1,汉诺塔问题【还是看了源码才记起来的,记忆逐渐清晰】
汉诺塔:汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题是源于印度一个古老传说的益智玩具。大梵天创造世界的时候做了三根金刚石柱子,在一根柱子上从下往上按照大小顺序摞着64片黄金圆盘。大梵天命令婆罗门把圆盘从下面开始按大小顺序重新摆放在另一根柱子上。并且规定,在小圆盘上不能放大圆盘,在三根柱子之间一次只能移动一个圆盘。角色变换!!!
package com.cnblogs.mufasa; public class Answer1_Hanoi { public static int Solution1(int i){//递归调用 if(i==1){ return 1; }else if(i==2){ return 3; }else { return 2*Solution1(i-1)+1; } } public static int Solution2(int i) {//数学直接计算 return (int) Math.pow(2,i)-1; } public static void Solution3(int i, String loc1, String loc2, String loc3) {//递归调用 if (i == 1) { System.out.println("from " + loc1 + " to " + loc3); return; } Solution3(i - 1, loc1, loc3, loc2);//将LOC1中的除最后一个圆盘,全部搬到第二个柱子上去 Solution3( 1, loc1, loc2, loc3);//将LOC1中最后一个圆盘,直接搬到第三个柱子上 Solution3( i-1, loc2, loc1, loc3);//将LOC2上的所有圆盘搬到第三个柱子上去
//疯狂递归搬运,内部搬运的过程中有的不能一次搬完,那么问题就又进一步拆分下去了 } }
2,哈夫曼编码【节省通信带宽】底层核心:①二叉树;②优先队列;完全掌握
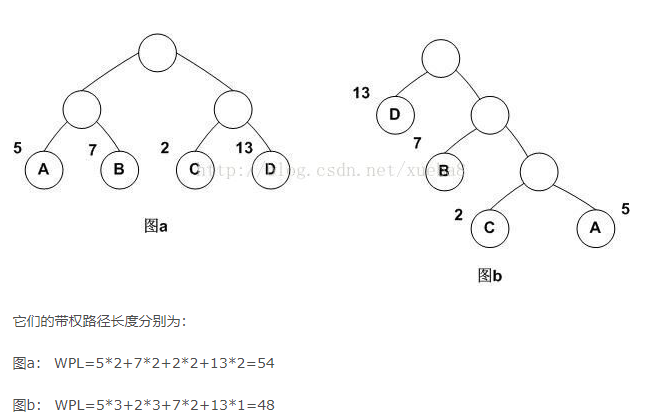
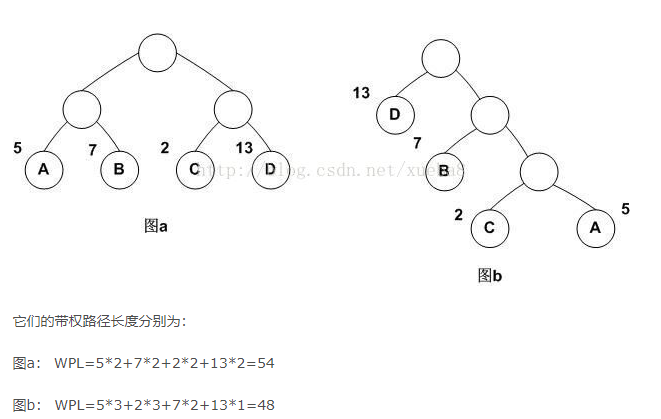
注意:哈夫曼树带权路径长度
哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字,有时称之为最佳编码,一般就叫做Huffman编码(有时也称为霍夫曼编码)。
流程:①依照使用频次进行由大到小排序;②构建二叉树结构;③读取数据
//结构很清晰明了
package com.cnblogs.mufasa; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class Answer2_Huffman2 { private class Node implements Comparable<Node> {//内部类 char ch; int freq; boolean isLeaf; Node left, right; public Node(char ch, int freq) {//叶节点 this.ch = ch; this.freq = freq; isLeaf = true; } public Node(Node left, Node right, int freq) {//父节点 this.left = left; this.right = right; this.freq = freq; isLeaf = false; } @Override public int compareTo(Node o) { return this.freq - o.freq; } } public Map<Character, String> encode(Map<Character, Integer> frequencyForChar) { PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();//优先队列,compareTo已经完善过 for (Character c : frequencyForChar.keySet()) {//优先队列输入,相当于排序 priorityQueue.add(new Node(c, frequencyForChar.get(c))); } while (priorityQueue.size() != 1) {//当只有一个节点的时候就是root节点 Node node1 = priorityQueue.poll();//输出 Node node2 = priorityQueue.poll(); priorityQueue.add(new Node(node1, node2, node1.freq + node2.freq));//新构建的父节点 } return encode(priorityQueue.poll());//经由父节点进行输出 } private Map<Character, String> encode(Node root) { Map<Character, String> encodingForChar = new HashMap<>(); encode(root, "", encodingForChar); return encodingForChar; } private void encode(Node node, String encoding, Map<Character, String> encodingForChar) { if (node.isLeaf) { encodingForChar.put(node.ch, encoding); return; } encode(node.left, encoding + '0', encodingForChar); encode(node.right, encoding + '1', encodingForChar); } }
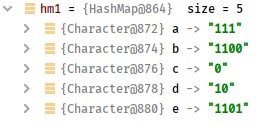
3,验证程序
package com.cnblogs.mufasa; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // System.out.println(Answer1_Hanoi.Solution1(3));//输出次数 // System.out.println(Answer1_Hanoi.Solution2(3));//输出次数 // Answer1_Hanoi.Solution3(3,"1","2","3");//输出次数 char[] chars={'a','b','c','d','e'}; int[] nums={5,1,9,8,3}; HashMap<Character,Integer> hm=new HashMap<>(); for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){ hm.put(chars[i],nums[i]); } Answer2_Huffman2 huffma=new Answer2_Huffman2(); Map<Character, String> hm1= huffma.encode(hm); } } /* 7 7 from 1 to 3 from 1 to 2 from 3 to 2 from 1 to 3 from 2 to 1 from 2 to 3 from 1 to 3 */