返回false或者抛出异常是就不会在继续往下执行(即:不会在今日conroller层,也不会执行postHandle和afterCompletion)
5.2.2 postHandle
调用controller之后视图渲染完成之前
技巧01:如果controller层中的方法抛出了异常就会不会执行该方法了
5.2.3 afterCompletion
视图渲染完成之后
技巧01:不管controller层是否抛出异常都会执行该方法,只有preHandle返回false或者preHandle方法中抛出异常才不会执行该方法
5.3 配置自定义拦截器
spring为我们提供了 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 我们只需要重写addInterceptors方法就可以实现自定义拦截器的配置
技巧01:继承了WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类后我们可以通过该重写相关方法来实现配置
坑01:从spring5.0和springBoot2.0开始WebMvcConfigurerAdapter就失效了,解决办法在下面一节
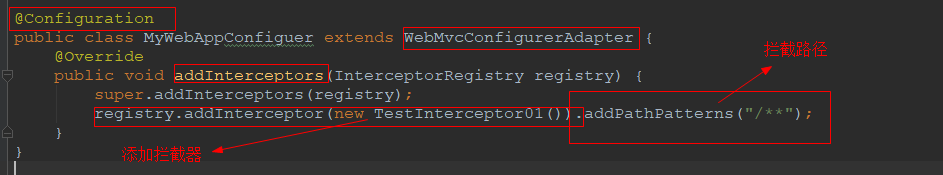

package cn.xiangxu.springboottest.config; import cn.xiangxu.springboottest.commons.intereceptors.TestInterceptor01; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; @Configuration public class MyWebAppConfiguer extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { super.addInterceptors(registry); registry.addInterceptor(new TestInterceptor01()).addPathPatterns("/**"); } }
6 切面(AOP)
6.1 切面三要素
》切哪里 -> 切入点
》什么时候切 -> 增强
》干什么 -> 增强逻辑
6.2 自定义切面类
技巧01:在切面类上添加@Aspect 和 @Component

package cn.xiangxu.web.aspects; import java.util.Date; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class TimeAspect { /** * * @param pjp ProceedingJoinPoint对象,该对象包含了切面方法的所有信息 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Around("execution(* cn.xiangxu.web.controller.UserController.*(..))") public Object handleControllerMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("AOP TimeAspect start"); Long start = new Date().getTime(); Object [] args = pjp.getArgs(); // 获取方法参数 for (Object arg : args) { System.out.println("arg is : " + arg); } Object result = pjp.proceed(); // 执行切面方法,返回值就是切面方法的返回值(获取方法返回值) System.out.println("AOP TimeAspect result is : " + result.toString()); System.out.println("AOP TimeAspect use time : " + (new Date().getTime() - start)); System.out.println("AOP TimeAspect end"); return result; } }
6.3 AOP参考博文
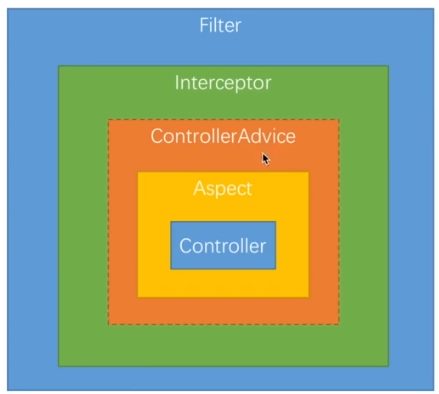
6.4 过滤器、拦截器、切面执行顺序
7 webmvcconfigureradapter过时问题
在修改一些SpringBoot的默认配置时需要继承webmvcconfigureradapter,但是从spring5.0和springboot2.0开始这个类就逐渐被废弃掉了;但是从webmvcconfigureradapter的源码可以看出这个类实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口,所以我们可以在自定义的配置类中直接实现WebMvcConfigurer接口即可
技巧01:虽然是实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口,但是不需要重写WebMvcConfigurer中的所有方法,仅仅根据需求进行重写就可以啦
参考博文:点击前往
·下面是我的公众号二维码,欢迎关注·
尋渝記

微信号:xyj_fury
