1 方法的参数
1.1 必选参数
调用方法时实参的个数必须和定义方法时形参在数量和类型上匹配
1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(x: number): number { 5 return x + 10; 6 } 7 8 let y = test(210); 9 console.log(y); 10 11 // let y02 = test(); // 报错:缺少参数信息

1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(x) { 5 return x + 10; 6 } 7 var y = test(210); 8 console.log(y); 9 // let y02 = test(); // 报错:缺少参数信息
1.2 可选参数
调用方法时该参数可以不传入值
/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function test(x?: number): number { if(x) { return x + 100; } else { return 999; } } let y = test(); // 不传入参数 console.log(y); let y02 = test(100); // 传入参数 console.log((y02));

1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(x) { 5 if (x) { 6 return x + 100; 7 } 8 else { 9 return 999; 10 } 11 } 12 var y = test(); // 不传入参数 13 console.log(y); 14 var y02 = test(100); // 传入参数 15 console.log((y02));
1.3 默认参数
调用方法时该参数可以传入,也可以不传入;不传入时就使用默认值
1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(x: number = 100): number { 5 return x + 100; 6 } 7 8 let y = test(899); // 传入参数 9 console.log(y); 10 11 let y02 = test(); // 不传入参数 12 console.log(y02);

1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(x) { 5 if (x === void 0) { x = 100; } 6 return x + 100; 7 } 8 var y = test(899); // 传入参数 9 console.log(y); 10 var y02 = test(); // 不传入参数 11 console.log(y02);
1.4 参数的顺序
必选参数 -> 可选参数 -> 默认参数
注意:可选参数必须在必选参数后面,默认参数没有要求,但是如果默认参数在必选参数前面,那么在不传入默认参数时就需要传入一个undefined去占位置
2 参数个数
2.1 任意多个单数01
调用方法时可以传入任意多个参数,而且参数的类型没有限定
/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function test(...args) { args.forEach(function (arg) { console.log(arg); }); } test(1,"warrior",2,"fury",[11,22,33],"fury",{name:"warrior", age: 24});

/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function test() { var args = []; for (var _i = 0; _i < arguments.length; _i++) { args[_i] = arguments[_i]; } args.forEach(function (arg) { console.log(arg); }); } test(1, "warrior", 2, "fury", [11, 22, 33], "fury", { name: "warrior", age: 24 });
运行JS代码的结果为
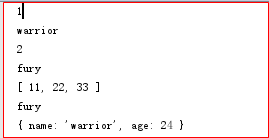
2.2 任意多个单数02
将要传入的任意多个实参组合成一个数组,然后再传到方法中去
1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. 3 */ 4 function test(...args) { 5 args.forEach(function (arg) { 6 console.log(arg); 7 }); 8 } 9 10 // test(1,"warrior",2,"fury",[11,22,33],"fury",{name:"warrior", age: 24}); 11 12 var arg02 = [1,"warrior",2,"fury",[11,22,33],"fury",{name:"warrior", age: 24}]; 13 test(...arg02);

/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function test() { var args = []; for (var _i = 0; _i < arguments.length; _i++) { args[_i] = arguments[_i]; } args.forEach(function (arg) { console.log(arg); }); } // test(1,"warrior",2,"fury",[11,22,33],"fury",{name:"warrior", age: 24}); var arg02 = [1, "warrior", 2, "fury", [11, 22, 33], "fury", { name: "warrior", age: 24 }]; test.apply(void 0, arg02);
运行JS代码的结果为
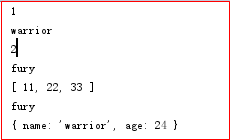
3 generate方法
调用不同,函数体遇到yield就会停下来
/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function* test() { console.log("start"); yield console.log("second"); // 相当于设置了一个断点,执行完yield后面的代码就会停下来 console.log("finish"); } let foo = test(); // 不能直接用 test() 去调用方法 foo.next(); // 执行完yield后面的代码就会停下来 // foo.next();

var __generator = (this && this.__generator) || function (thisArg, body) { var _ = { label: 0, sent: function() { if (t[0] & 1) throw t[1]; return t[1]; }, trys: [], ops: [] }, f, y, t, g; return g = { next: verb(0), "throw": verb(1), "return": verb(2) }, typeof Symbol === "function" && (g[Symbol.iterator] = function() { return this; }), g; function verb(n) { return function (v) { return step([n, v]); }; } function step(op) { if (f) throw new TypeError("Generator is already executing."); while (_) try { if (f = 1, y && (t = y[op[0] & 2 ? "return" : op[0] ? "throw" : "next"]) && !(t = t.call(y, op[1])).done) return t; if (y = 0, t) op = [0, t.value]; switch (op[0]) { case 0: case 1: t = op; break; case 4: _.label++; return { value: op[1], done: false }; case 5: _.label++; y = op[1]; op = [0]; continue; case 7: op = _.ops.pop(); _.trys.pop(); continue; default: if (!(t = _.trys, t = t.length > 0 && t[t.length - 1]) && (op[0] === 6 || op[0] === 2)) { _ = 0; continue; } if (op[0] === 3 && (!t || (op[1] > t[0] && op[1] < t[3]))) { _.label = op[1]; break; } if (op[0] === 6 && _.label < t[1]) { _.label = t[1]; t = op; break; } if (t && _.label < t[2]) { _.label = t[2]; _.ops.push(op); break; } if (t[2]) _.ops.pop(); _.trys.pop(); continue; } op = body.call(thisArg, _); } catch (e) { op = [6, e]; y = 0; } finally { f = t = 0; } if (op[0] & 5) throw op[1]; return { value: op[0] ? op[1] : void 0, done: true }; } }; /** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function test() { return __generator(this, function (_a) { switch (_a.label) { case 0: console.log("start"); return [4 /*yield*/, console.log("second")]; case 1: _a.sent(); // 相当于设置了一个断点,执行完yield后面的代码就会停下来 console.log("finish"); return [2 /*return*/]; } }); } var foo = test(); // 不能直接用 test() 去调用方法 foo.next(); // 执行完yield后面的代码就会停下来 // foo.next();
运行JS代码的结果为
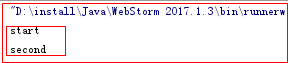
3.1 generate方法小案例
模拟股票价格变化,当达到预定值后就进行买入操作
/** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function* getStockPrice() { while(true) { yield Math.random()*100; // 产生随机数来模拟股票价格 } } let priceGenerate = getStockPrice(); let currentPrice = 150; // 设定一个当前价格 let limitPrice = 20; // 设定一个买入价格 while(currentPrice > limitPrice) { // 到上一时刻的价格大于买入价格时就获取当前时刻的价格并打印当前时刻的价格 currentPrice = priceGenerate.next().value; console.log(`当前股票的价格为:${currentPrice}`); } console.log(`当前股票的价格已经低于${limitPrice},所以进行了自动买入操作。`); // 当股票价格低于买入价格时,就进行自动买入操作

var __generator = (this && this.__generator) || function (thisArg, body) { var _ = { label: 0, sent: function() { if (t[0] & 1) throw t[1]; return t[1]; }, trys: [], ops: [] }, f, y, t, g; return g = { next: verb(0), "throw": verb(1), "return": verb(2) }, typeof Symbol === "function" && (g[Symbol.iterator] = function() { return this; }), g; function verb(n) { return function (v) { return step([n, v]); }; } function step(op) { if (f) throw new TypeError("Generator is already executing."); while (_) try { if (f = 1, y && (t = y[op[0] & 2 ? "return" : op[0] ? "throw" : "next"]) && !(t = t.call(y, op[1])).done) return t; if (y = 0, t) op = [0, t.value]; switch (op[0]) { case 0: case 1: t = op; break; case 4: _.label++; return { value: op[1], done: false }; case 5: _.label++; y = op[1]; op = [0]; continue; case 7: op = _.ops.pop(); _.trys.pop(); continue; default: if (!(t = _.trys, t = t.length > 0 && t[t.length - 1]) && (op[0] === 6 || op[0] === 2)) { _ = 0; continue; } if (op[0] === 3 && (!t || (op[1] > t[0] && op[1] < t[3]))) { _.label = op[1]; break; } if (op[0] === 6 && _.label < t[1]) { _.label = t[1]; t = op; break; } if (t && _.label < t[2]) { _.label = t[2]; _.ops.push(op); break; } if (t[2]) _.ops.pop(); _.trys.pop(); continue; } op = body.call(thisArg, _); } catch (e) { op = [6, e]; y = 0; } finally { f = t = 0; } if (op[0] & 5) throw op[1]; return { value: op[0] ? op[1] : void 0, done: true }; } }; /** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/2 0002. */ function getStockPrice() { return __generator(this, function (_a) { switch (_a.label) { case 0: if (!true) return [3 /*break*/, 2]; return [4 /*yield*/, Math.random() * 100]; case 1: _a.sent(); // 产生随机数来模拟股票价格 return [3 /*break*/, 0]; case 2: return [2 /*return*/]; } }); } var priceGenerate = getStockPrice(); var currentPrice = 150; // 设定一个当前价格 var limitPrice = 20; // 设定一个买入价格 while (currentPrice > limitPrice) { currentPrice = priceGenerate.next().value; console.log("u5F53u524Du80A1u7968u7684u4EF7u683Cu4E3AuFF1A" + currentPrice); } console.log("u5F53u524Du80A1u7968u7684u4EF7u683Cu5DF2u7ECFu4F4Eu4E8E" + limitPrice + ",u6240u4EE5u8FDBu884Cu4E86u81EAu52A8u4E70u5165u64CDu4F5Cu3002"); // 当股票价格低于买入价格时,就进行自动买入操作
运行JS代码的结果

4 析构表达式
通过表达式将对象或者数组拆解成任意属性的变量
4.1 对象析构表达式
注意:对象析构表达式的中变量的数量必须保持一致,而且变量名和对象的key值也要保持一致
let {nam, age ,address} = {nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"渝足"};
// let {nam, age ,address} = {nam:"warrior", age:24}; // 报错
// let {nam, age} = {nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"渝足"}; // 报错
console.log(nam)
console.log(age)
console.log(address)

var _a = { nam: "warrior", age: 24, address: "渝足" }, nam = _a.nam, age = _a.age, address = _a.address; // let {nam, age ,address} = {nam:"warrior", age:24}; // 报错 // let {nam, age} = {nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"渝足"}; // 报错 console.log(nam); console.log(age); console.log(address);
运行JS代码的结果

4.1.1 变量名和对象的key值不一致时的解决办法
let {nam: myName, age:myAge ,address:myAdress} = {nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"重庆"};
console.log(myName)
console.log(myAge)
console.log(myAdress)

var _a = { nam: "warrior", age: 24, address: "重庆" }, myName = _a.nam, myAge = _a.age, myAdress = _a.address; console.log(myName); console.log(myAge); console.log(myAdress);
运行JS代码的结果为

4.1.2 对象的一个key对应的value为一个对象的情况
let { nam: myName, age:myAge , address:myAdress, habbit // :{habbit01,habbit02} } = { nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"重庆", habbit: { habbit01: "篮球", habbit02: "足球" } }; console.log(myName) console.log(myAge) console.log(myAdress) console.log(habbit)

var _a = { nam: "warrior", age: 24, address: "重庆", habbit: { habbit01: "篮球", habbit02: "足球" } }, myName = _a.nam, myAge = _a.age, myAdress = _a.address, habbit = _a.habbit // :{habbit01,habbit02} ; console.log(myName); console.log(myAge); console.log(myAdress); console.log(habbit);
运行JS代码的结果为

4.1.3 将对象中某个key对应的对象中的数据拆解成变量
let { nam: myName, age:myAge , address:myAdress, habbit :{habbit01,habbit02}, // 将对象中某个key对应的对象中的值拆解成变量 } = { nam:"warrior", age:24, address:"重庆", habbit: { habbit01: "篮球", habbit02: "足球" } }; console.log(myName) console.log(myAge) console.log(myAdress) console.log(habbit01) console.log(habbit02)

var _a = { nam: "warrior", age: 24, address: "重庆", habbit: { habbit01: "篮球", habbit02: "足球" } }, myName = _a.nam, myAge = _a.age, myAdress = _a.address, _b = _a.habbit, habbit01 = _b.habbit01, habbit02 = _b.habbit02; console.log(myName); console.log(myAge); console.log(myAdress); console.log(habbit01); console.log(habbit02);
运行JS代码的结果为

4.2 数组的析构表达式
4.2.1 变量个数和数组长度相等时
let arr = [1,2,3,4]; let [num1,num2,num3,num4] = arr; console.log(num1) console.log(num2) console.log(num3) console.log(num4)

var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; var num1 = arr[0], num2 = arr[1], num3 = arr[2], num4 = arr[3]; console.log(num1); console.log(num2); console.log(num3); console.log(num4);
运行JS代码的结果为

4.2.2 变量个数小于数组长度时
利用逗号站位即可
let arr = [1,2,3,4]; let [,,num3,num4] = arr; // console.log(num1) // console.log(num2) console.log(num3) console.log(num4)

var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; var num3 = arr[2], num4 = arr[3]; // console.log(num1) // console.log(num2) console.log(num3); console.log(num4);
运行JS代码的结果为

4.2.3 将数组的多个元素放到一个数组变量中
let arr = [1,2,3,4]; let [num1,num2,...args] = arr; console.log(num1) console.log(num2) console.log(args) // console.log(num3) // console.log(num4)

var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; var num1 = arr[0], num2 = arr[1], args = arr.slice(2); console.log(num1); console.log(num2); console.log(args); // console.log(num3) // console.log(num4)
运行JS代码的结果为

5 箭头表达式
用于声明匿名表达式
注意:参数只有一个是可以不用写括号,方法体只用一行时不用写大括号
注意:箭头表达式可以有效的避免this的指向问题【详情请参见“揭秘Angular2”】
let test = (x:number, y:number):number => { x += 10; y += 20; return x + y; }; console.log(test(12,3))

var test = function (x, y) { x += 10; y += 20; return x + y; }; console.log(test(12, 3));
运行JS代码的结果

6 循环
6.1 forEach循环
会循环数组中的元素,但是会忽略掉数组中的属性;而且不能够跳出循环;循环替代者的类型是数组元素原来的类型
let arr01 = [1,2,3,4] arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 arr01.forEach((value) => {console.log(value)})

var arr01 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 arr01.forEach(function (value) { console.log(value); });
运行JS代码的结果为

6.2 for...in...循环
可以循环元素和属性,循环到的元素都变成了string类型;这种循环可以被打断
let arr01 = [1,2,3,4] arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 for(var value in arr01) { if(value == "3") { break; } console.log(value); }

var arr01 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 for (var value in arr01) { // if (value == "3") { // 虽然数组中的元素都是number类型,但是循环替代者value是字符串类型 // break; // } console.log(value); }
运行JS代码的结果为

6.3 for...of...循环
会循环数组元素和数组属性,还可以被打断;循环替代者的类型是数组元素的类型
let arr01 = [1,2,3,4] arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 for(var value of arr01) { if(value == 3) { console.log("Hello Boy"); break; } console.log(value); }

var arr01 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; arr01.desc = "我是arr01数组的描述属性哟。"; // ts不支持,但是js支持 for (var _i = 0, arr01_1 = arr01; _i < arr01_1.length; _i++) { var value = arr01_1[_i]; if (value == 3) { console.log("Hello Boy"); break; } console.log(value); }
运行JS代码的结果为

7、类、接口、泛型、注解、类型定义文件
待更新...2017年8月2日17:58:51
可以参见手册或相关书籍
