day2
1.昨日回顾
编译型:一次性将全部代码编译成二进制文件
C,C++
优点:执行效率高
缺点:开发速度慢,不能跨平台
解释型:当程序运行时从上至下一行一行的解释成二进制
优点:开发速度快,效率高,可以跨平台
缺点:运行效率低
Python2x和Python3x宏观上的区别:
Python2x源码重复率高,不规范,而且Python崇尚的是简单优美,清晰
所以创建了Python3,规范化
day1作业解答:
#1、使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
'''
count = 0
while count < 10:
count += 1 # count = count + 1
if count == 7:
print(' ')
else:
print(count)
count = 0
while count < 10:
count += 1 # count = count + 1
if count == 7:
continue
print(count)
'''
#3、输出 1-100 内的所有奇数
#方法一:
# count = 1
# while count < 101:
# print(count)
# count += 2
#方法二:
# count = 1
# while count < 101:
# if count % 2 == 1:
# print(count)
# count += 1
#5、求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
# sum = 0
# count = 1
# while count < 100:
# if count % 2 == 0:
# sum = sum - count
# else:
# sum = sum + count
# count += 1
# print(sum)
#6、用户登陆(三次机会重试)
#input 心中有账号,密码 while
i = 0
while i < 3:
username = input('请输入账号:')
password = int(input('请输入密码:'))
if username == '咸鱼哥' and password == 123:
print('登录成功')
else:
print('登录失败请重新登录')
i += 1
1.#格式化输出
# % s d
# name = input('请输入姓名')
# age = input('请输入年龄')
# height = input('请输入身高')
# msg = "我叫%s,今年%s 身高 %s" %(name,age,height)
# print(msg)
"""
name = input('请输入姓名:')
age = input('请输入年龄:')
job = input('请输入工作:')
hobbie = input('你的爱好:')
msg = '''------------ info of %s -----------
Name : %s
Age : %d
job : %s
Hobbie: %s
------------- end -----------------''' %(name,name,int(age),job,hobbie)
print(msg)
"""
name = input('请输入姓名')
age = input('请输入年龄')
height = input('请输入身高')
msg = "我叫%s,今年%s 身高 %s 学习进度为3%%s" %(name,age,height)
print(msg)
2.while else
count = 0
while count <= 5 :
count += 1
if count == 3:break
print("Loop",count)
else:
print("循环正常执行完啦")
print("-----out of while loop ------")
3.初始编码
01010100 新
11010000 开
11010100 一
01100000 家
11000000 看
11000000 看
01010100011101110101011110110
A B C
01000001 01000010 01000011
电报,电脑的传输,存储都是01010101
最早的'密码本' ascii 涵盖了英文字母大小写,特殊字符,数字。
01010101
ascii 只能表示256种可能,太少,
创办了万国码 unicode
16表示一个字符不行,32位表示一个字符。
A 01000001010000010100000101000001
B 01000010010000100100001001000010
我 01000010010000100100001001000010
Unicode 升级 utf-8 utf-16 utf-32
8位 = 1字节bytes
utf-8 一个字符最少用8位去表示,英文用8位 一个字节
欧洲文字用16位去表示 两个字节
中文用24 位去表示 三个字节
utf-16 一个字符最少用16位去表示
gbk 中国人自己发明的,一个中文用两个字节 16位去表示。
11000000
1bit 8bit = 1bytes
1byte 1024byte = 1KB
1KB 1024kb = 1MB
1MB 1024MB = 1GB
1GB 1024GB = 1TB
4.逻辑运算及优先级
#and or not
#优先级,()> not > and > or
# print(2 > 1 and 1 < 4)
# print(2 > 1 and 1 < 4 or 2 < 3 and 9 > 6 or 2 < 4 and 3 < 2)
# T or T or F
#T or F
# print(3>4 or 4<3 and 1==1) # F
# print(1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1>2) # T
# print(2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1) # T
# print(1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8) # F
# print(1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # F
# print(not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # F
#ps int ----> bool 非零转换成bool True 0 转换成bool 是False
# print(bool(2))
# print(bool(-2))
# print(bool(0))
# #bool --->int
# print(int(True)) # 1
# print(int(False)) # 0
'''x or y x True,则返回x'''
# print(1 or 2) # 1
# print(3 or 2) # 3
# print(0 or 2) # 2
# print(0 or 100) # 100
# print(2 or 100 or 3 or 4) # 2
# print(0 or 4 and 3 or 2)
'''x and y x True,则返回y'''
# print(1 and 2)
# print(0 and 2)
print(2 or 1 < 3)
print(3 > 1 or 2 and 2)
day2-6
3.初始编码
电脑的传输,还有储存的实际上都是0101010101
8位bit == 1个字节(byte)
1024byte(字节) == 1kb
1024kb == 1MB
1024MB == 1GB
1024GB == 1TB
为了解决全球化的文字问题:创建了万国码Unicode
1个字节,表示所有的英文,特殊字符,数字等
升级版:utf-8,一个中文,3个字节去表示
gbk:国内使用,一个中文用2个字节
day2-7运算符
4.运算符

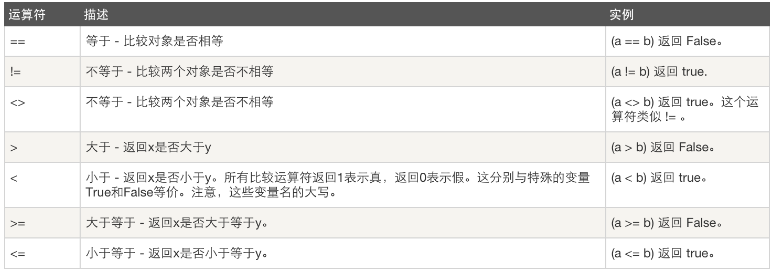
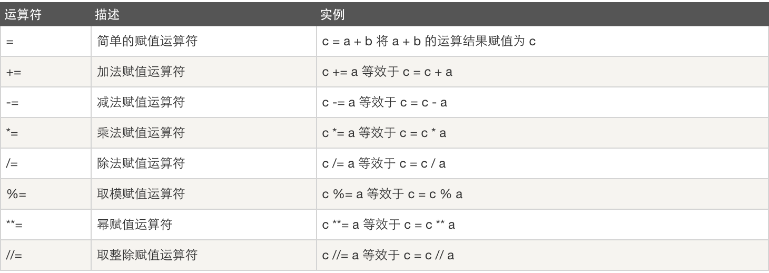


示例:
'''#优先级:()> not > and < or
print(2>1 and 1<4 or 2<3 and 9>6 or 2<4 and 3<2)
#T or T or F
#T or F
#备注:同一种运算符优先级从左至右计算'''
'''
1.3>4 or 4<3 and 1==1
2.1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1>2
3.2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1
4.1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8
5.1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6
6.not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6'''
#1
print(3>4 or 4<3 and 1==1)#False
#3>4 or F
#F or F
#2
print(1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1>2 )#True
#T or T
#3
print(2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1)#True
#T or F
#4
print(1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8)#Fasle
#F or F or F
#5
print(1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6)#False
#F or F and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6
#F or F or F
#6
print(not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6)#False
#F and 3 < 4 or F and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6
#F or F or F
#x or y x为非零,则返回x
#ps:int--->bool x为非零转换成bool 为True,0转换成bool 为false;and则相反;x为真,则返回y
print(1 or 2)
print(3 or 2)
print(0 or 2)
print(0 or 100)
print(bool(2))
print(bool(-2))
print(bool(0))
print(int(True))
print(int(False))
运行结果:
1
3
2
100
True
True
False
1
0
'''x or y x True,则返回x'''
# print(1 or 2) # 1
# print(3 or 2) # 3
# print(0 or 2) # 2
# print(0 or 100) # 100
# print(2 or 100 or 3 or 4) # 2
# print(0 or 4 and 3 or 2)
'''x and y x True,则返回y'''
# print(1 and 2)
# print(0 and 2)
print(2 or 1 < 3)#2
print(3 > 1 or 2 and 2)#True