目录
1、array模板类的定义
(1)array模板类的声明
(2)容器属性
(3)array模板类的说明
(4)array模板类的头文件
2、array模板类的使用
(1)Iterators
(2)Capacity
(3)Element access
(4)Modifiers
(5)Compare
(6)Other
3、普通数组、array和vector的简单比较
本章是对c++ array模板类的知识归纳,讲述了c++中array模板类的使用,不涉及原理方面的内容。c++中的数组类型是继承了c语言的特性,在使用数组的时候要注意数组越界操作问题。为了更安全的对数组进行操作,c++提出了数组模板类array。
1、array模板类的定义
(1)array模板类的声明
template <class T,size_t N> class array;
数组类是固定大小的序列容器,它们包含以严格线性序列排序的特定数量的元素。数组类具有固定大小,并且不通过分配器管理其元素的分配,它们是封装固定大小元素数组的聚合类型。
(2)容器属性
序列容器中的元素按严格的线性顺序排序。各个元素按其顺序访问它们的位置。
元素存储在连续的存储器位置,允许对元素进行恒定时间随机访问。可以偏移元素的指针以访问其他元素。
容器使用隐式构造函数和析构函数静态分配所需的空间。它的大小是编译时常量。没有内存或时间开销。
(3)array模板类的说明
array模板类中T为包含元素的类型(std::array::value_type),N为元素个数。
(4)array模板类头文件
使用array模板类之前需要包含#include <array>头文件!
2、array模板类的使用
(1)Iterators
Iterators迭代器的作用是遍历array数组类中的元素。可以通过begin/end()、rbegin/rend()、cbegin/cend()、crbegin/crend()等函数进行访问。
| begin | Return iterator to beginning |
| end | Return iterator to end |
| rbegin | Return reverse iterator to reverse beginning |
| rend | Return reverse iterator to reverse end |
| cbegin | Return const_iterator to beginning |
| cend | Return const_iterator to end |
| crbegin | Return const_reverse_iterator to reverse beginning |
| crend | Return const_reverse_iterator to reverse end |
参考代码如下所示:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
int main(void) {
std::array<int, 5> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::cout << "array values: ";
for (auto it = arr.begin(); it != arr.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
array values: 1 2 3 4 5
(2)Capacity
array数组容器的大小是固定的。可以通过sizeof()、size()、max_size()、empty()等函数进行检测。
| size | Return size |
| max_size | Return maximum size |
| empty | Test whether list is empty |
测试array数组容器大小的参考代码如下所示:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
int main(void) {
std::array<int, 5> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::cout << "sizeof(array) = " << sizeof(arr) << std::endl;
std::cout << "size of array = " << arr.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "max_size of array = " << arr.max_size() << std::endl;
if (arr.empty()) {
std::cout << "array is empty!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "array is not empty!" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
sizeof(array) = 20
size of array = 5
max_size of array = 5
array is not empty!
(3)Element access
可以通过下标[ ]、at()、front()、back()、data()等函数访问array容器内的元素。
| operator[ ] | Access element |
| at | Access element |
| front | Access first element |
| back | Access last element |
| data | Get pointer to first data |
参考代码如下:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
int main(void) {
std::array<int, 5> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::cout << "array[0] = " << arr[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "array.at(4) = " << arr.at(4) << std::endl;
std::cout << "array.front() = " << arr.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << "array.back() = " << arr.back() << std::endl;
std::cout << "&array: " << arr.data() << " = " << &arr << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
array[0] = 1
array.at(4) = 5
array.front() = 1
array.back() = 5
&array: 0x7ffd22df6e50 = 0x7ffd22df6e50
(4)Modifiers
可以使用fill()、swap()等函数对array容器整体进行操作。
| fill | Fill array with value |
| swap | Swap content |
参考代码如下所示:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
int main(void) {
std::array<int, 5> arr;
arr.fill(5); // fill
std::cout << "array values: ";
for (auto i : arr) {
std::cout << i << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::array<int, 3> first = {1, 2, 3};
std::array<int, 3> second = {6, 5, 4};
std::cout << "first array values: ";
for (auto it = first.begin(); it != first.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "second array values: ";
for (auto it = second.begin(); it != second.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
first.swap(second); // swap
std::cout << "swap array success!" << std::endl;
std::cout << "first array values: ";
for (auto it = first.begin(); it != first.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "second array values: ";
for (auto it = second.begin(); it != second.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
array values: 5 5 5 5 5
first array values: 1 2 3
second array values: 6 5 4
swap array success!
first array values: 6 5 4
second array values: 1 2 3
(5)Compare
还可以使用> < ==等符号对两个array数组容器进行比较。
参考代码如下所示:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
int main(void) {
std::array<int,5> a = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
std::array<int,5> b = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
std::array<int,5> c = {50, 40, 30, 20, 10};
if (a == b) {
std::cout << "a == b" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "a != b" << std::endl;
}
if (a == c) {
std::cout << "a == c" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "a != c" << std::endl;
}
if (a < c) {
std::cout << "a < c" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "a >= c" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
a == b
a != c
a < c
6)Other
c++重载了get()函数来访问数组容器中的元素,为了和元组相似,还重载了tuple_size和tuple_element类型。
| get( array) | Get element (tuple interface) |
| tuple_element<array> | Tuple element type for array |
| tuple_size<array> | Tuple size traits for array |
参考代码如下所示:
/*****************************************************
Copyright (C) 2018. All rights reserved.
File name : array.cpp
Version : v1.0
Author : zhengqijun
Date : 2018-08-10
Function List :
Description : array container.
******************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <tuple>
int main(void) {
std::array<int,3> myarray = {10, 20, 30};
std::tuple<int, int, int> mytuple (10, 20, 30);
std::tuple_element<0, decltype(myarray)>::type myelement; // int myelement
myelement = std::get<2>(myarray);
std::get<2>(myarray) = std::get<0>(myarray);
std::get<0>(myarray) = myelement;
std::cout << "first element in myarray: " << std::get<0>(myarray) << std::endl;
std::cout << "first element in mytuple: " << std::get<0>(mytuple) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下所示:
first element in myarray: 30
first element in mytuple: 10
3、普通数组、array和vector的简单比较
(1)普通数组
typeName arrayName[ayyaySize];
int ragnar[7]; //创建一个包含7个int类型的数组ragnar
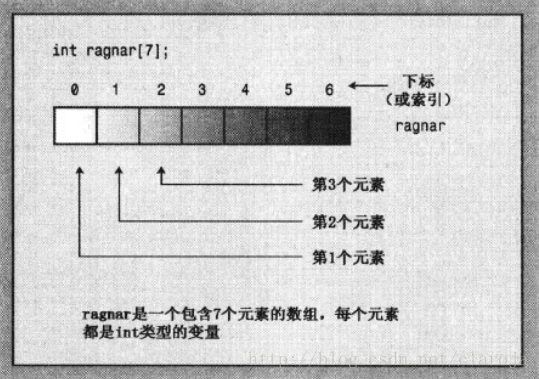
创建数组的过程其实是在内存中申请了一个连续的int类型宽度的空间,用下标来代替每个元素的变量名.
赋值的方式
1)初始化数组,一个一个赋值
int ragnar[3];
ragnar[0]=1;
2)初始化数组,并全部赋值
int ragnar[3]={}; //全部赋值为0
int ragnar[3]={1,2,3};//分别赋值
int ragnar[]={1,2,3};//自动识别长度
(2)vector
模板类vector类似于string类,也是一种动态数组.可以在运行阶段设置vector对象的长度,可在末尾附加新数据,还可以在中间插入新数据.它是new创建动态数组的替代品.实际上,vector类确实使用new和delete来管理内存,但这种工作是自动完成的.
首先,使用vector对象,必须包含头文件vector.
其次,vcetor包含在命名空间std中,因此可以使用using编译命令/using声明或std::vector
第三,模板使用不同的语法来支出它的存储的数据类型
第四,vector类使用不同的语法来指定元素数
vector<typeName> vt(nElem)
include <vector>
using namespace std;//创建一个0长度的vector
vector<int> vi;
vector<double> vd(10); // 创建10个double类型的vector
(3)Array
array也位于名称空间std中,与数组一样,array对象的长度也是固定的,也使用栈(静态内存分配),而不是自由存储区,因此其效率与数组相同,但更方便,更安全.
array<typeName, nElem> arr;
# include <array>
using namespace std;
array<int, 5> ai;
array<double, 4> ad = {1.1,1.2,1.2,1.3};
比较三者之间的区别
| 数组 | vector | array |
|---|---|---|
| 访问方式 | 支持标准访问 | 支持标准访问 |
| 存储位置 | 堆 | 栈 |
| 复制 | 逐个复制 |