今天我们来了解一下 Redis 命令执行的过程。在之前的文章中《当 Redis 发生高延迟时,到底发生了什么》我们曾简单的描述了一条命令的执行过程,本篇文章展示深入说明一下,加深读者对 Redis 的了解。
上篇
如下图所示,一条命令执行完成并且返回数据一共涉及三部分,第一步是建立连接阶段,响应了socket的建立,并且创建了client对象;第二步是处理阶段,从socket读取数据到输入缓冲区,然后解析并获得命令,执行命令并将返回值存储到输出缓冲区中;第三步是数据返回阶段,将返回值从输出缓冲区写到socket中,返回给客户端,最后关闭client。
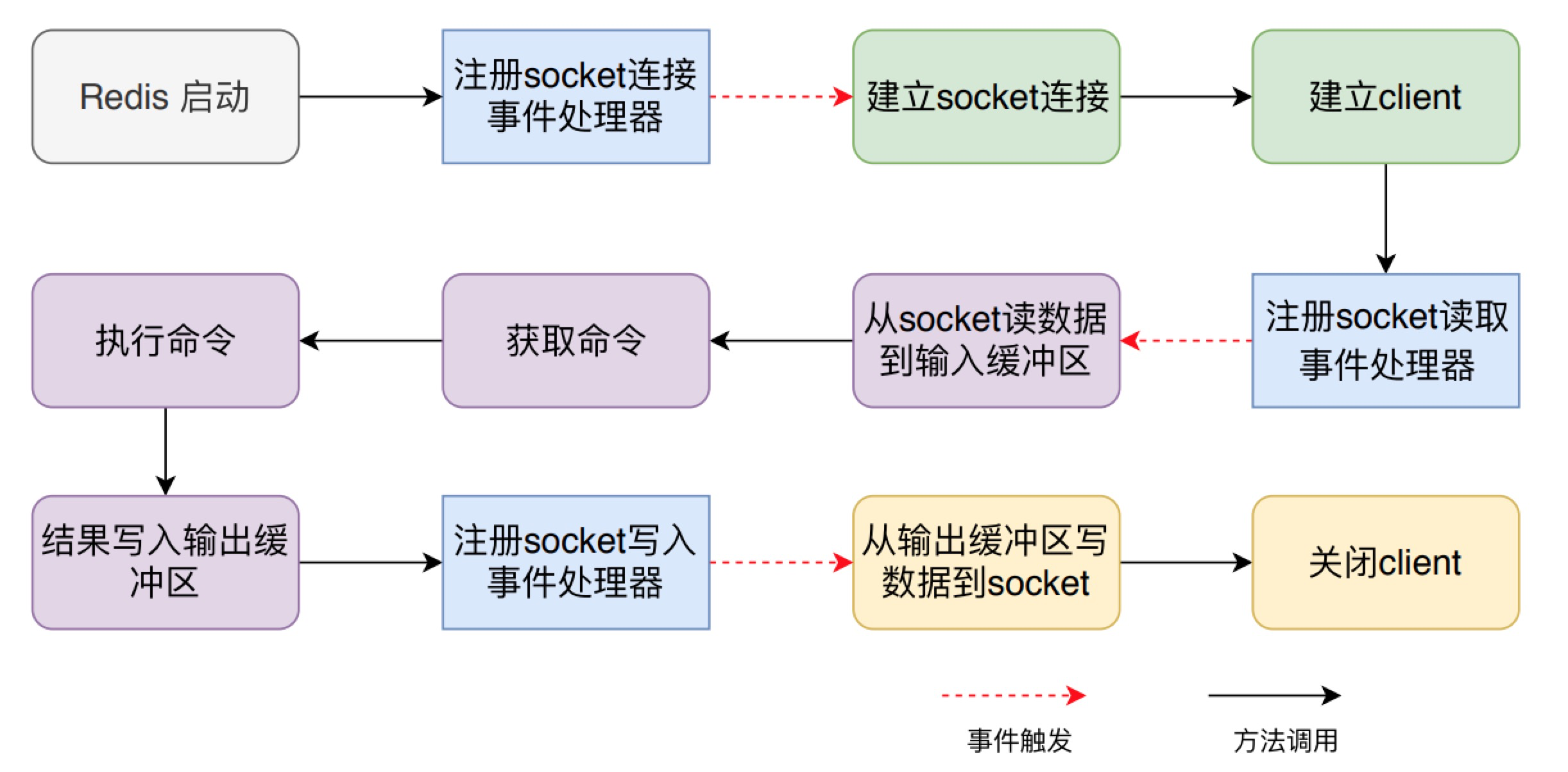
这三个阶段之间是通过事件机制串联了,在 Redis 启动阶段首先要注册socket连接建立事件处理器:
- 当客户端发来建立socket的连接的请求时,对应的处理器方法会被执行,建立连接阶段的相关处理就会进行,然后注册socket读取事件处理器
- 当客户端发来命令时,读取事件处理器方法会被执行,对应处理阶段的相关逻辑都会被执行,然后注册socket写事件处理器
- 当写事件处理器被执行时,就是将返回值写回到socket中。
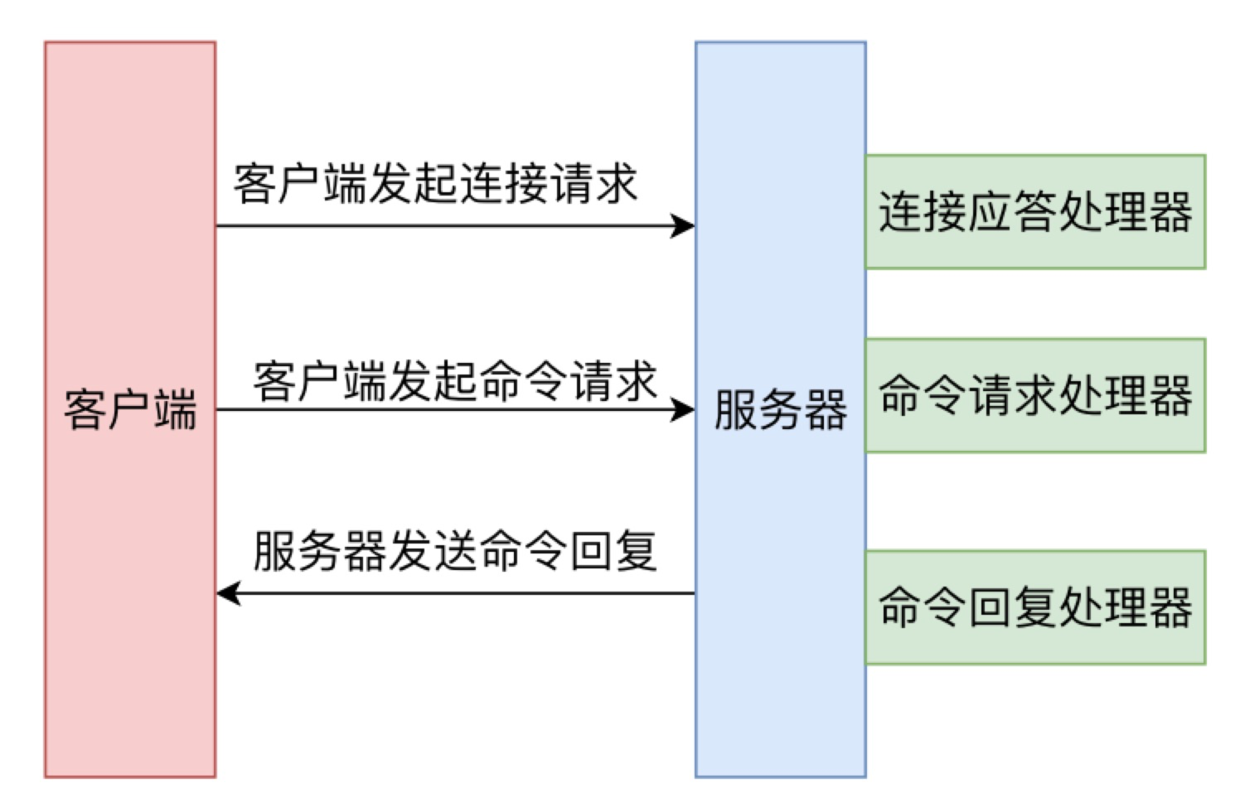
接下来,我们分别来看一下各个步骤的具体原理和代码实现。
启动时监听socket
Redis 服务器启动时,会调用 initServer 方法,首先会建立 Redis 自己的事件机制 eventLoop,然后在其上注册周期时间事件处理器,最后在所监听的 socket 上创建文件事件处理器,监听 socket 建立连接的事件,其处理函数为 acceptTcpHandler。
1 void initServer(void) { // server.c
2 ....
3 //创建aeEventLoop
4 server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+CONFIG_FDSET_INCR);
5 if (server.el == NULL) {
6 serverLog(LL_WARNING,
7 "Failed creating the event loop. Error message: '%s'",
8 strerror(errno));
9 exit(1);
10 }
11 server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum);
12 /* Open the TCP listening socket for the user commands. */
13
14 if (server.port != 0 &&
15 listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == C_ERR)
16 exit(1);
17
18 ···
19
20 /**
21 * 注册周期时间事件,处理后台操作,比如说客户端操作、过期键等
22 */
23 if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
24 serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers.");
25 exit(1);
26 }
27 /**
28 * 为所有监听的socket创建文件事件,监听可读事件;事件处理函数为acceptTcpHandler
29 *
30 */
31 for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
32 if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
33 acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
34 {
35 serverPanic(
36 "Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
37 }
38 }
39 ....
40 }
我们曾详细介绍过 Redis 的事件机制,可以说,Redis 命令执行过程中都是由事件机制协调管理的,也就是 initServer 方法中生成的 aeEventLoop。当socket发生对应的事件时,aeEventLoop 对调用已经注册的对应的事件处理器。
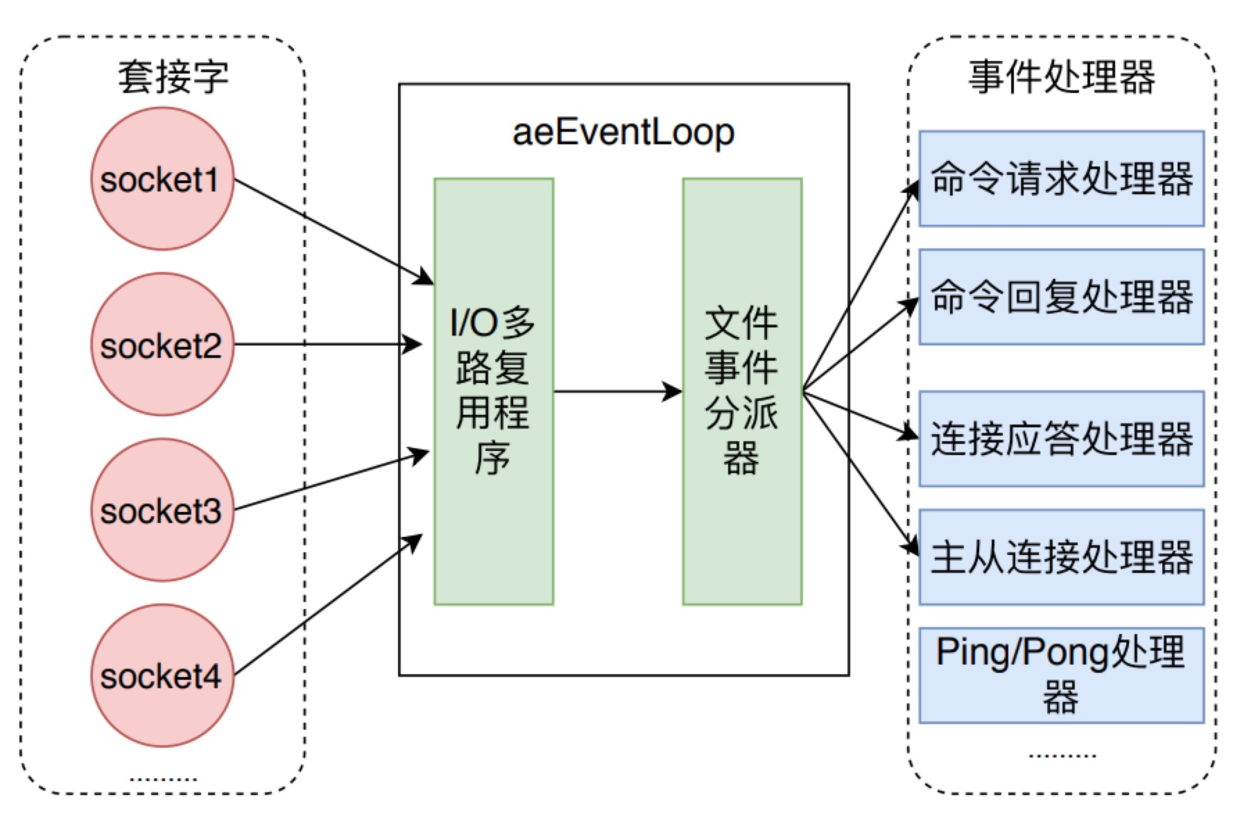
建立连接和Client
当客户端向 Redis 建立 socket时,aeEventLoop 会调用 acceptTcpHandler 处理函数,服务器会为每个链接创建一个 Client 对象,并创建相应文件事件来监听socket的可读事件,并指定事件处理函数。acceptTcpHandler 函数会首先调用 anetTcpAccept方法,它底层会调用 socket 的 accept 方法,也就是接受客户端来的建立连接请求,然后调用 acceptCommonHandler方法,继续后续的逻辑处理。
1 /**
2 * 创建一个TCP的连接处理程序
3 *
4 * 为了对连接服务器的各个客户端进行应答, 服务器要为监听套接字关联连接应答处理器。
5 * 这个处理器用于对连接服务器监听套接字的客户端进行应答,具体实现为sys/socket.h/accept函数的包装。
6 * 当Redis服务器进行初始化的时候,程序会将这个连接应答处理器和服务器监听套接字的AE_READABLE事件关联起来,
7 * 当有客户端用sys/socket.h/connect函数连接服务器监听套接字的时候, 套接字就会产生AE_READABLE 事件,
8 * 引发连接应答处理器执行, 并执行相应的套接字应答操作,
9 */
10 void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
11 //#define MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL 1000
12 int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
13 char cip[NET_IP_STR_LEN];
14 UNUSED(el);
15 UNUSED(mask);
16 UNUSED(privdata);
17
18 while(max--) {
19 cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
20 if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
21 if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
22 //连接失败,日志记录
23 serverLog(LL_WARNING,
24 "Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
25 return;
26 }
27 //连接成功,日志记录
28 serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
29 //为通信文件描述符创建对应的客户端结构体
30 acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0,cip);
31 }
32 }
acceptCommonHandler 则首先调用 createClient 创建 client,接着判断当前 client 的数量是否超出了配置的 maxclients,如果超过,则给客户端发送错误信息,并且释放 client。
1 #define MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL 1000
2 // TCP连接处理程序,创建一个client的连接状态
3 static void acceptCommonHandler(int fd, int flags, char *ip) {
4 client *c;
5 // 创建一个新的client
6 if ((c = createClient(fd)) == NULL) {
7 serverLog(LL_WARNING,
8 "Error registering fd event for the new client: %s (fd=%d)",
9 strerror(errno),fd);
10 close(fd); /* May be already closed, just ignore errors */
11 return;
12 }
13 /**
14 * If maxclient directive is set and this is one client more... close the
15 * connection. Note that we create the client instead to check before
16 * for this condition, since now the socket is already set in non-blocking
17 * mode and we can send an error for free using the Kernel I/O
18 *
19 * 如果新的client超过server规定的maxclients的限制,那么想新client的fd写入错误信息,关闭该client
20 * 先创建client,在进行数量检查,是因为更好的写入错误信息
21 */
22 if (listLength(server.clients) > server.maxclients) {
23 char *err = "-ERR max number of clients reached
";
24
25 /* That's a best effort error message, don't check write errors */
26 if (write(c->fd,err,strlen(err)) == -1) {
27 /* Nothing to do, Just to avoid the warning... */
28 }
29 // 更新拒接连接的个数
30 server.stat_rejected_conn++;
31 freeClient(c);
32 return;
33 }
34
35 /**
36 * If the server is running in protected mode (the default) and there
37 * is no password set, nor a specific interface is bound, we don't accept
38 * requests from non loopback interfaces. Instead we try to explain the
39 * user what to do to fix it if needed.
40 *
41 * 如果服务器正在以保护模式运行(默认),且没有设置密码,也没有绑定指定的接口,
42 * 我们就不接受非回环接口的请求。相反,如果需要,我们会尝试解释用户如何解决问题
43 */
44 if (server.protected_mode &&
45 server.bindaddr_count == 0 &&
46 server.requirepass == NULL &&
47 !(flags & CLIENT_UNIX_SOCKET) &&
48 ip != NULL)
49 {
50 if (strcmp(ip,"127.0.0.1") && strcmp(ip,"::1")) {
51 char *err =
52 "-DENIED Redis is running in protected mode because protected "
53 "mode is enabled, no bind address was specified, no "
54 "authentication password is requested to clients. In this mode "
55 "connections are only accepted from the loopback interface. "
56 "If you want to connect from external computers to Redis you "
57 "may adopt one of the following solutions: "
58 "1) Just disable protected mode sending the command "
59 "'CONFIG SET protected-mode no' from the loopback interface "
60 "by connecting to Redis from the same host the server is "
61 "running, however MAKE SURE Redis is not publicly accessible "
62 "from internet if you do so. Use CONFIG REWRITE to make this "
63 "change permanent. "
64 "2) Alternatively you can just disable the protected mode by "
65 "editing the Redis configuration file, and setting the protected "
66 "mode option to 'no', and then restarting the server. "
67 "3) If you started the server manually just for testing, restart "
68 "it with the '--protected-mode no' option. "
69 "4) Setup a bind address or an authentication password. "
70 "NOTE: You only need to do one of the above things in order for "
71 "the server to start accepting connections from the outside.
";
72 if (write(c->fd,err,strlen(err)) == -1) {
73 /* Nothing to do, Just to avoid the warning... */
74 }
75 // 更新拒接连接的个数
76 server.stat_rejected_conn++;
77 freeClient(c);
78 return;
79 }
80 }
81
82 // 更新连接的数量
83 server.stat_numconnections++;
84 // 更新client状态的标志
85 c->flags |= flags;
86 }
createClient 方法用于创建 client,它代表着连接到 Redis 客户端,每个客户端都有各自的输入缓冲区和输出缓冲区,输入缓冲区存储客户端通过 socket 发送过来的数据,输出缓冲区则存储着 Redis 对客户端的响应数据。client一共有三种类型,不同类型的对应缓冲区的大小都不同。
- 普通客户端是除了复制和订阅的客户端之外的所有连接
- 从客户端用于主从复制,主节点会为每个从节点单独建立一条连接用于命令复制
- 订阅客户端用于发布订阅功能
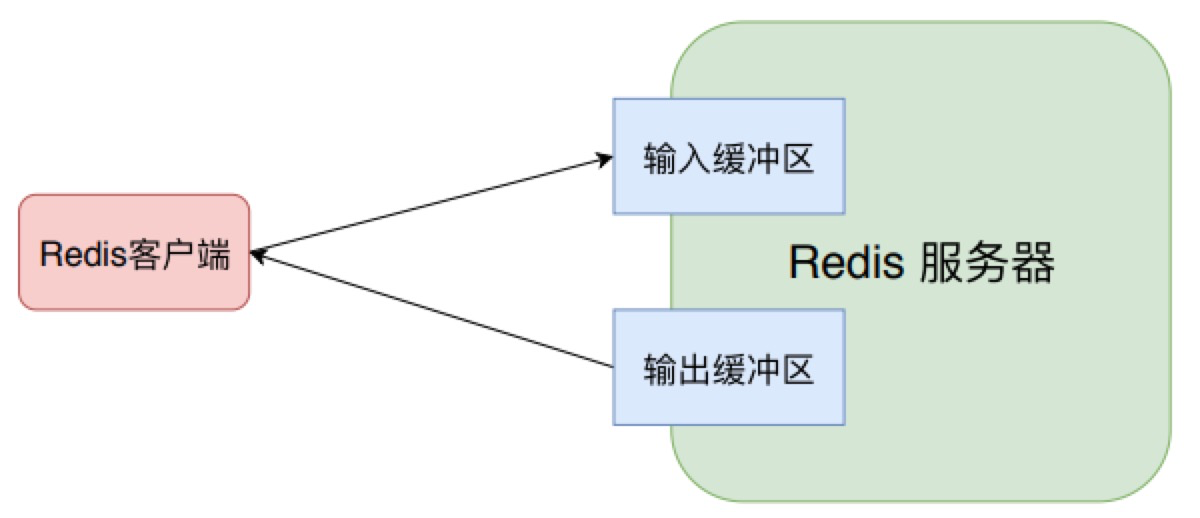
createClient 方法除了创建 client 结构体并设置其属性值外,还会对 socket进行配置并注册读事件处理器,设置 socket 为 非阻塞 socket、设置 NO_DELAY 和 SO_KEEPALIVE标志位来关闭 Nagle 算法并且启动 socket 存活检查机制。设置读事件处理器,当客户端通过 socket 发送来数据后,Redis 会调用 readQueryFromClient 方法。

1 client *createClient(int fd) { 2 //分配空间 3 client *c = zmalloc(sizeof(client)); 4 5 /** 6 * passing -1 as fd it is possible to create a non connected client. 7 * This is useful since all the commands needs to be executed 8 * in the context of a client. When commands are executed in other 9 * contexts (for instance a Lua script) we need a non connected client. 10 * 11 * 如果fd为-1,表示创建的是一个无网络连接的伪客户端,用于执行lua脚本的时候。 12 * 如果fd不等于-1,表示创建一个有网络连接的客户端 13 */ 14 if (fd != -1) { 15 // 设置fd为非阻塞模式 16 anetNonBlock(NULL,fd); 17 // 禁止使用 Nagle 算法,client向内核递交的每个数据包都会立即发送给server出去,TCP_NODELAY 18 anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd); 19 // 如果开启了tcpkeepalive,则设置 SO_KEEPALIVE 20 if (server.tcpkeepalive) 21 anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);// 设置tcp连接的keep alive选项 22 /** 23 * 使能AE_READABLE事件,readQueryFromClient是该事件的回调函数 24 * 25 * 创建一个文件事件状态el,且监听读事件,开始接受命令的输入 26 */ 27 if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE, 28 readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR) 29 { 30 close(fd); 31 zfree(c); 32 return NULL; 33 } 34 } 35 36 // 默认选0号数据库 37 selectDb(c,0); 38 uint64_t client_id; 39 // 设置client的ID 40 atomicGetIncr(server.next_client_id,client_id,1); 41 c->id = client_id; 42 // client的套接字 43 c->fd = fd; 44 // client的名字 45 c->name = NULL; 46 // 回复固定(静态)缓冲区的偏移量 47 c->bufpos = 0; 48 c->qb_pos = 0; 49 // 输入缓存区 50 c->querybuf = sdsempty(); 51 c->pending_querybuf = sdsempty(); 52 // 输入缓存区的峰值 53 c->querybuf_peak = 0; 54 // 请求协议类型,内联或者多条命令,初始化为0 55 c->reqtype = 0; 56 // 参数个数 57 c->argc = 0; 58 // 参数列表 59 c->argv = NULL; 60 // 当前执行的命令和最近一次执行的命令 61 c->cmd = c->lastcmd = NULL; 62 // 查询缓冲区剩余未读取命令的数量 63 c->multibulklen = 0; 64 // 读入参数的长度 65 c->bulklen = -1; 66 // 已发的字节数 67 c->sentlen = 0; 68 // client的状态 69 c->flags = 0; 70 // 设置创建client的时间和最后一次互动的时间 71 c->ctime = c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime; 72 // 认证状态 73 c->authenticated = 0; 74 // replication复制的状态,初始为无 75 c->replstate = REPL_STATE_NONE; 76 // 设置从节点的写处理器为ack,是否在slave向master发送ack 77 c->repl_put_online_on_ack = 0; 78 // replication复制的偏移量 79 c->reploff = 0; 80 c->read_reploff = 0; 81 // 通过ack命令接收到的偏移量 82 c->repl_ack_off = 0; 83 // 通过ack命令接收到的偏移量所用的时间 84 c->repl_ack_time = 0; 85 // 从节点的端口号 86 c->slave_listening_port = 0; 87 // 从节点IP地址 88 c->slave_ip[0] = '�'; 89 // 从节点的功能 90 c->slave_capa = SLAVE_CAPA_NONE; 91 // 回复链表 92 c->reply = listCreate(); 93 // 回复链表的字节数 94 c->reply_bytes = 0; 95 // 回复缓冲区的内存大小软限制 96 c->obuf_soft_limit_reached_time = 0; 97 // 回复链表的释放和复制方法 98 listSetFreeMethod(c->reply,freeClientReplyValue); 99 listSetDupMethod(c->reply,dupClientReplyValue); 100 // 阻塞类型 101 c->btype = BLOCKED_NONE; 102 // 阻塞超过时间 103 c->bpop.timeout = 0; 104 // 造成阻塞的键字典 105 c->bpop.keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyHeapPointerValueDictType,NULL); 106 // 存储解除阻塞的键,用于保存PUSH入元素的键,也就是dstkey 107 c->bpop.target = NULL; 108 c->bpop.xread_group = NULL; 109 c->bpop.xread_consumer = NULL; 110 c->bpop.xread_group_noack = 0; 111 // 阻塞状态 112 c->bpop.numreplicas = 0; 113 // 要达到的复制偏移量 114 c->bpop.reploffset = 0; 115 // 全局的复制偏移量 116 c->woff = 0; 117 // 监控的键 118 c->watched_keys = listCreate(); 119 // 订阅频道 120 c->pubsub_channels = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL); 121 // 订阅模式 122 c->pubsub_patterns = listCreate(); 123 // 被缓存的peerid,peerid就是 ip:port 124 c->peerid = NULL; 125 c->client_list_node = NULL; 126 // 订阅发布模式的释放和比较方法 127 listSetFreeMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,decrRefCountVoid); 128 listSetMatchMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,listMatchObjects); 129 // 将真正的client放在服务器的客户端链表中 130 if (fd != -1) 131 linkClient(c);//将当前客户端加入全局的链表中 132 // 初始化client的事物状态 133 initClientMultiState(c); 134 return c; 135 }
client 的属性中有很多属性,有一些也许没有标注到,感兴趣的同学可以自行阅读源码。
读取socket数据到输入缓冲区
readQueryFromClient 方法会调用 read 方法从 socket 中读取数据到输入缓冲区中,然后判断其大小是否大于系统设置的 client_max_querybuf_len,如果大于,则向 Redis返回错误信息,并关闭 client。将数据读取到输入缓冲区后,readQueryFromClient 方法会根据 client 的类型来做不同的处理,如果是普通类型,则直接调用 processInputBuffer 来处理;如果是主从客户端,还需要将命令同步到自己的从服务器中。也就是说,Redis实例将主实例传来的命令执行后,继续将命令同步给自己的从实例。
源码如下

1 /**
2 * 为了接收客户端传来的命令请求, 服务器要为客户端套接字关联命令请求处理器。
3 *
4 * readQueryFromClient函数是Redis的命令请求处理器,这个处理器负责从套接字中读入客户端发送的命令请求内容,
5 * 具体实现为unistd.h/read函数的包装。
6 *
7 * 当一个客户端通过连接应答处理器成功连接到服务器之后,
8 * 服务器会将客户端套接字的AE_READABLE事件和命令请求处理器关联起来,当客户端向服务器发送命令请求的时候,
9 * 套接字就会产生 AE_READABLE事件,引发命令请求处理器执行,并执行相应的套接字读入操作,
10 *
11 * 在客户端连接服务器的整个过程中,服务器都会一直为客户端套接字的AE_READABLE事件关联命令请求处理器。
12 */
13 void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
14 //指向之前设置的对象指针
15 client *c = (client*) privdata;
16 //readlen:REDIS_IOBUF_LEN
17 int nread, readlen;
18 //指示之前已经读的数据
19 size_t qblen;
20 //设置几个变量
21 UNUSED(el);
22 UNUSED(mask);
23
24 //每次想读的数据长度16K
25 readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN;
26 /* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
27 * that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
28 * buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
29 * at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
30 * processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
31 * Redis Object representing the argument. */
32 // 如果是多条请求,根据请求的大小,设置读入的长度readlen
33 if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
34 && c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
35 {
36 ssize_t remaining = (size_t)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf);
37
38 /* Note that the 'remaining' variable may be zero in some edge case,
39 * for example once we resume a blocked client after CLIENT PAUSE. */
40 if (remaining > 0 && remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
41 }
42
43 //之前缓冲区里已经存在的数据的长度
44 qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
45 // 更新缓冲区的峰值
46 if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
47 //保证有足够的空间
48 c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen);
49 // 从 fd 对应的socket中读取到 client 中的 querybuf 输入缓冲区
50 nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
51 // 读操作出错
52 if (nread == -1) {
53 if (errno == EAGAIN) {
54 return;
55 } else {
56 // 出错释放 client
57 serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",strerror(errno));
58 freeClient(c);
59 return;
60 }
61 } else if (nread == 0) {
62 // 读操作完成
63 // 客户端主动关闭 connection
64 serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection");
65 freeClient(c);
66 return;
67 } else if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) {
68 /**
69 * Append the query buffer to the pending (not applied) buffer
70 * of the master. We'll use this buffer later in order to have a
71 * copy of the string applied by the last command executed.
72 *
73 * 当这个client代表主从的master节点时,将query buffer和 pending_querybuf结合
74 * 用于主从复制中的命令传播????
75 *
76 * 将查询缓冲区附加到 master 的挂起(未应用)缓冲区。 稍后我们将使用此缓冲区,
77 * 以便获得执行的最后一个命令所应用的字符串的副本。
78 */
79 c->pending_querybuf = sdscatlen(c->pending_querybuf,
80 c->querybuf+qblen,nread);
81 }
82
83 // 更新输入缓冲区的已用大小和未用大小。
84 sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
85 // 设置最后一次服务器和client交互的时间
86 c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
87 // 如果是主节点,则更新复制操作的偏移量
88 if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->read_reploff += nread;
89 // 更新从网络输入的字节数
90 server.stat_net_input_bytes += nread;
91 // 如果大于系统配置的最大客户端缓存区大小,也就是配置文件中的client-query-buffer-limit:1G
92 if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) {
93 // 将client信息转换为sds
94 sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty();
95
96 // 返回错误信息,并且关闭client
97 bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64);
98 // 打印到日志
99 serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)", ci, bytes);
100 // 释放空间
101 sdsfree(ci);
102 sdsfree(bytes);
103 freeClient(c);
104 return;
105 }
106
107 /* Time to process the buffer. If the client is a master we need to
108 * compute the difference between the applied offset before and after
109 * processing the buffer, to understand how much of the replication stream
110 * was actually applied to the master state: this quantity, and its
111 * corresponding part of the replication stream, will be propagated to
112 * the sub-slaves and to the replication backlog. */
113 // 处理client输入的命令内容
114 processInputBufferAndReplicate(c);
115 }
该函数又会调用processInputBufferAndReplicate,对输入数据根据不同的角色做不同的操作,源码如下
1 /**
2 * This is a wrapper for processInputBuffer that also cares about handling
3 * the replication forwarding to the sub-slaves, in case the client 'c'
4 * is flagged as master. Usually you want to call this instead of the
5 * raw processInputBuffer().
6 *
7 * 这是 processInputBuffer 的一个包装器,它也关心处理复制转发到子从站,
8 * 以防客户端“c”被标记为主站。 通常你想调用它而不是原始的 processInputBuffer()。
9 */
10 void processInputBufferAndReplicate(client *c) {
11 if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER)) {
12 // processInputBuffer 处理输入缓冲区,解析获取命令
13 processInputBuffer(c);
14 } else {
15 // 如果client是master的连接
16 size_t prev_offset = c->reploff;
17 processInputBuffer(c);
18 // 判断是否同步偏移量发生变化,则通知到后续的slave
19 size_t applied = c->reploff - prev_offset;
20 if (applied) {
21 replicationFeedSlavesFromMasterStream(server.slaves,
22 c->pending_querybuf, applied);
23 sdsrange(c->pending_querybuf,applied,-1);
24 }
25 }
26 }
解析获取命令
processInputBuffer 主要是将输入缓冲区中的数据解析成对应的命令,根据命令类型是 PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK 还是 PROTO_REQ_INLINE,来分别调用 processInlineBuffer 和 processMultibulkBuffer 方法来解析命令。然后调用 processCommand 方法来执行命令。执行成功后,如果是主从客户端,还需要更新同步偏移量 reploff 属性,然后重置 client,让client可以接收一条命令。

1 /**
2 * This function is called every time, in the client structure 'c', there is
3 * more query buffer to process, because we read more data from the socket
4 * or because a client was blocked and later reactivated, so there could be
5 * pending query buffer, already representing a full command, to process.
6 *
7 * 在客户端结构“c”中,每次调用此函数时,有更多的查询缓冲区要处理,因为我们从套接字读取了更多数据,
8 * 或者因为客户端被阻塞并稍后重新激活,因此可能已经有一个要处理完整的命令位待处理的查询缓冲区。
9 *
10 * processInputBuffer 主要是将输入缓冲区中的数据解析成对应的命令,
11 * 根据命令类型是 PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK 还是 PROTO_REQ_INLINE,来分别调用 processInlineBuffer 和
12 * processMultibulkBuffer 方法来解析命令。
13 *
14 * 然后调用 processCommand 方法来执行命令。执行成功后,如果是主从客户端,
15 * 还需要更新同步偏移量 reploff 属性,然后重置 client,让client可以接收一条命令。
16 */
17 void processInputBuffer(client *c) {
18 server.current_client = c;
19
20 /* Keep processing while there is something in the input buffer */
21 /* 当缓冲区中还有数据时就一直处理 */
22 while(c->qb_pos < sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
23 /* Return if clients are paused. */
24 // 如果处于暂停状态,直接返回
25 if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) && clientsArePaused()) break;
26
27 // 处理 client 的各种状态
28
29 /**
30 * Immediately abort if the client is in the middle of something.
31 * 如果client处于被阻塞状态,直接返回
32 */
33 if (c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) break;
34
35 /**
36 * Don't process input from the master while there is a busy script
37 * condition on the slave. We want just to accumulate the replication
38 * stream (instead of replying -BUSY like we do with other clients) and
39 * later resume the processing.
40 * 当从站上有繁忙的脚本条件时,不要处理来自主站的输入。
41 * 我们只想累积复制流(而不是像我们对其他客户端那样回复 -BUSY)并且稍后恢复处理。
42 */
43 if (server.lua_timedout && c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) break;
44
45 /* CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY closes the connection once the reply is
46 * written to the client. Make sure to not let the reply grow after
47 * this flag has been set (i.e. don't process more commands).
48 *
49 * The same applies for clients we want to terminate ASAP.
50 *
51 * 一旦回复写入客户端,CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY 将关闭连接。
52 * 确保在设置此标志后不要再次回复(即不要处理更多命令)。 这同样适用于我们希望尽快终止的客户。
53 *
54 * 如果client处于关闭状态,则直接返回
55 */
56 if (c->flags & (CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY|CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP)) break;
57
58 /* Determine request type when unknown. */
59 // 如果是未知的请求类型,则判定请求类型
60 if (!c->reqtype) {
61 if (c->querybuf[c->qb_pos] == '*') {
62 // 如果是"*"开头,则是多条请求,是client发来的
63 c->reqtype = PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK;
64 } else {
65 // 否则就是内联请求,是Telnet发来的
66 c->reqtype = PROTO_REQ_INLINE;
67 }
68 }
69
70 // 如果是Telnet内联请求
71 if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_INLINE) {
72 // 处理Telnet发来的内联命令,并创建成对象,保存在client的参数列表中
73 if (processInlineBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
74 } else if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
75 // 将client的querybuf中的协议内容转换为client的参数列表中的对象
76 if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
77 } else {
78 serverPanic("Unknown request type");
79 }
80
81 /* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
82 // 如果参数为0,则重置client
83 if (c->argc == 0) {
84 resetClient(c);
85 } else {
86 /* Only reset the client when the command was executed. */
87 // 只有执行命令成功后才会重置client
88 if (processCommand(c) == C_OK) {
89 if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER && !(c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI)) {
90 /* Update the applied replication offset of our master. */
91 c->reploff = c->read_reploff - sdslen(c->querybuf) + c->qb_pos;
92 }
93
94 /**
95 * Don't reset the client structure for clients blocked in a
96 * module blocking command, so that the reply callback will
97 * still be able to access the client argv and argc field.
98 * The client will be reset in unblockClientFromModule().
99 * 如果当前客户端是非阻塞的或者当前客户端的命令是非阻塞的就重置客户端
100 */
101 if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) || c->btype != BLOCKED_MODULE)
102 resetClient(c);
103 }
104 /* freeMemoryIfNeeded may flush slave output buffers. This may
105 * result into a slave, that may be the active client, to be
106 * freed. */
107 if (server.current_client == NULL) break;
108 }
109 }
110
111 /* Trim to pos */
112 if (c->qb_pos) {
113 sdsrange(c->querybuf,c->qb_pos,-1);
114 c->qb_pos = 0;
115 }
116
117 // 执行成功,则将用于崩溃报告的client设置为NULL
118 server.current_client = NULL;
119 }
解析命令就是将 redis 命令文本信息,记录到client的argv/argc属性中
执行命令
processCommand 方法会处理很多逻辑,不过大致可以分为三个部分:首先是调用 lookupCommand 方法获得对应的 redisCommand;接着是检测当前 Redis 是否可以执行该命令;最后是调用 call 方法真正执行命令。
processCommand会做如下逻辑处理:
- 1 如果命令名称为 quit,则直接返回,并且设置客户端标志位。
- 2 根据 argv[0] 查找对应的 redisCommand,所有的命令都存储在命令字典 redisCommandTable 中,根据命令名称可以获取对应的命令。
- 3 进行用户权限校验。
- 4 如果是集群模式,处理集群重定向。当命令发送者是 master 或者 命令没有任何 key 的参数时可以不重定向。
- 5 预防 maxmemory 情况,先尝试回收一下,如果不行,则返回异常。
- 6 当此服务器是 master 时:aof 持久化失败时,或上一次 bgsave 执行错误,且配置 bgsave 参数和 stop_writes_on_bgsave_err;禁止执行写命令。
- 7 当此服务器时master时:如果配置了 repl_min_slaves_to_write,当slave数目小于时,禁止执行写命令。
- 8 当时只读slave时,除了 master 的不接受其他写命令。
- 9 当客户端正在订阅频道时,只会执行部分命令。
- 10 服务器为slave,但是没有连接 master 时,只会执行带有 CMD_STALE 标志的命令,如 info 等
- 11 正在加载数据库时,只会执行带有 CMD_LOADING 标志的命令,其余都会被拒绝。
- 12 当服务器因为执行lua脚本阻塞时,只会执行部分命令,其余都会拒绝
- 13 如果是事务命令,则开启事务,命令进入等待队列;否则直接执行命令。
函数源码

1 /** 2 * If this function gets called we already read a whole 3 * command, arguments are in the client argv/argc fields. 4 * processCommand() execute the command or prepare the 5 * server for a bulk read from the client. 6 * 如果这个函数被调用,就表明我们已经读取了整个命令,参数在客户端 argv/argc 字段中 7 * processCommand() 执行命令或准备服务器以从客户端进行批量读取。 8 * 9 * If C_OK is returned the client is still alive and valid and 10 * other operations can be performed by the caller. Otherwise 11 * if C_ERR is returned the client was destroyed (i.e. after QUIT). 12 * 如果返回 C_OK,则客户端仍处于活动状态且有效,并且调用者可以执行其他操作。 13 * 否则,如果返回 C_ERR,则客户端被销毁(即在 QUIT 之后)。 14 * 15 * processCommand 方法会处理很多逻辑,不过大致可以分为三个部分:首先是调用 lookupCommand 方法获得对应的 16 * redisCommand;接着是检测当前 Redis 是否可以执行该命令;最后是调用 call 方法真正执行命令。 17 * 18 * processCommand会做如下逻辑处理: 19 * 1 如果命令名称为 quit,则直接返回,并且设置客户端标志位。 20 * 2 根据 argv[0] 查找对应的 redisCommand,所有的命令都存储在命令字典 redisCommandTable 中,根据命令名称可以获取对应的命令。 21 * 3 进行用户权限校验。 22 * 4 如果是集群模式,处理集群重定向。当命令发送者是 master 或者 命令没有任何 key 的参数时可以不重定向。 23 * 5 预防 maxmemory 情况,先尝试回收一下,如果不行,则返回异常。 24 * 6 当此服务器是 master 时:aof 持久化失败时,或上一次 bgsave 执行错误,且配置 bgsave 参数和 stop_writes_on_bgsave_err;禁止执行写命令。 25 * 7 当此服务器时master时:如果配置了 repl_min_slaves_to_write,当slave数目小于时,禁止执行写命令。 26 * 8 当时只读slave时,除了 master 的不接受其他写命令。 27 * 9 当客户端正在订阅频道时,只会执行部分命令。 28 * 10 服务器为slave,但是没有连接 master 时,只会执行带有 CMD_STALE 标志的命令,如 info 等 29 * 11 正在加载数据库时,只会执行带有 CMD_LOADING 标志的命令,其余都会被拒绝。 30 * 12 当服务器因为执行lua脚本阻塞时,只会执行部分命令,其余都会拒绝 31 * 13 如果是事务命令,则开启事务,命令进入等待队列;否则直接执行命令。 32 */ 33 int processCommand(client *c) { 34 /* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will 35 * go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble 36 * when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in 37 * a regular command proc. */ 38 // 1 处理 quit 命令 39 if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr,"quit")) { 40 addReply(c,shared.ok); 41 c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY; 42 return C_ERR; 43 } 44 45 /* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions 46 * such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */ 47 /** 48 * 根据 argv[0] 查找对应的 command 49 * 2 命令字典查找指定命令;所有的命令都存储在命令字典中 struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[]={} 50 */ 51 c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr); 52 if (!c->cmd) { 53 // 处理未知命令 54 flagTransaction(c); 55 sds args = sdsempty(); 56 int i; 57 for (i=1; i < c->argc && sdslen(args) < 128; i++) 58 args = sdscatprintf(args, "`%.*s`, ", 128-(int)sdslen(args), (char*)c->argv[i]->ptr); 59 addReplyErrorFormat(c,"unknown command `%s`, with args beginning with: %s", 60 (char*)c->argv[0]->ptr, args); 61 sdsfree(args); 62 return C_OK; 63 } else if ((c->cmd->arity > 0 && c->cmd->arity != c->argc) || 64 (c->argc < -c->cmd->arity)) { 65 // 处理参数错误 66 flagTransaction(c); 67 addReplyErrorFormat(c,"wrong number of arguments for '%s' command", 68 c->cmd->name); 69 return C_OK; 70 } 71 72 /* Check if the user is authenticated */ 73 // 3 检查用户验证 74 if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand) 75 { 76 flagTransaction(c); 77 addReply(c,shared.noautherr); 78 return C_OK; 79 } 80 81 /* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here. 82 * However we don't perform the redirection if: 83 * 1) The sender of this command is our master. 84 * 2) The command has no key arguments. */ 85 /** 86 * 4 如果是集群模式,处理集群重定向。当命令发送者是master或者 命令没有任何key的参数时可以不重定向 87 */ 88 if (server.cluster_enabled && 89 !(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) && 90 !(c->flags & CLIENT_LUA && 91 server.lua_caller->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) && 92 !(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0 && 93 c->cmd->proc != execCommand)) 94 { 95 int hashslot; 96 int error_code; 97 // 查询可以执行的node信息 98 clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c,c->cmd,c->argv,c->argc, 99 &hashslot,&error_code); 100 if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) { 101 if (c->cmd->proc == execCommand) { 102 discardTransaction(c); 103 } else { 104 flagTransaction(c); 105 } 106 clusterRedirectClient(c,n,hashslot,error_code); 107 return C_OK; 108 } 109 } 110 111 /* Handle the maxmemory directive. 112 * 113 * First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile 114 * keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do 115 * is returning an error. 116 * 117 * Note that we do not want to reclaim memory if we are here re-entering 118 * the event loop since there is a busy Lua script running in timeout 119 * condition, to avoid mixing the propagation of scripts with the propagation 120 * of DELs due to eviction. */ 121 // 5 处理maxmemory请求,先尝试回收一下,如果不行,则返回异常 122 if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) { 123 int out_of_memory = freeMemoryIfNeeded() == C_ERR; 124 /* freeMemoryIfNeeded may flush slave output buffers. This may result 125 * into a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */ 126 if (server.current_client == NULL) return C_ERR; 127 128 /* It was impossible to free enough memory, and the command the client 129 * is trying to execute is denied during OOM conditions or the client 130 * is in MULTI/EXEC context? Error. */ 131 if (out_of_memory && 132 (c->cmd->flags & CMD_DENYOOM || 133 (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI && c->cmd->proc != execCommand))) { 134 flagTransaction(c); 135 addReply(c, shared.oomerr); 136 return C_OK; 137 } 138 } 139 140 /** 141 * Don't accept write commands if there are problems persisting on disk 142 * and if this is a master instance. 143 * 如果出现AOF或者RDB错误,这进制写入 144 */ 145 int deny_write_type = writeCommandsDeniedByDiskError(); 146 if (deny_write_type != DISK_ERROR_TYPE_NONE && 147 server.masterhost == NULL && 148 (c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE || 149 c->cmd->proc == pingCommand)) 150 { 151 flagTransaction(c); 152 if (deny_write_type == DISK_ERROR_TYPE_RDB) 153 addReply(c, shared.bgsaveerr); 154 else 155 addReplySds(c, 156 sdscatprintf(sdsempty(), 157 "-MISCONF Errors writing to the AOF file: %s ", 158 strerror(server.aof_last_write_errno))); 159 return C_OK; 160 } 161 162 /* Don't accept write commands if there are not enough good slaves and 163 * user configured the min-slaves-to-write option. */ 164 /** 165 * 7 当此服务器是master时:如果配置了repl_min_slaves_to_write, 166 * 当slave数目小于时,禁止执行写命令 167 */ 168 if (server.masterhost == NULL && 169 server.repl_min_slaves_to_write && 170 server.repl_min_slaves_max_lag && 171 c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE && 172 server.repl_good_slaves_count < server.repl_min_slaves_to_write) 173 { 174 flagTransaction(c); 175 addReply(c, shared.noreplicaserr); 176 return C_OK; 177 } 178 179 /** 180 * Don't accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But 181 * accept write commands if this is our master. 182 * 如果这是只读从站,则不接受写入命令。 但是如果这是我们的主人,请接受写入命令。 183 * 因为一个从站可能是另一个从站的主站 184 */ 185 /** 186 * 8 当是只读slave时,除了master的不接受其他写命令 187 */ 188 if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro && 189 !(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) && 190 c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE) 191 { 192 addReply(c, shared.roslaveerr); 193 return C_OK; 194 } 195 196 /* Only allow SUBSCRIBE and UNSUBSCRIBE in the context of Pub/Sub */ 197 /** 198 * 9 当客户端正在订阅频道时,只会执行以下命令 199 */ 200 if (c->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB && 201 c->cmd->proc != pingCommand && 202 c->cmd->proc != subscribeCommand && 203 c->cmd->proc != unsubscribeCommand && 204 c->cmd->proc != psubscribeCommand && 205 c->cmd->proc != punsubscribeCommand) { 206 addReplyError(c,"only (P)SUBSCRIBE / (P)UNSUBSCRIBE / PING / QUIT allowed in this context"); 207 return C_OK; 208 } 209 210 /* Only allow commands with flag "t", such as INFO, SLAVEOF and so on, 211 * when slave-serve-stale-data is no and we are a slave with a broken 212 * link with master. */ 213 /** 214 * 10 服务器为slave,但没有正确连接master时,只会执行带有CMD_STALE标志的命令,如info等 215 */ 216 if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_CONNECTED && 217 server.repl_serve_stale_data == 0 && 218 !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_STALE)) 219 { 220 flagTransaction(c); 221 addReply(c, shared.masterdownerr); 222 return C_OK; 223 } 224 225 /* Loading DB? Return an error if the command has not the 226 * CMD_LOADING flag. */ 227 /** 228 * 11 正在加载数据库时,只会执行带有CMD_LOADING标志的命令,其余都会被拒绝 229 */ 230 if (server.loading && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_LOADING)) { 231 addReply(c, shared.loadingerr); 232 return C_OK; 233 } 234 235 /* Lua script too slow? Only allow a limited number of commands. */ 236 /** 237 * 12 当服务器因为执行lua脚本阻塞时,只会执行以下几个命令,其余都会拒绝 238 */ 239 if (server.lua_timedout && 240 c->cmd->proc != authCommand && 241 c->cmd->proc != replconfCommand && 242 !(c->cmd->proc == shutdownCommand && 243 c->argc == 2 && 244 tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'n') && 245 !(c->cmd->proc == scriptCommand && 246 c->argc == 2 && 247 tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'k')) 248 { 249 flagTransaction(c); 250 addReply(c, shared.slowscripterr); 251 return C_OK; 252 } 253 254 /* Exec the command */ 255 /** 256 * 13 开始执行命令 257 */ 258 if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI && 259 c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand && 260 c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand) 261 { 262 /** 263 * 开启了事务,命令只会入队列 264 */ 265 queueMultiCommand(c); 266 addReply(c,shared.queued); 267 } else { 268 /** 269 * 直接执行命令 270 */ 271 call(c,CMD_CALL_FULL); 272 c->woff = server.master_repl_offset; 273 if (listLength(server.ready_keys)) 274 handleClientsBlockedOnKeys(); 275 } 276 return C_OK; 277 }
call 方法是 Redis 中执行命令的通用方法,它会处理通用的执行命令的前置和后续操作。
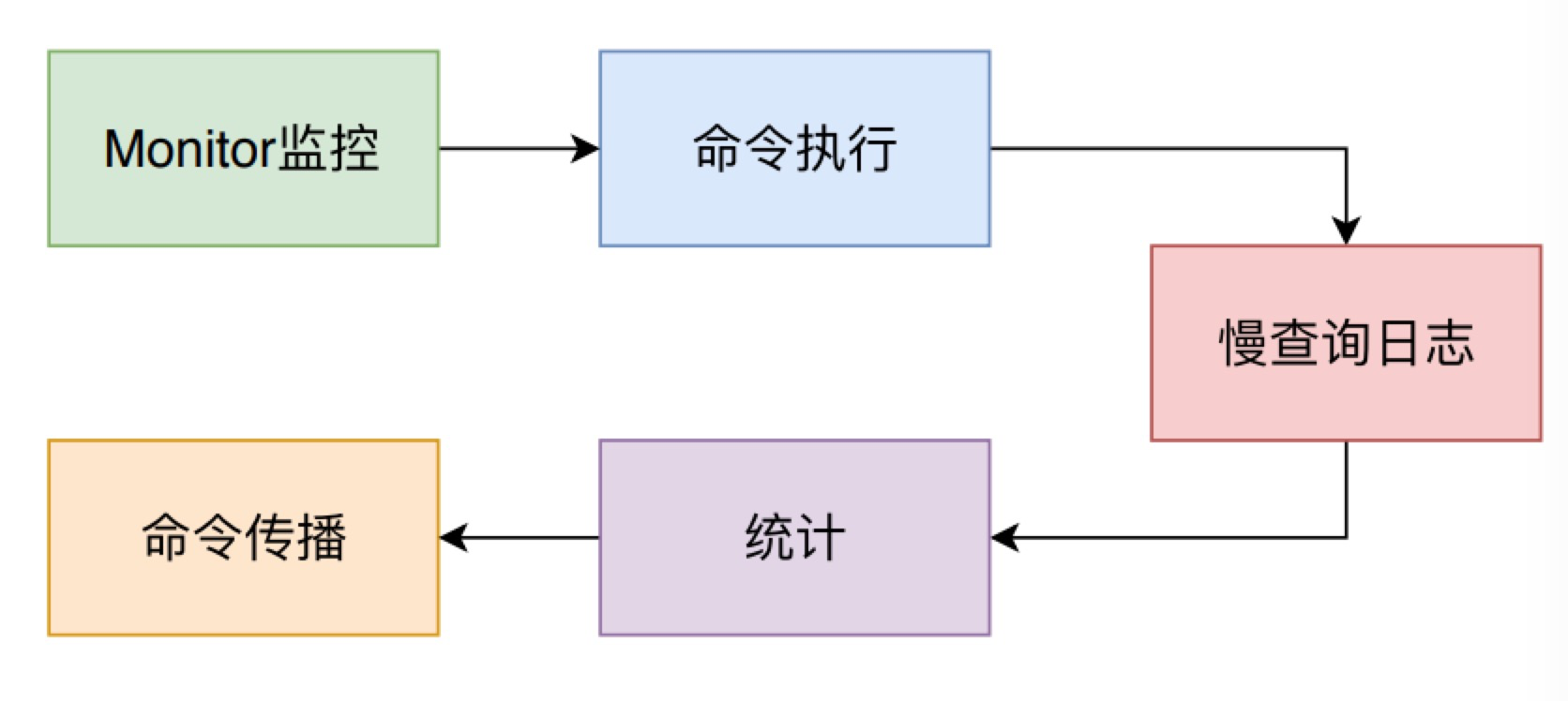
- 如果有监视器 monitor,则需要将命令发送给监视器。
- 调用 redisCommand 的proc 方法,执行对应具体的命令逻辑。
- 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG,则需要记录慢查询日志
- 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_STATS,则需要记录一些统计信息
- 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE,则当 dirty大于0时,需要调用 propagate 方法来进行命令传播。
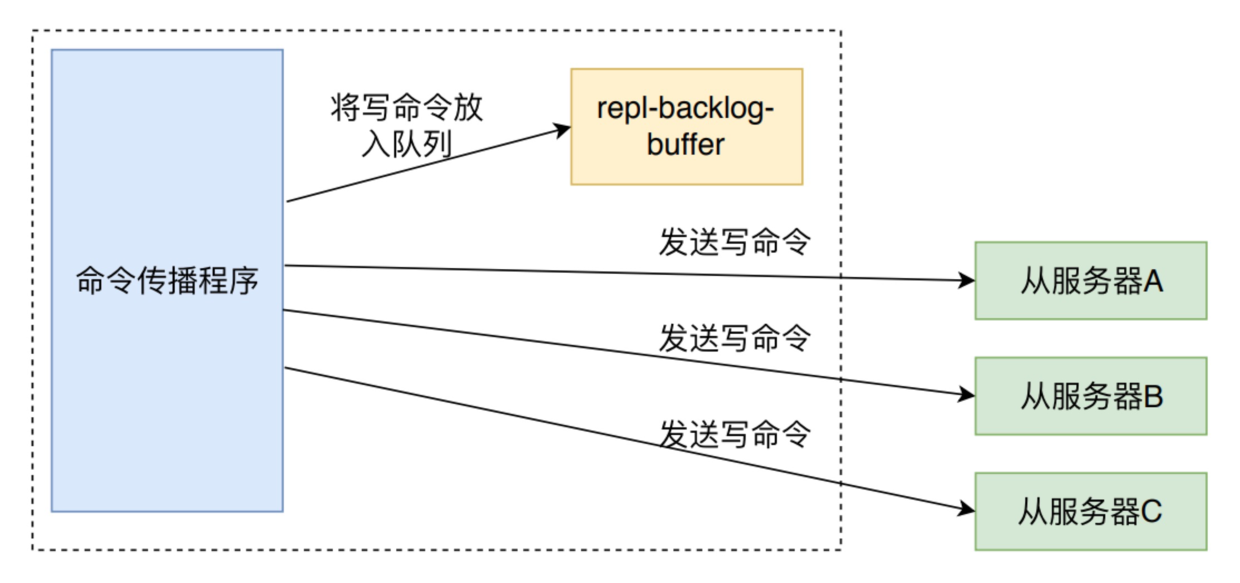
命令传播就是将命令写入 repl-backlog-buffer 缓冲中,并发送给各个从服务器中。
call函数源码如下

1 /* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command. 2 * 3 * The following flags can be passed: 4 * CMD_CALL_NONE No flags. 5 * CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG Check command speed and log in the slow log if needed. 6 * CMD_CALL_STATS Populate command stats. 7 * CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF Append command to AOF if it modified the dataset 8 * or if the client flags are forcing propagation. 9 * CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL Send command to salves if it modified the dataset 10 * or if the client flags are forcing propagation. 11 * CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE Alias for PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL. 12 * CMD_CALL_FULL Alias for SLOWLOG|STATS|PROPAGATE. 13 * 14 * The exact propagation behavior depends on the client flags. 15 * Specifically: 16 * 17 * 1. If the client flags CLIENT_FORCE_AOF or CLIENT_FORCE_REPL are set 18 * and assuming the corresponding CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF/REPL is set 19 * in the call flags, then the command is propagated even if the 20 * dataset was not affected by the command. 21 * 2. If the client flags CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP or CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP 22 * are set, the propagation into AOF or to slaves is not performed even 23 * if the command modified the dataset. 24 * 25 * Note that regardless of the client flags, if CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF 26 * or CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL are not set, then respectively AOF or 27 * slaves propagation will never occur. 28 * 29 * Client flags are modified by the implementation of a given command 30 * using the following API: 31 * 32 * forceCommandPropagation(client *c, int flags); 33 * preventCommandPropagation(client *c); 34 * preventCommandAOF(client *c); 35 * preventCommandReplication(client *c); 36 * 37 * call 方法是 Redis 中执行命令的通用方法,它会处理通用的执行命令的前置和后续操作。 38 * 39 * 执行client中持有的 redisCommand 命令 40 * 41 */ 42 void call(client *c, int flags) { 43 long long dirty, start, duration; 44 /** 45 * dirty记录数据库修改次数;start记录命令开始执行时间us;duration记录命令执行花费时间 46 */ 47 int client_old_flags = c->flags; 48 struct redisCommand *real_cmd = c->cmd; 49 50 /** 51 * Sent the command to clients in MONITOR mode, only if the commands are 52 * not generated from reading an AOF. 53 * 有监视器的话,需要将不是从AOF获取的命令会发送给监视器。当然,这里会消耗时间 54 */ 55 if (listLength(server.monitors) && 56 !server.loading && 57 !(c->cmd->flags & (CMD_SKIP_MONITOR|CMD_ADMIN))) 58 { 59 replicationFeedMonitors(c,server.monitors,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc); 60 } 61 62 /* Initialization: clear the flags that must be set by the command on 63 * demand, and initialize the array for additional commands propagation. */ 64 c->flags &= ~(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF|CLIENT_FORCE_REPL|CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP); 65 redisOpArray prev_also_propagate = server.also_propagate; 66 redisOpArrayInit(&server.also_propagate); 67 68 /* Call the command. */ 69 dirty = server.dirty; 70 start = ustime(); 71 // 处理命令,调用命令处理函数 72 c->cmd->proc(c); 73 duration = ustime()-start; 74 dirty = server.dirty-dirty; 75 if (dirty < 0) dirty = 0; 76 77 /* When EVAL is called loading the AOF we don't want commands called 78 * from Lua to go into the slowlog or to populate statistics. */ 79 // Lua 脚本的一些特殊处理 80 if (server.loading && c->flags & CLIENT_LUA) 81 flags &= ~(CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG | CMD_CALL_STATS); 82 83 /* If the caller is Lua, we want to force the EVAL caller to propagate 84 * the script if the command flag or client flag are forcing the 85 * propagation. */ 86 if (c->flags & CLIENT_LUA && server.lua_caller) { 87 if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_REPL) 88 server.lua_caller->flags |= CLIENT_FORCE_REPL; 89 if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_AOF) 90 server.lua_caller->flags |= CLIENT_FORCE_AOF; 91 } 92 93 /** 94 * Log the command into the Slow log if needed, and populate the 95 * per-command statistics that we show in INFO commandstats. 96 * 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG,则需要记录慢查询日志 97 */ 98 if (flags & CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG && c->cmd->proc != execCommand) { 99 char *latency_event = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_FAST) ? 100 "fast-command" : "command"; 101 latencyAddSampleIfNeeded(latency_event,duration/1000); 102 slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(c,c->argv,c->argc,duration); 103 } 104 /** 105 * CMD_CALL_STATS 表示要统计 106 * 107 * 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_STATS,则需要记录一些统计信息 108 */ 109 if (flags & CMD_CALL_STATS) { 110 /* use the real command that was executed (cmd and lastamc) may be 111 * different, in case of MULTI-EXEC or re-written commands such as 112 * EXPIRE, GEOADD, etc. */ 113 real_cmd->microseconds += duration; 114 real_cmd->calls++; 115 } 116 117 /** 118 * Propagate the command into the AOF and replication link 119 * 如果开启了 CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE,则当 dirty大于0时,需要调用 propagate 方法来进行命令传播 120 * CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE表示要进行广播命令 121 */ 122 if (flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE && 123 (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP) != CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP) 124 { 125 int propagate_flags = PROPAGATE_NONE; 126 127 /** 128 * Check if the command operated changes in the data set. If so 129 * set for replication / AOF propagation. 130 * dirty大于0时,需要广播命令给slave和aof 131 */ 132 if (dirty) propagate_flags |= (PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL); 133 134 /* If the client forced AOF / replication of the command, set 135 * the flags regardless of the command effects on the data set. */ 136 if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_REPL) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_REPL; 137 if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_AOF) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_AOF; 138 139 /* However prevent AOF / replication propagation if the command 140 * implementations called preventCommandPropagation() or similar, 141 * or if we don't have the call() flags to do so. */ 142 if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP || 143 !(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL)) 144 propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_REPL; 145 if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP || 146 !(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF)) 147 propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_AOF; 148 149 /** 150 * Call propagate() only if at least one of AOF / replication 151 * propagation is needed. Note that modules commands handle replication 152 * in an explicit way, so we never replicate them automatically. 153 * 仅当至少需要 AOF / 复制传播之一时才调用传播()。 154 * 请注意,模块命令以显式方式处理复制,因此我们从不自动复制它们。 155 * 156 * 广播命令,写如aof,发送命令到slave 157 * 也就是传说中的传播命令 158 */ 159 if (propagate_flags != PROPAGATE_NONE && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_MODULE)) 160 propagate(c->cmd,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc,propagate_flags); 161 } 162 163 /* Restore the old replication flags, since call() can be executed 164 * recursively. */ 165 c->flags &= ~(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF|CLIENT_FORCE_REPL|CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP); 166 c->flags |= client_old_flags & 167 (CLIENT_FORCE_AOF|CLIENT_FORCE_REPL|CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP); 168 169 /* Handle the alsoPropagate() API to handle commands that want to propagate 170 * multiple separated commands. Note that alsoPropagate() is not affected 171 * by CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP flag. */ 172 if (server.also_propagate.numops) { 173 int j; 174 redisOp *rop; 175 176 if (flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE) { 177 for (j = 0; j < server.also_propagate.numops; j++) { 178 rop = &server.also_propagate.ops[j]; 179 int target = rop->target; 180 /* Whatever the command wish is, we honor the call() flags. */ 181 if (!(flags&CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF)) target &= ~PROPAGATE_AOF; 182 if (!(flags&CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL)) target &= ~PROPAGATE_REPL; 183 if (target) 184 propagate(rop->cmd,rop->dbid,rop->argv,rop->argc,target); 185 } 186 } 187 redisOpArrayFree(&server.also_propagate); 188 } 189 server.also_propagate = prev_also_propagate; 190 server.stat_numcommands++; 191 }
下篇
在上面了解 Redis 命令执行的整体流程,然后细致分析了从 Redis 启动到建立 socket 连接,再到读取 socket 数据到输入缓冲区,解析命令,执行命令等过程的原理和实现细节。接下来,我们来具体看一下 set 和 get 命令的实现细节和如何将命令结果通过输出缓冲区和 socket 发送给 Redis 客户端。
set 和 get 命令具体实现
上面讲到 processCommand 方法会从输入缓冲区中解析出对应的 redisCommand,然后调用 call 方法执行解析出来的 redisCommand的 proc 方法。不同命令的的 proc 方法是不同的,比如说名为 set 的 redisCommand 的 proc 是 setCommand 方法,而 get 的则是 getCommand 方法。通过这种形式实现多态策略。
1 void call(client *c, int flags) {
2 ....
3 c->cmd->proc(c);
4 ....
5 }
6 // redisCommand结构体
7 struct redisCommand {
8 char *name;
9 // 对应方法的函数范式
10 redisCommandProc *proc;
11 .... // 其他定义
12 };
13 // 使用 typedef 定义的别名
14 typedef void redisCommandProc(client *c);
15 // 不同的命令,调用不同的方法。
16 struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[] = {
17 {"get",getCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
18 {"set",setCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
19 {"hmset",hsetCommand,-4,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
20 .... // 所有的 redis 命令都有
21 }
命令结构
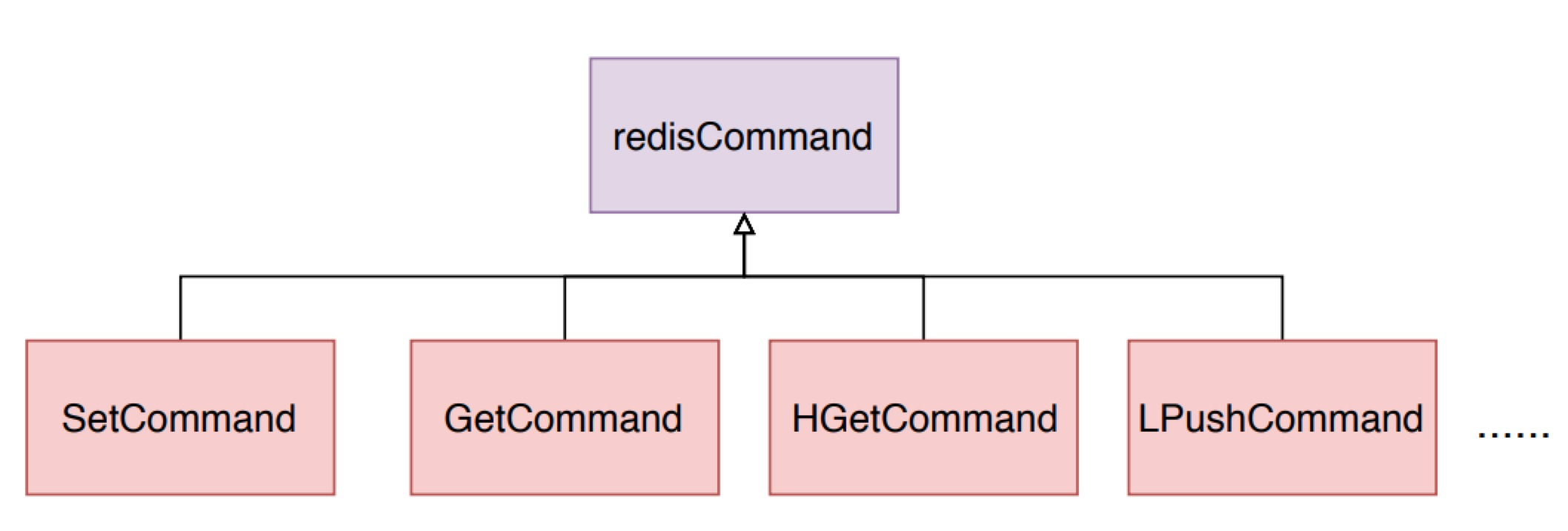
setCommand 会判断set命令是否携带了nx、xx、ex或者px等可选参数,然后调用setGenericCommand命令。我们直接来看 setGenericCommand 方法。
setGenericCommand 方法的处理逻辑如下所示:
- 首先判断 set 的类型是 set_nx 还是 set_xx,如果是 nx 并且 key 已经存在则直接返回;如果是 xx 并且 key 不存在则直接返回。
- 调用 setKey 方法将键值添加到对应的 Redis 数据库中。
- 如果有过期时间,则调用 setExpire 将设置过期时间
- 进行键空间通知
- 返回对应的值给客户端。
1 #define OBJ_SET_NO_FLAGS 0
2 #define OBJ_SET_NX (1<<0) /* Set if key not exists. */
3 #define OBJ_SET_XX (1<<1) /* Set if key exists. */
4 #define OBJ_SET_EX (1<<2) /* Set if time in seconds is given */
5 #define OBJ_SET_PX (1<<3) /* Set if time in ms in given */
6
7 void setGenericCommand(client *c, int flags, robj *key, robj *val, robj *expire, int unit, robj *ok_reply, robj *abort_reply) {
8 long long milliseconds = 0; /* initialized to avoid any harmness warning */
9
10 /**
11 * 设置了过期时间;expire是robj类型,获取整数值
12 */
13 if (expire) {
14 if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c, expire, &milliseconds, NULL) != C_OK)
15 return;
16 if (milliseconds <= 0) {
17 addReplyErrorFormat(c,"invalid expire time in %s",c->cmd->name);
18 return;
19 }
20 if (unit == UNIT_SECONDS) milliseconds *= 1000;
21 }
22
23 /**
24 * NX,key存在时直接返回;XX,key不存在时直接返回
25 * lookupKeyWrite 是在对应的数据库中寻找键值是否存在
26 */
27 if ((flags & OBJ_SET_NX && lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) != NULL) ||
28 (flags & OBJ_SET_XX && lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) == NULL))
29 {
30 addReply(c, abort_reply ? abort_reply : shared.nullbulk);
31 return;
32 }
33 /**
34 * 添加到数据字典
35 */
36 setKey(c->db,key,val);
37 server.dirty++;
38 /**
39 * 过期时间添加到过期字典
40 */
41 if (expire) setExpire(c,c->db,key,mstime()+milliseconds);
42 /**
43 * 键空间通知
44 */
45 notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_STRING,"set",key,c->db->id);
46 if (expire) notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,
47 "expire",key,c->db->id);
48 /**
49 * 返回值,addReply 在 get 命令时再具体讲解
50 */
51 addReply(c, ok_reply ? ok_reply : shared.ok);
52 }
具体 setKey 和 setExpire 的方法实现我们这里就不细讲,其实就是将键值添加到db的 dict 数据哈希表中,将键和过期时间添加到 expires 哈希表中,如下图所示。
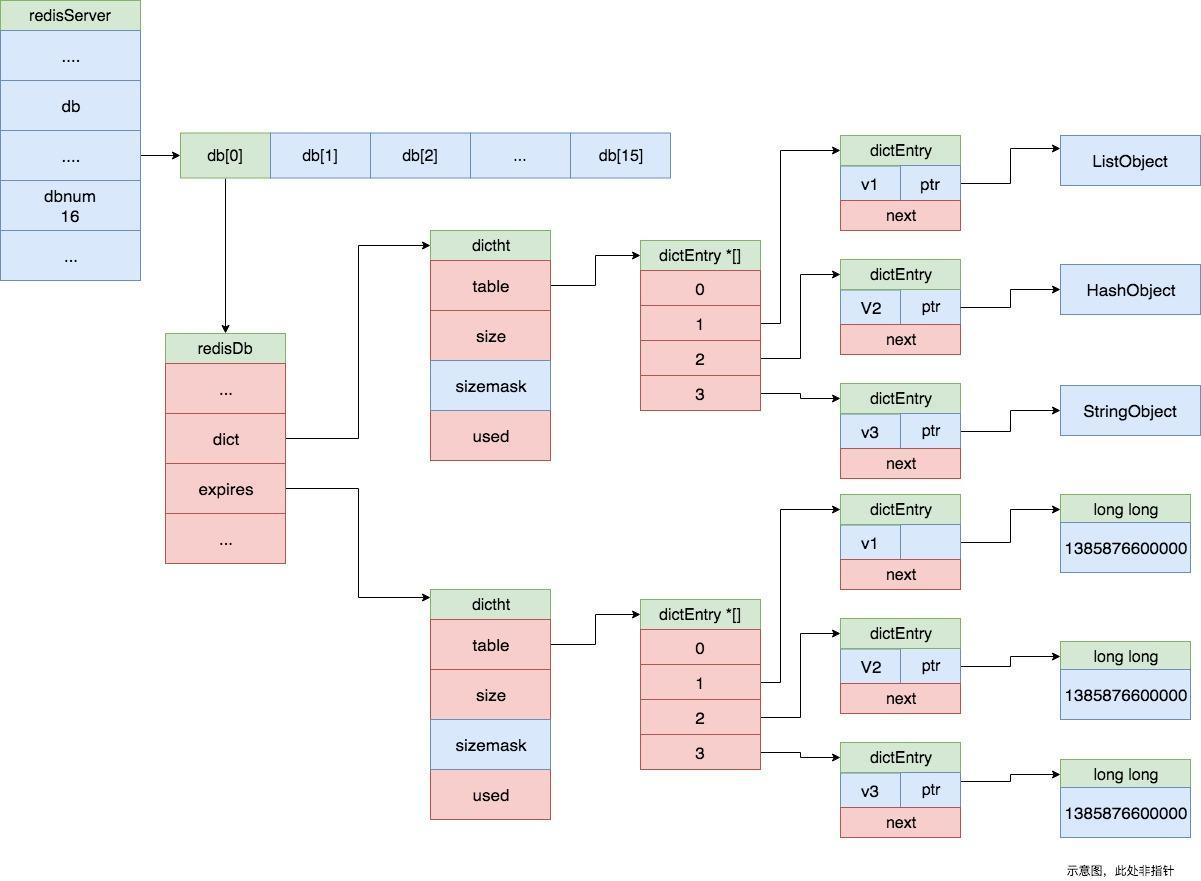
接下来看 getCommand 的具体实现,同样的,它底层会调用 getGenericCommand 方法。getGenericCommand 方法会调用 lookupKeyReadOrReply 来从 dict 数据哈希表中查找对应的 key值。如果找不到,则直接返回 C_OK;如果找到了,则根据值的类型,调用 addReply 或者 addReplyBulk 方法将值添加到输出缓冲区中。
1 int getGenericCommand(client *c) {
2 robj *o;
3
4 // 调用 lookupKeyReadOrReply 从数据字典中查找对应的键
5 if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL)
6 return C_OK;
7
8 // 如果是string类型,调用 addReply 单行返回。如果是其他对象类型,则调用 addReplyBulk
9 if (o->type != OBJ_STRING) {
10 addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
11 return C_ERR;
12 } else {
13 addReplyBulk(c,o);
14 return C_OK;
15 }
16 }
lookupKeyReadWithFlags 会从 redisDb 中查找对应的键值对,它首先会调用 expireIfNeeded判断键是否过期并且需要删除,如果为过期,则调用 lookupKey 方法从 dict 哈希表中查找并返回。具体解释可以看代码中的详细注释
1 /**
2 * Lookup a key for read operations, or return NULL if the key is not found
3 * in the specified DB.
4 *
5 * As a side effect of calling this function:
6 * 1. A key gets expired if it reached it's TTL.
7 * 2. The key last access time is updated.
8 * 3. The global keys hits/misses stats are updated (reported in INFO).
9 *
10 * This API should not be used when we write to the key after obtaining
11 * the object linked to the key, but only for read only operations.
12 *
13 * Flags change the behavior of this command:
14 *
15 * LOOKUP_NONE (or zero): no special flags are passed.
16 * LOOKUP_NOTOUCH: don't alter the last access time of the key.
17 *
18 * Note: this function also returns NULL if the key is logically expired
19 * but still existing, in case this is a slave, since this API is called only
20 * for read operations. Even if the key expiry is master-driven, we can
21 * correctly report a key is expired on slaves even if the master is lagging
22 * expiring our key via DELs in the replication link.
23 * 查找key的读操作,如果key找不到或者已经逻辑上过期返回 NULL,有一些副作用
24 * 1 如果key到达过期时间,它会被设备为过期,并且删除
25 * 2 更新key的最近访问时间
26 * 3 更新全局缓存击中概率
27 * flags 有两个值: LOOKUP_NONE 一般都是这个;LOOKUP_NOTOUCH 不修改最近访问时间
28 */
29 robj *lookupKeyReadWithFlags(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
30 robj *val;
31
32 // 检查键是否过期
33 if (expireIfNeeded(db,key) == 1) {
34 // master和 slave 对这种情况的特殊处理
35 /* Key expired. If we are in the context of a master, expireIfNeeded()
36 * returns 0 only when the key does not exist at all, so it's safe
37 * to return NULL ASAP. */
38 if (server.masterhost == NULL) {
39 server.stat_keyspace_misses++;
40 return NULL;
41 }
42
43 /* However if we are in the context of a slave, expireIfNeeded() will
44 * not really try to expire the key, it only returns information
45 * about the "logical" status of the key: key expiring is up to the
46 * master in order to have a consistent view of master's data set.
47 *
48 * However, if the command caller is not the master, and as additional
49 * safety measure, the command invoked is a read-only command, we can
50 * safely return NULL here, and provide a more consistent behavior
51 * to clients accessign expired values in a read-only fashion, that
52 * will say the key as non existing.
53 *
54 * Notably this covers GETs when slaves are used to scale reads. */
55 if (server.current_client &&
56 server.current_client != server.master &&
57 server.current_client->cmd &&
58 server.current_client->cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY)
59 {
60 server.stat_keyspace_misses++;
61 return NULL;
62 }
63 }
64 // 查找键值字典
65 val = lookupKey(db,key,flags);
66 // 更新全局缓存命中率
67 if (val == NULL)
68 server.stat_keyspace_misses++;
69 else
70 server.stat_keyspace_hits++;
71 return val;
72 }
Redis 在调用查找键值系列方法前都会先调用 expireIfNeeded 来判断键是否过期,然后根据 Redis 是否配置了懒删除来进行同步删除或者异步删除。
在判断键释放过期的逻辑中有两个特殊情况:
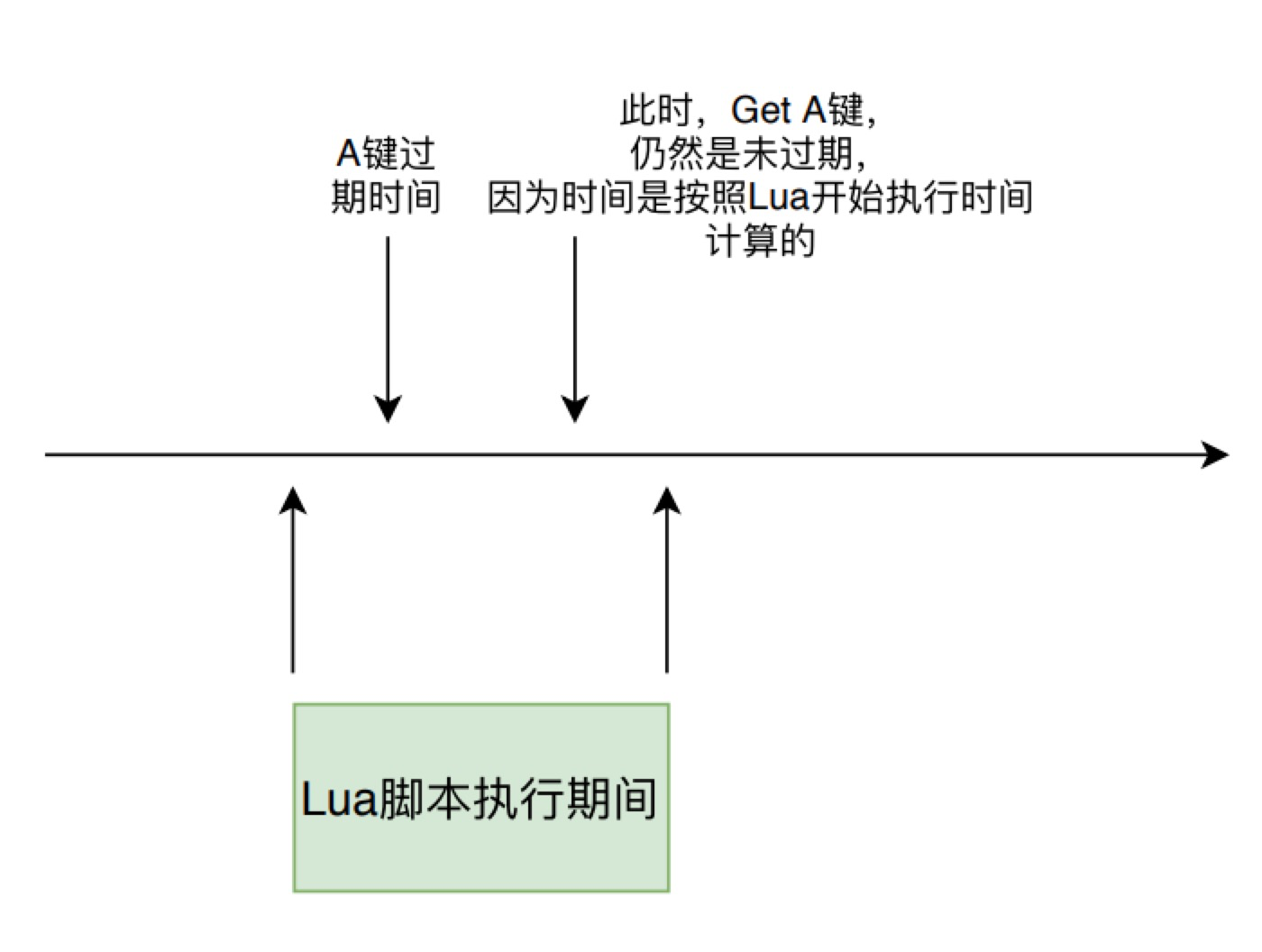
- 如果当前 Redis 是主从结构中的从实例,则只判断键是否过期,不直接对键进行删除,而是要等待主实例发送过来的删除命令后再进行删除。如果当前 Redis 是主实例,则调用 propagateExpire 来传播过期指令。
- 如果当前正在进行 Lua 脚本执行,因为其原子性和事务性,整个执行过期中时间都按照其开始执行的那一刻计算,也就是说lua执行时未过期的键,在它整个执行过程中也都不会过期。
函数源码
1 /* Check if the key is expired. */
2 int keyIsExpired(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
3 // 获取键的过期时间
4 mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
5
6 // 键没有过期时间
7 if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
8
9 /* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
10 // 实例正在从硬盘 laod 数据,比如说 RDB 或者 AOF
11 if (server.loading) return 0;
12
13 /**
14 * If we are in the context of a Lua script, we pretend that time is
15 * blocked to when the Lua script started. This way a key can expire
16 * only the first time it is accessed and not in the middle of the
17 * script execution, making propagation to slaves / AOF consistent.
18 * See issue #1525 on Github for more information.
19 * 当执行lua脚本时,只有键在lua一开始执行时
20 * 就到了过期时间才算过期,否则在lua执行过程中不算失效
21 */
22 mstime_t now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
23
24 return now > when;
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * This function is called when we are going to perform some operation
29 * in a given key, but such key may be already logically expired even if
30 * it still exists in the database. The main way this function is called
31 * is via lookupKey*() family of functions.
32 *
33 * The behavior of the function depends on the replication role of the
34 * instance, because slave instances do not expire keys, they wait
35 * for DELs from the master for consistency matters. However even
36 * slaves will try to have a coherent return value for the function,
37 * so that read commands executed in the slave side will be able to
38 * behave like if the key is expired even if still present (because the
39 * master has yet to propagate the DEL).
40 *
41 * In masters as a side effect of finding a key which is expired, such
42 * key will be evicted from the database. Also this may trigger the
43 * propagation of a DEL/UNLINK command in AOF / replication stream.
44 *
45 * The return value of the function is 0 if the key is still valid,
46 * otherwise the function returns 1 if the key is expired.
47 * 在调用 lookupKey*系列方法前调用该方法。
48 * 如果是slave:
49 * slave 并不主动过期删除key,但是返回值仍然会返回键已经被删除。
50 * master 如果key过期了,会主动删除过期键,并且触发 AOF 和同步操作。
51 * 返回值为0表示键仍然有效,否则返回1
52 */
53 int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
54 //KEY是否过期
55 if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
56
57 /**
58 * If we are running in the context of a slave, instead of
59 * evicting the expired key from the database, we return ASAP:
60 * the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
61 * send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
62 *
63 * Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
64 * that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
65 * we think the key is expired at this time.
66 * 当本实例是slave时,过期键的删除由master发送过来的
67 * del 指令控制。但是这个函数还是将正确的信息返回给调用者。
68 */
69 if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
70
71 /* Delete the key */
72 // 代码到这里,说明键已经过期,而且需要被删除
73 server.stat_expiredkeys++;
74 // 命令传播,到 slave 和 AOF
75 propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
76 // 键空间通知使得客户端可以通过订阅频道或模式, 来接收那些以某种方式改动了 Redis 数据集的事件。
77 notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
78 "expired",key,db->id);
79 // 如果是惰性删除,调用dbAsyncDelete,否则调用 dbSyncDelete
80 return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
81 dbSyncDelete(db,key);
82 }
lookupKey 方法则是通过 dictFind 方法从 redisDb 的 dict 哈希表中查找键值,如果能找到,则根据 redis 的 maxmemory_policy 策略来判断是更新 lru 的最近访问时间,还是调用 updateFU 方法更新其他指标,这些指标可以在后续内存不足时对键值进行回收。
1 /**
2 * Low level key lookup API, not actually called directly from commands
3 * implementations that should instead rely on lookupKeyRead(),
4 * lookupKeyWrite() and lookupKeyReadWithFlags().
5 * lookupKey 方法则是通过 dictFind 方法从 redisDb 的 dict 哈希表中查找键值,
6 * 如果能找到,则根据 redis 的 maxmemory_policy 策略来判断是更新 lru 的最近访问时间,
7 * 还是调用 updateFU 方法更新其他指标,这些指标可以在后续内存不足时对键值进行回收。
8 */
9 robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
10 // dictFind 根据 key 获取字典的entry
11 dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
12 if (de) {
13 // 获取 value
14 robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
15
16 /**
17 * Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
18 * Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
19 * a copy on write madness.
20 * 当处于 rdb aof 子进程复制阶段或者 flags 不是 LOOKUP_NOTOUCH
21 */
22 if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&
23 server.aof_child_pid == -1 &&
24 !(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH))
25 {
26 // 如果是 MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU 则进行相应操作
27 if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
28 updateLFU(val);
29 } else {
30 // 更新最近访问时间
31 val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
32 }
33 }
34 return val;
35 } else {
36 return NULL;
37 }
38 }
将命令结果写入输出缓冲区
在所有的 redisCommand 执行的最后,一般都会调用 addReply 方法进行结果返回,我们的分析也来到了 Redis 命令执行的返回数据阶段。
addReply 方法做了两件事情:
- prepareClientToWrite 判断是否需要返回数据,并且将当前 client 添加到等待写返回数据队列中。
- 调用 _addReplyToBuffer 和 _addReplyObjectToList 方法将返回值写入到输出缓冲区中,等待写入 socekt。
函数源码
1 /**
2 * Add the object 'obj' string representation to the client output buffer.
3 * addReply 方法做了两件事情:
4 * prepareClientToWrite 判断是否需要返回数据,并且将当前 client 添加到等待写返回数据队列中。
5 * 调用 _addReplyToBuffer 和 _addReplyObjectToList 方法将返回值写入到输出缓冲区中,等待写入 socekt。
6 */
7 void addReply(client *c, robj *obj) {
8 if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != C_OK) return;
9
10 if (sdsEncodedObject(obj)) {
11 /**
12 * 需要将响应内容添加到output buffer中。总体思路是,先尝试向固定buffer添加,
13 * 添加失败的话,在尝试添加到响应链表
14 */
15 if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr)) != C_OK)
16 _addReplyStringToList(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr));
17 } else if (obj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) {// 特殊情况的优化
18 /**
19 * For integer encoded strings we just convert it into a string
20 * using our optimized function, and attach the resulting string
21 * to the output buffer.
22 * 对于整数编码的字符串,我们只需使用我们优化的函数将其转换为字符串,并将结果字符串附加到输出缓冲区。
23 */
24 char buf[32];
25 size_t len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)obj->ptr);
26 if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,buf,len) != C_OK)
27 _addReplyStringToList(c,buf,len);
28 } else {
29 serverPanic("Wrong obj->encoding in addReply()");
30 }
31 }
prepareClientToWrite 首先判断了当前 client是否需要返回数据:
- Lua 脚本执行的 client 则需要返回值;
- 如果客户端发送来 REPLY OFF 或者 SKIP 命令,则不需要返回值;
- 如果是主从复制时的主实例 client,则不需要返回值;
- 当前是在 AOF loading 状态的假 client,则不需要返回值。
接着如果这个 client 还未处于延迟等待写入 (CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE)的状态,则将其设置为该状态,并将其加入到 Redis 的等待写入返回值客户端队列中,也就是 clients_pending_write队列。
1 /**
2 * This function is called every time we are going to transmit new data
3 * to the client. The behavior is the following:
4 * 每当我们调用这个函数就代表我们将要发送新的数据给客户端,执行步骤如下:
5 *
6 * If the client should receive new data (normal clients will) the function
7 * returns C_OK, and make sure to install the write handler in our event
8 * loop so that when the socket is writable new data gets written.
9 * 如果客户端应该接收新数据(普通客户端会),该函数返回 C_OK,并确保在我们的事件循环中安装写入处理程序,
10 * 以便在套接字可写时写入新数据。
11 *
12 * If the client should not receive new data, because it is a fake client
13 * (used to load AOF in memory), a master or because the setup of the write
14 * handler failed, the function returns C_ERR.
15 * 如果客户端不应该接收新数据,因为它是一个假客户端(用于将 AOF 加载到内存中)、
16 * 一个 master 或者因为写处理程序的设置失败,该函数返回 C_ERR。
17 *
18 * The function may return C_OK without actually installing the write
19 * event handler in the following cases:
20 * 在以下情况下,该函数可能会在不没有安装写入事件处理程序的情况下返回 C_OK
21 *
22 * 1) The event handler should already be installed since the output buffer
23 * already contains something.
24 * 事件处理程序应该已经安装,因为输出缓冲区已经包含一些东西。
25 * 2) The client is a slave but not yet online, so we want to just accumulate
26 * writes in the buffer but not actually sending them yet.
27 * 客户端是一个从设备但尚未在线,因此我们只想在缓冲区中累积写入但尚未实际发送它们。
28 *
29 * Typically gets called every time a reply is built, before adding more
30 * data to the clients output buffers. If the function returns C_ERR no
31 * data should be appended to the output buffers.
32 * 通常在每次构建回复时调用,然后向客户端输出缓冲区添加更多数据。 如果函数返回 C_ERR,则不应将数据附加到输出缓冲区。
33 *
34 * prepareClientToWrite 首先判断了当前 client是否需要返回数据:
35 * Lua 脚本执行的 client 则需要返回值;
36 * 如果客户端发送来 REPLY OFF 或者 SKIP 命令,则不需要返回值;
37 * 如果是主从复制时的主实例 client,则不需要返回值;
38 * 当前是在 AOF loading 状态的假 client,则不需要返回值。
39 * 接着如果这个 client 还未处于延迟等待写入 (CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE)的状态,则将其设置为该状态,
40 * 并将其加入到 Redis 的等待写入返回值客户端队列中,也就是 clients_pending_write队列。
41 */
42 int prepareClientToWrite(client *c) {
43 /**
44 * If it's the Lua client we always return ok without installing any
45 * handler since there is no socket at all.
46 * 如果是 lua client 则直接OK
47 */
48 if (c->flags & (CLIENT_LUA|CLIENT_MODULE)) return C_OK;
49
50 /**
51 * CLIENT REPLY OFF / SKIP handling: don't send replies.
52 * 客户端发来过 REPLY OFF 或者 SKIP 命令,不需要发送返回值
53 */
54 if (c->flags & (CLIENT_REPLY_OFF|CLIENT_REPLY_SKIP)) return C_ERR;
55
56 /**
57 * Masters don't receive replies, unless CLIENT_MASTER_FORCE_REPLY flag
58 * is set.
59 * master 作为client 向 slave 发送命令,不需要接收返回值
60 */
61 if ((c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
62 !(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER_FORCE_REPLY)) return C_ERR;
63
64 // AOF loading 时的假client 不需要返回值
65 if (c->fd <= 0) return C_ERR; /* Fake client for AOF loading. */
66
67 /**
68 * Schedule the client to write the output buffers to the socket, unless
69 * it should already be setup to do so (it has already pending data).
70 * 将client加入到等待写入返回值队列中,下次事件周期会进行返回值写入。
71 */
72 if (!clientHasPendingReplies(c)) clientInstallWriteHandler(c);
73
74 /**
75 * Authorize the caller
76 * 表示已经在排队,进行返回数据
77 */
78 return C_OK;
79 }
Redis 将存储等待返回的响应数据的空间,也就是输出缓冲区分成两部分,一个固定大小的 buffer 和一个响应内容数据的链表。在链表为空并且 buffer 有足够空间时,则将响应添加到 buffer 中。如果 buffer 满了则创建一个节点追加到链表上。_addReplyToBuffer 和 _addReplyObjectToList 就是分别向这两个空间写数据的方法。
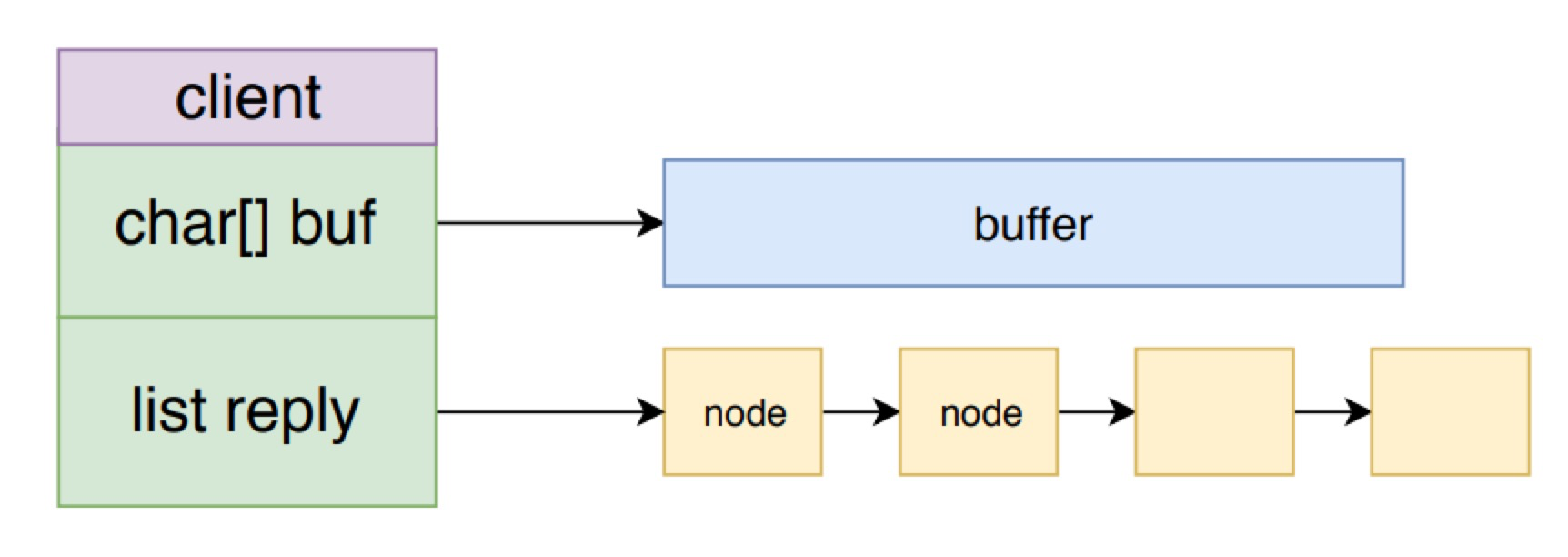
固定buffer和响应链表,整体上构成了一个队列。这么组织的好处是,既可以节省内存,不需一开始预先分配大块内存,并且可以避免频繁分配、回收内存。 上面就是响应内容写入输出缓冲区的过程,下面看一下将数据从输出缓冲区写入 socket 的过程。
prepareClientToWrite 函数,将客户端加入到了Redis 的等待写入返回值客户端队列中,也就是 clients_pending_write 队列。请求处理的事件处理逻辑就结束了,等待 Redis 下一次事件循环处理时,将响应从输出缓冲区写入到 socket 中。
将命令返回值从输出缓冲区写入 socket
Redis 在两次事件循环之间会调用 beforeSleep 方法处理一些事情,而对 clients_pending_write 列表的处理就在其中。下面的 aeMain 方法就是 Redis 事件循环的主逻辑,可以看到每次循环时都会调用 beforesleep 方法。
1 // 事件轮询的主函数
2 void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
3 eventLoop->stop = 0;
4 // 一直处理事件
5 while (!eventLoop->stop) {
6 /**
7 * 执行处理事件之前的函数,实际上就是server.c中的void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop)函数
8 * 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么执行它
9 */
10 if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
11 eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
12 //处理到时的时间事件和就绪的文件事件
13 aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
14 }
15 }
beforeSleep 函数会调用 handleClientsWithPendingWrites 函数来处理 clients_pending_write 列表。handleClientsWithPendingWrites 方法会遍历 clients_pending_write 列表,对于每个 client 都会先调用 writeToClient 方法来尝试将返回数据从输出缓存区写入到 socekt中,如果还未写完,则只能调用 aeCreateFileEvent 方法来注册一个写数据事件处理器 sendReplyToClient,等待 Redis 事件机制的再次调用。
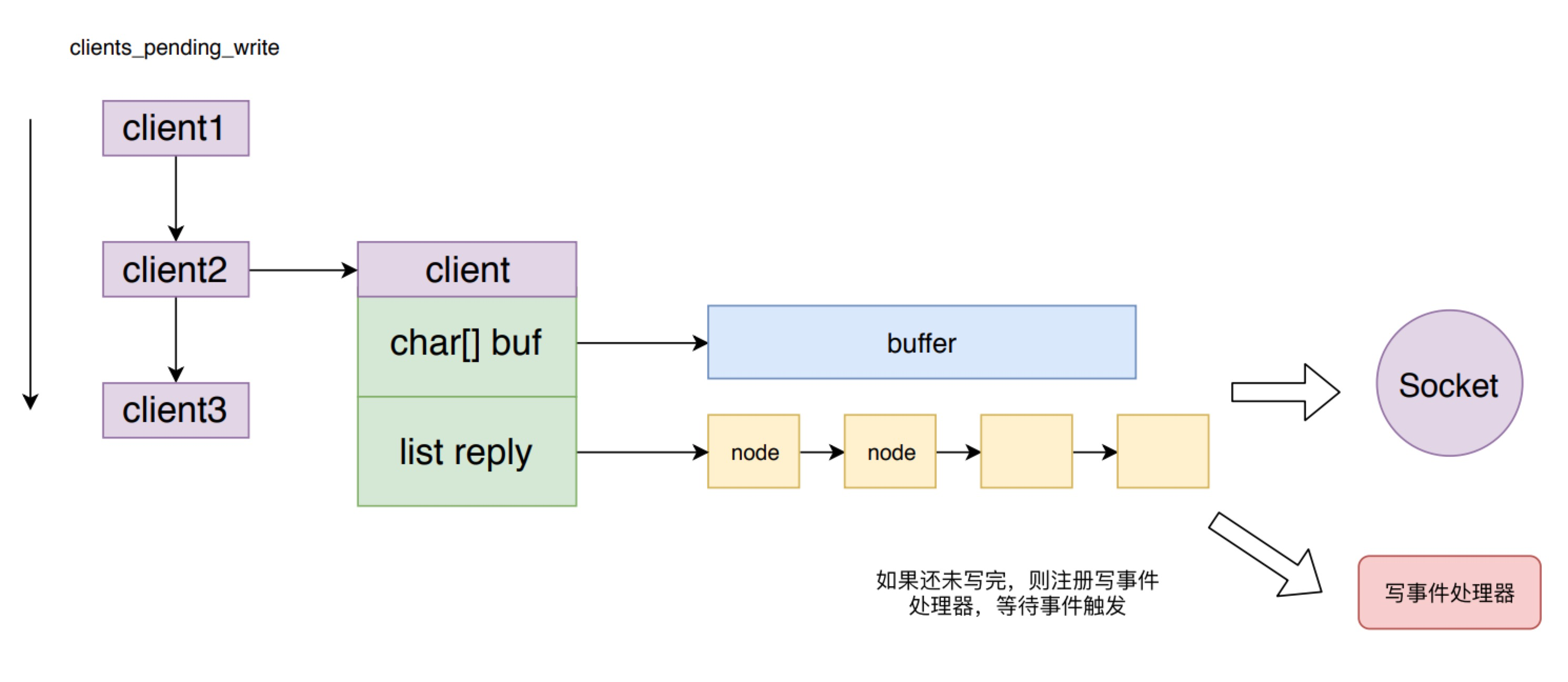
这样的好处是对于返回数据较少的客户端,不需要麻烦的注册写数据事件,等待事件触发再写数据到 socket,而是在下一次事件循环周期就直接将数据写到 socket中,加快了数据返回的响应速度。但是从这里也会发现,如果 clients_pending_write 队列过长,则处理时间也会很久,阻塞正常的事件响应处理,导致 Redis 后续命令延时增加。
1 /**
2 * This function is called just before entering the event loop, in the hope
3 * we can just write the replies to the client output buffer without any
4 * need to use a syscall in order to install the writable event handler,
5 * get it called, and so forth.
6 * 直接将返回值写到client的输出缓冲区中,不需要进行系统调用,也不需要注册写事件处理器
7 */
8 int handleClientsWithPendingWrites(void) {
9 listIter li;
10 listNode *ln;
11 // 获取系统延迟写队列的长度
12 int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
13
14 listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
15 // 依次处理
16 while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
17 client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
18 c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;
19 listDelNode(server.clients_pending_write,ln);
20
21 /* If a client is protected, don't do anything,
22 * that may trigger write error or recreate handler. */
23 if (c->flags & CLIENT_PROTECTED) continue;
24
25 /* Try to write buffers to the client socket. */
26 // 将缓冲值写入client的socket中,如果写完,则跳过之后的操作。
27 if (writeToClient(c->fd,c,0) == C_ERR) continue;
28
29 /* If after the synchronous writes above we still have data to
30 * output to the client, we need to install the writable handler. */
31 // 还有数据未写入,只能注册写事件处理器了
32 if (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {
33 int ae_flags = AE_WRITABLE;
34 /* For the fsync=always policy, we want that a given FD is never
35 * served for reading and writing in the same event loop iteration,
36 * so that in the middle of receiving the query, and serving it
37 * to the client, we'll call beforeSleep() that will do the
38 * actual fsync of AOF to disk. AE_BARRIER ensures that. */
39 if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON &&
40 server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_ALWAYS)
41 {
42 ae_flags |= AE_BARRIER;
43 }
44 // 注册写事件处理器 sendReplyToClient,等待执行
45 if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, c->fd, ae_flags,
46 sendReplyToClient, c) == AE_ERR)
47 {
48 freeClientAsync(c);
49 }
50 }
51 }
52 return processed;
53 }
sendReplyToClient 方法其实也会调用 writeToClient 方法,该方法就是将输出缓冲区中的 buf 和 reply 列表中的数据都尽可能多的写入到对应的 socket中。
1 /**
2 * Write event handler. Just send data to the client.写IO事件的回调函数
3 * 为了向客户端返回命令的执行结果, 服务器要为客户端套接字关联命令回复处理器。
4 *
5 * sendReplyToClient函数是Redis的命令回复处理器,
6 * 这个处理器负责将服务器执行命令后得到的命令回复通过套接字返回给客户端,具体实现为unistd.h/write函数的包装。
7 *
8 * 当服务器有命令回复需要传送给客户端的时候,服务器会将客户端套接字的AE_WRITABLE事件和命令回复处理器关联起来,
9 * 当客户端准备好接收服务器传回的命令回复时,就会产生AE_WRITABLE事件,引发命令回复处理器执行,
10 * 并执行相应的套接字写入操作,
11 *
12 * 当命令回复发送完毕之后, 服务器就会解除命令回复处理器与客户端套接字的 AE_WRITABLE 事件之间的关联。
13 */
14 void sendReplyToClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
15 UNUSED(el);
16 UNUSED(mask);
17 // 发送完数据会删除fd的可读事件
18 writeToClient(fd,privdata,1);
19 }
writeToClient 方法分析

1 /** 2 * Write data in output buffers to client. Return C_OK if the client 3 * is still valid after the call, C_ERR if it was freed. 4 * 这个函数实际上是对write()函数的封装,将静态回复缓冲区buf或回复链表reply中的数据循环写到文件描述符fd中。 5 * 如果写完了,则将当前客户端的AE_WRITABLE事件删除。 6 * 7 * 将输出缓冲区的数据写给client,如果client被释放则返回C_ERR,没被释放则返回C_OK 8 */ 9 int writeToClient(int fd, client *c, int handler_installed) { 10 ssize_t nwritten = 0, totwritten = 0; 11 size_t objlen; 12 clientReplyBlock *o; 13 14 // 如果指定的client的回复缓冲区中还有数据,则返回真,表示可以写socket 15 while(clientHasPendingReplies(c)) { 16 // 固定缓冲区发送未完成 17 if (c->bufpos > 0) { 18 // 将缓冲区的数据写到fd中 19 nwritten = write(fd,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen); 20 // 写失败跳出循环 21 if (nwritten <= 0) break; 22 // 更新发送的数据计数器 23 c->sentlen += nwritten; 24 totwritten += nwritten; 25 26 /* If the buffer was sent, set bufpos to zero to continue with 27 * the remainder of the reply. */ 28 // 如果发送的数据等于buf的偏移量,表示发送完成 29 if ((int)c->sentlen == c->bufpos) { 30 // 则将其重置 31 c->bufpos = 0; 32 c->sentlen = 0; 33 } 34 } else {// 固定缓冲区发送完成,发送回复链表的内容 35 // 回复链表的第一条回复对象,和对象值的长度和所占的内存 36 o = listNodeValue(listFirst(c->reply)); 37 objlen = o->used; 38 39 // 跳过空对象,并删除这个对象 40 if (objlen == 0) { 41 c->reply_bytes -= o->size; 42 listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); 43 continue; 44 } 45 46 // 将当前节点的值写到fd中 47 nwritten = write(fd, o->buf + c->sentlen, objlen - c->sentlen); 48 // 写失败跳出循环 49 if (nwritten <= 0) break; 50 // 更新发送的数据计数器 51 c->sentlen += nwritten; 52 totwritten += nwritten; 53 54 /* If we fully sent the object on head go to the next one */ 55 // 发送完成,则删除该节点,重置发送的数据长度,更新回复链表的总字节数 56 if (c->sentlen == objlen) { 57 c->reply_bytes -= o->size; 58 listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); 59 c->sentlen = 0; 60 /* If there are no longer objects in the list, we expect 61 * the count of reply bytes to be exactly zero. */ 62 if (listLength(c->reply) == 0) 63 serverAssert(c->reply_bytes == 0); 64 } 65 } 66 /** 67 * Note that we avoid to send more than NET_MAX_WRITES_PER_EVENT 68 * bytes, in a single threaded server it's a good idea to serve 69 * other clients as well, even if a very large request comes from 70 * super fast link that is always able to accept data (in real world 71 * scenario think about 'KEYS *' against the loopback interface). 72 * 73 * However if we are over the maxmemory limit we ignore that and 74 * just deliver as much data as it is possible to deliver. 75 * 76 * Moreover, we also send as much as possible if the client is 77 * a slave (otherwise, on high-speed traffic, the replication 78 * buffer will grow indefinitely) 79 * 80 * 如果这次写的总量大于NET_MAX_WRITES_PER_EVENT的限制,则会中断本次的写操作, 81 * 将处理时间让给其他的client,以免一个非常的回复独占服务器,剩余的数据下次继续在写 82 * 83 * 但是,如果当服务器的内存数已经超过maxmemory,即使超过最大写NET_MAX_WRITES_PER_EVENT的限制, 84 * 也会继续执行写入操作,是为了尽快写入给客户端 85 */ 86 if (totwritten > NET_MAX_WRITES_PER_EVENT && 87 (server.maxmemory == 0 || 88 zmalloc_used_memory() < server.maxmemory) && 89 !(c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE)) break; 90 } 91 // 更新写到网络的字节数 92 server.stat_net_output_bytes += totwritten; 93 // 处理写入失败 94 if (nwritten == -1) { 95 if (errno == EAGAIN) { 96 nwritten = 0; 97 } else { 98 serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, 99 "Error writing to client: %s", strerror(errno)); 100 freeClient(c); 101 return C_ERR; 102 } 103 } 104 // 写入成功 105 if (totwritten > 0) { 106 /** 107 * For clients representing masters we don't count sending data 108 * as an interaction, since we always send REPLCONF ACK commands 109 * that take some time to just fill the socket output buffer. 110 * We just rely on data / pings received for timeout detection. 111 * 如果不是主节点服务器,则更新最近和服务器交互的时间 112 */ 113 if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER)) c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime; 114 } 115 // 如果指定的client的回复缓冲区中已经没有数据,发送完成 116 if (!clientHasPendingReplies(c)) { 117 c->sentlen = 0; 118 // 如果内容已经全部输出,删除当前client的可读事件的监听 119 if (handler_installed) aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_WRITABLE); 120 121 /* Close connection after entire reply has been sent. */ 122 // 如果指定了写入按成之后立即关闭的标志,也就是数据全部返回,则释放client 123 if (c->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) { 124 freeClient(c); 125 return C_ERR; 126 } 127 } 128 return C_OK; 129 }
参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/remcarpediem/p/12024468.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/remcarpediem/p/12038377.html
