问题 消息队列id 和键值KEY区别?
首先要注意一个概念:IPC结构都是内核的结构。也就是说IPC结构由内核维护,对于每个进程都是公共的,不属于某个特定进程。只有这样,IPC结构才能支持它们“进程间通信”的功能。
有两个东西可以标识一个IPC结构:标识符(ID)和键(key)。
Key是IPC结构的内部名。内部即在进程内部使用,这样的标识方法是不能支持进程间通信的。
ID就是IPC结构的外部名。这些进程得到的ID其实是标识了同一个IPC结构,如消息队列同时被进程A和进程B访问。多个进程间就可以通过这个IPC结构通信。
已知一个key,当希望利用这个key创建一个新的IPC时,可以使用get函数,并在flag中指定IPC_CREAT位,例如队列的情况,就是qid = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT)
一、基本概念
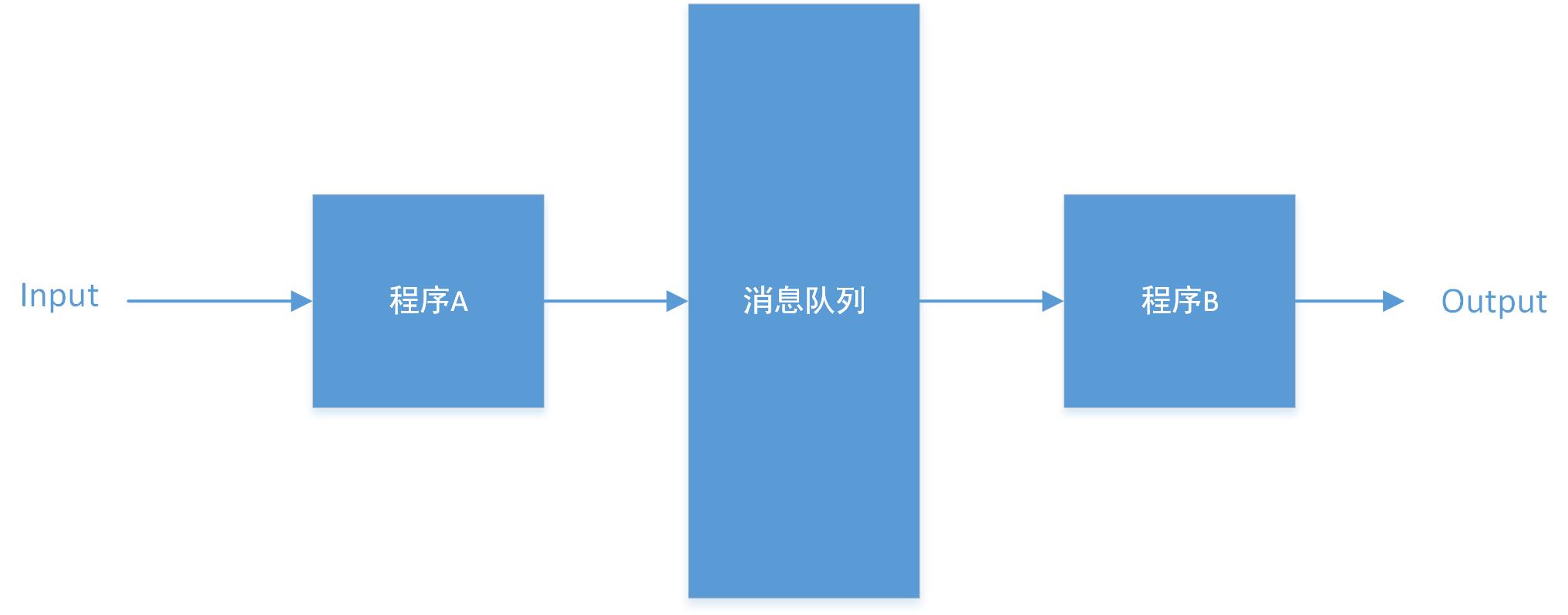
- 消息队列就是一个消息的链表。一条消息可以看作一个有结构的记录。
- IPC方式之一(进程间通信)
- 消息可以通过结构类型区分
二、函数学习
2.1 创建消息队列
2.1.1 函数名
msgget
2.1.2 函数原型
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);
2.1.3 函数功能
打开或创建消息队列
2.1.4 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
2.1.5 返回值
success:the message queue identifier(消息队列ID)
error:-1
2.1.6 参数说明
key:键值
msgflg:打开标志. IPC_CREAT:标明新创建一个消息队列。
IPC_EXCL:标明打开一个消息队列
2.2 写消息
2.2.1 函数名
msgsnd
2.2.2 函数原型
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);
2.2.3 功能
发送消息到消息队列
2.2.4 头文件
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
2.2.5 返回值
success:0
error:-1
2.2.6 参数说明
msqid:消息队列的ID
msgp:指向要发送的消息
msgsz:消息的长度(与结构有关,不含message type)
msgflg:标志位
P.S.General Form of message
struct msgbuf {
long mtype; /* message type, must be > 0 */
char mtext[1]; /* message data */
};
The mtext field is an array (or other structure) whose size is speci-
fied by msgsz, a non-negative integer value.
2.3 读消息
2.3.1 函数名
msgrcv
2.3.2 函数原型
ssize_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp,int msgflg);
2.3.3 功能
从消息队列中接收消息
2.3.4 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
2.3.5 返回值
success:实际接收消息的数据长度
error: -1
2.3.6 参数
msqid:消息队列的id
msgp :存放取出的消息
msgsz:希望取到消息的最大长度
msgtyp:消息的类型
msgtyp = 0 ,忽略类型,直接取队列中的第一条
msgtyp >0, 取 消息队列中类型等于msgtyp的第一条消息
msgtyp <0, 取 类型比msgtyp的绝对值要小或者等于的消息,如果有多条消息满足该条件,则取类型号最小的一条。
If msgtyp is less than 0, then the first message in the queue with
the lowest type less than or equal to the absolute value of msgtyp
will be read.
msgflg:标志
2.4 删除消息队列(控制)
2.4.1 函数名
msgctl
2.4.2 函数原型
int msgctl(int msqid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf);
2.4.3 函数功能
控制消息队列
2.4.4 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
2.4.5 返回值
success:0
error :-1
2.4.6 参数说明
msqid:消息队列的id
cmd:操作命令,IPC_RMID 用于删除消息队列
buf :获取内核中的msqid_ds 结构
三、综合实例
发送
/* Send.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
struct msgbuf
{
long msgtype;
char msgtext[1024];
};
int main()
{
int msqid;
int msg_type;
char str[256];
struct msgbuf msgs;
/* 创建消息队列 */
msqid = msgget(1024,IPC_CREAT);
while (1)
{
printf("Please input message type,0 for quit!
");
/* 获取消息类型 */
scanf("%d",&msg_type);
/* 如果用户输入的消息类型为0,退出该循环 */
if (msg_type == 0)
break;
/* 获取消息数据 */
printf("Please input message content!
");
scanf("%s",str);
msgs.msgtype = msg_type;
strcpy(msgs.msgtext,str);
/* 发送消息 */
msgsnd(msqid,&msgs,sizeof(struct msgbuf),0);
}
/* 删除消息队列 */
msgctl(msqid,IPC_RMID,0);
return 0;
}
接收
/* Receive.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
//#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
/* 多进程-子进程 */
int msqid = 0;
struct msgt
{
long msgtype;
char msgtext[1024];
};
/* 创建子线程 */
void childprocess()
{
struct msgt msgs;
while(1)
{
/* 接收消息队列 */
msgrcv(msqid,&msgs,sizeof(struct msgt), 0, 0);
/* 打印消息队列中的数据 */
printf("message text: %s
",msgs.msgtext);
}
return;
}
void main()
{
int i;
int cpid;
/* 打开消息队列 */
msqid = msgget(1024, IPC_EXCL);
/* 创建3个子进程 */
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cpid = fork();//创建子线程???
if (cpid<0)
printf("Creat childprocess ERROR
");
else if(cpid == 0)
childprocess();
}
}